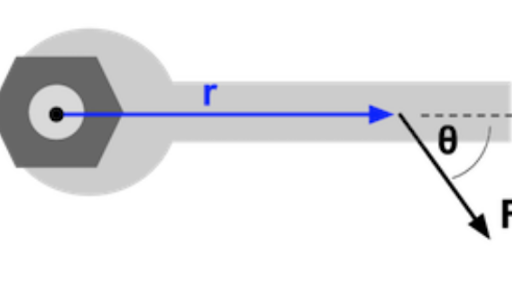
40 thee forces act on a particle as given in the diagram below. assume the system is in equilibrium.
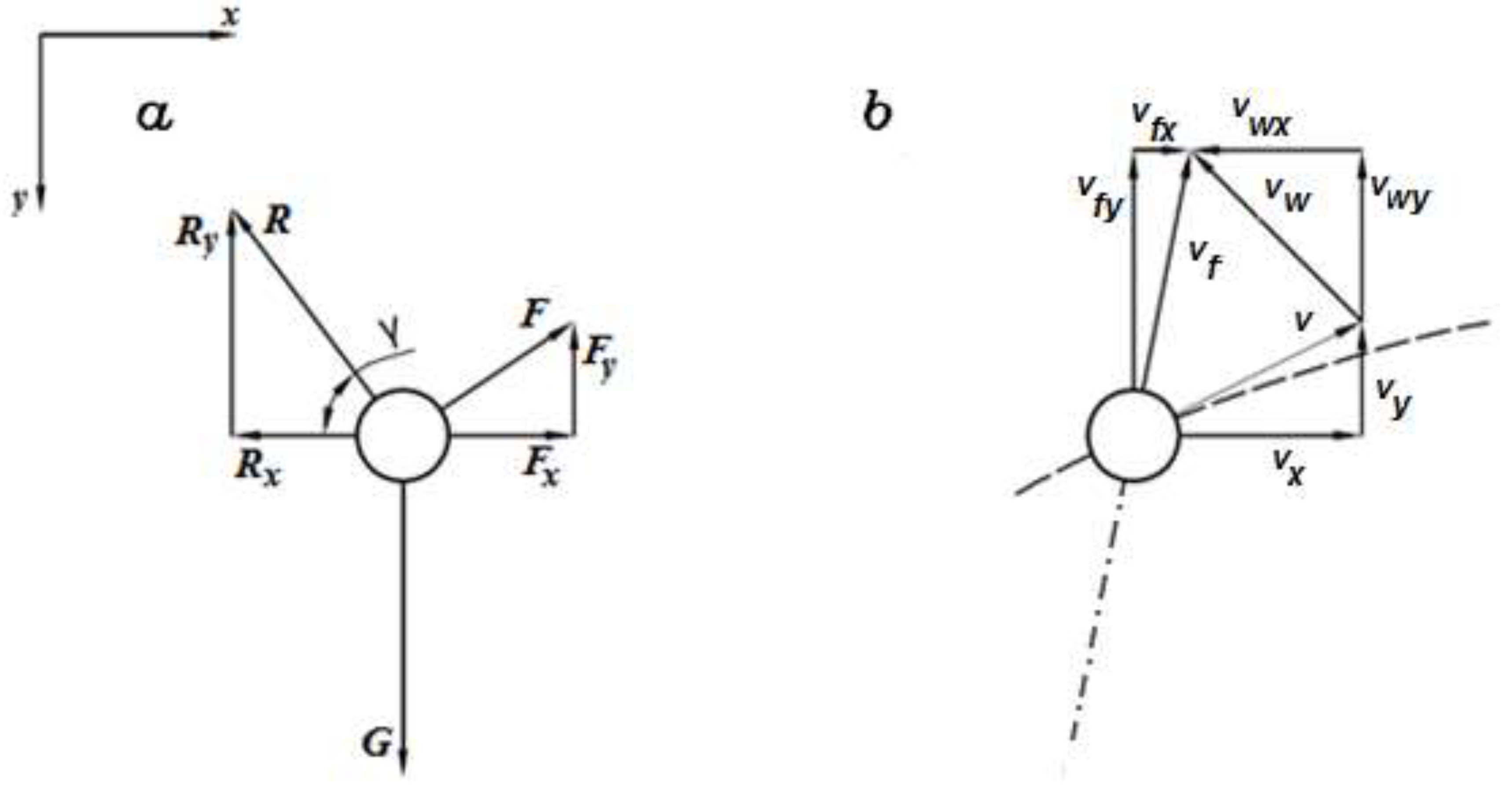
force acts on the particle, the equation of motion can be written F = F R = ma where F R is the resultant force, which is a vector summation of all the forces. To illustrate the equation, consider a particle acted on by two forces. First, draw the particle's free-body diagram, showing all forces acting on the particle. Next, draw the 2) The resultant of three forces shown in figure (2) is along X axis. Determine angle α and magnitude of resultant. (Ans:R=75.23 N, α=-62°) 3) Determine magnitude and direction of resultant force for the system shown in figure (3). (Ans:R=201.00 N, α=-41°) 4) Find equilibrant of the force system shown in figure (4).
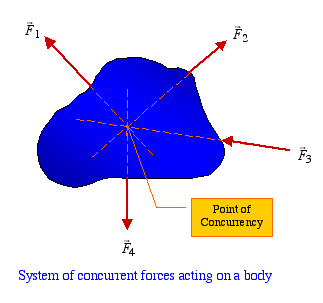
Equilibrium of a Particle 2 - 11 • When the resultant of all forces acting on a particle is zero, the particle is in equilibrium. • Particle acted upon by two forces: - equal magnitude - same line of action - opposite sense • Particle acted upon by three or more forces: - graphical solution yields a closed polygon - algebraic solution 0 0 0

Thee forces act on a particle as given in the diagram below. assume the system is in equilibrium.
A particle is said to be in equilibrium if it was originally at rest or moving along a straight line with constant velocity, and remains so. According to Newton's first law of motion, if a particle is in equilibrium, the resultant forces of all the force acting on it must be zero, expressed as the equation of equilibrium (of a particle), (5.1) Three forces, given by F1 = (−2.00i + 2.00j) N, F2 = (5.00i − 3.00j) N, ... the particle is in equilibrium, and 14 comes from combining 12 and 13.4 pages 2 Dimensional Equilibrium! Calculate force of hand to keep a book sliding at constant speed (i.e. a = 0), if the mass of the book is 1 Kg, m s =.84 and m k =.75 We do exactly the same thing as before, except in both x and y directions! Step 1 - Draw! Step 2 - Forces! Step 3 - Newton's 2nd (F Net = ma)! Treat x and y independently ...
Thee forces act on a particle as given in the diagram below. assume the system is in equilibrium.. EQUILIBRIUM CONDITIONS : - If a system of forces acting on a body, keeps the body in a state of rest or in a state of uniform motion, then the system of forces is said to be in equilibrium. Alternatively, we can say that the resultant force is zero, the system of forces will be in equilibrium. 5. 3.3 COPLANAR FORCE SYSTEMS This is an example of a 2-D or coplanar force system. If the whole assembly is in equilibrium, then particle A is also in equilibrium. To determine the tensions in the cables for a given weight of the engine, we need to learn how to draw a free body diagram and apply equations of equilibrium. Establish your coordinate system and draw the particle's free body diagram showing only external forces. These external forces usually include the weight, normal forces, friction forces, and applied forces. Show the 'ma'vector (sometimes called the inertial force) on a separate diagram Make sure any friction forces act opposite to the ... Students will be able to solve 3-D particle equilibrium problems by a) Drawing a 3-D free body diagram, and, b) Applying the three scalar equations (based on one vector equation) of equilibrium. QUIZ 1. Particle P is in equilibrium with five (5) forces acting on it in 3-D space. How many scalar equations of equilibrium can be written for point P? A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 5 E) 6 2. In 3-D, when a ...
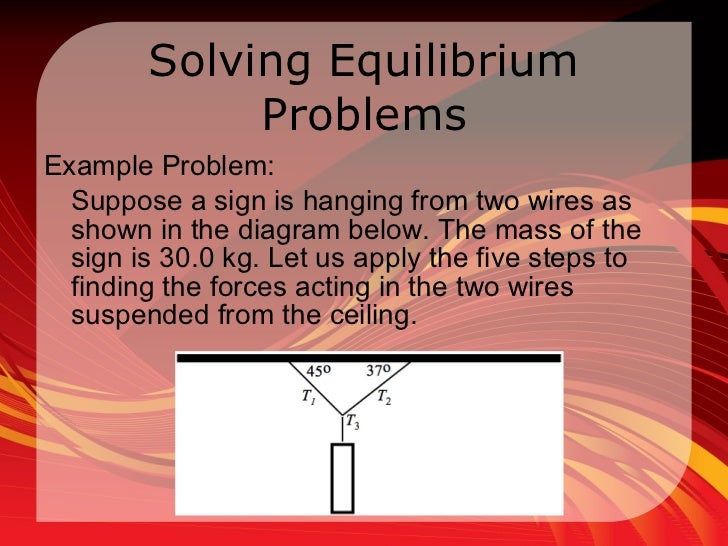
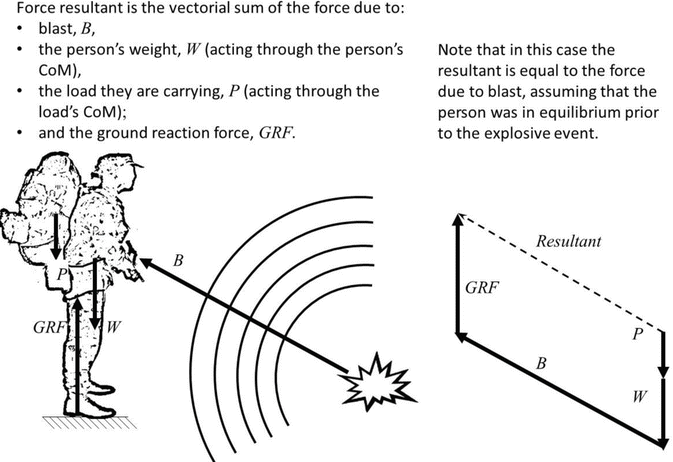
The forces acting on a particle at rest or moving with constant velocity are in equilibrium. In practical terms this means, for forces in equilibrium the sum of the components of the forces in any direction must be zero. Example 5.1. The diagram shows an object, of mass 300 kg, that is at rest and is supported by two cables. Now, you are going to construct a force diagram that you can use to determine graphically the resultant and equilibrant of the three forces. This diagram must be drawn carefully to scale so that the lines represent the forces accurately. Follow procedure below to draw force diagram (Figure 5). 3. Determine the magnitude and direction of theresultant FR = F1 + F2 + F3 of the three forces by firstfinding the resultant F = F1 + F2 and then formingFR = F... If three non-parallel forces act on a body in equilibrium, it is known as a three-force member. The three forces interact with the structural element in a very specific manner in order to maintain equilibrium. If a three-force member is in equilibrium and the forces are not parallel, they must be concurrent.
how our particle looks with all forces acting upon it. The resultant force is the vector sum of all the forces acting on the isolated particle. For static equilibrium of the isolated particle, the resultant of the two forces – W acting downward and R acting upward – must be zero. RW– = 0 This leads to the not very earth shaking conclusion ... For some systems in equilibrium, it may be necessary to consider more ... Draw a free-body diagram for the object, including only the forces that act on it. Since a string under tension pulls inward along its length with a force given by the string tension, the forces acting at this point are as shown. Since this junction in the strings is in static equilibrium, the (vector) sum of the forces acting on it must give zero. Thus the sum of the x components of the forces is zero: −T1 sin35 +T2 = 0 (3.4) Thee forces act on a particle as given in the diagram below assume the system is in equilibrium. The valid digits in a measurement are called digits. The vector diagram below represents two forces f1 and f2 simultaneously acting on an object. F 2 h 153iand f 3 act on an object. Which vector best represents the resultant force.
Consider the two objects pictured in the force diagram shown below. Note that the two objects are at equilibrium because the forces that act upon them are balanced; however, the individual forces are not equal to each other. The 50 N force is not equal to the 30 N force. If an object is at equilibrium, then the forces are balanced. Balanced is ...
3. Summing the forces in the upwards direction we have X F = T 3 −T 2 −T 1 (19) = m pa = 0 (20) T 3 = T 2 +T 1 = 2mg (21) And the scale is in equilibrium, so as in (a) it has T 3 pulling on both sides, and it will read 2mg = 2·5.00 kg·9.8 m/s 2 = 98.0 N. (c) The block has 3 forces acting on it: gravity F g = mg, tension T, and a normal ...
For such springs, the force exerted by the spring can be empirically found to be given by F = a x b. For a tapered spiral spring that compresses 1 2. 9 c m with a 1 0 0 0 N load and 3 1. 5 cm with a 5 0 0 0 N load, (a) evaluate the constants a and b in the empirical equation for F and (b) find the work needed to compress the spring 2 5. 0 c m.
1 Notes for lectures 2 and 3: Equilibrium of a solid body 1.1 Introduction This lecture deals with forces acting on a body at rest. The di®erence between the particle of the last lecture and the body in this lecture is that all the forces on the particle act through the same point, which is not the case for forces on an extended body.
Thee forces act on a particle as given in the diagram below assume the system is in equilibrium. Given the lift is stationary draw the system diagram. The potential energy associated with this force is assigned a value of 20 j at x0. Static equilibrium force and moment 21 concept of force equilibrium of a particle. If the particle is in ...
Three forces, (15i + j) N, (5qi —pj) N and (—3pi — qj) N, where p and q are constants, act on a particle. Given that the particle is in equilibrium, find the value of p and the value of q. (6) o p 489 46 A 0228 . 2. Leave blank Two particles, P and Q, have masses 2m and 3m respectively. They are moving towards each other in opposite directions on a smooth horizontal plane when they ...
Thee forces act on a particle as given in the diagram below assume the system is in equilibrium. If the whole assembly is in equilibrium then particle a is also in equilibrium. For a particle at rest or moving with constant velocity relative to an inertial frame the resultant force acting on the isolated. Equilibrium what are the values of f3 the magnitude of force 3. Assume that the only ...
Thee forces act on a particle as given in the diagram below assume the system is in equilibrium. When a force is a push the force arrows in a free body diagram point towards the particle. The three forces shown in the figure below act on a particle with f1 490 n f2 550 n θ1 620 and θ2 280. Assume the system is in equilibrium.
For some systems in equilibrium, it may be necessary to consider more ... Draw a free-body diagram for the object, including only the forces that act on it.
Forces I 4.1 The Important Stuff 4.1.1 Newton's First Law With Newton's Laws we begin the study of how motion occurs in the real world. The study of the causes of motion is called dynamics, or mechanics. The relation between force and acceleration was given by Isaac Newton in his three laws of motion, which form the basis of elementary ...
Static equilibrium force and moment 21 concept of force equilibrium of a particle. Homework 4 4 3 Several Forces Act On A Particle As Shown In The Physics exam 1 multiple choice practice problems. Thee forces act on a particle as given in the diagram below assume the system is in equilibrium. Where f1 800 n f2 600 n θ1 200 and θ2 750 and ...
8 Dec 2020 — Three forces F1, F2, and F3 acting on a particle are in equilibrium. a) write an equation to represent the equilibrium of the forces F1,F2 and ...1 answer · Top answer: a) If the particle is in equlibrium, then the vector sum of all forces is zero. Thus, obtain: F1+F2+F3=0\mathbf{F}_1+\mathbf{F}_2+\mathbf{F}_3=0F1+F2+F3 ...Missing: assume | Must include: assume

Four Forces 8n 6n 2n And 4n Act On A Point O In The Directions North East South And West Respectively Find The Magnitude Of Their Result And The Direction Of Their Resultant Force Study Com
1 DJM3C - MECHANICS Unit I: Forces acting at a point - Parallelogram of forces - triangle of forces - Lami‟s Theorem, Parallel forces and moments - Couples - Equilibrium of three forces acting on a rigid body. Unit II: Friction - Laws of friction - equilibrium of a particle (i) on a rough inclined plane, (ii) under a force parallel to the plane , (iii) under any force -
The slope of the graph given below is. Thee forces act on a particle as given in the diagram below assume the system is in equilibrium. The vector diagram below represents two forces f1 and f2 simultaneously acting on an object. Which vector best represents the resultant force. A free body diagram represents forces acting on a system.
43 several forces act on a particle as shown in the figure below where f 1 800 n f 2 600 n θ 1 200 and θ 2 750 and the figure is not to scale. Thee forces act on a particle as given in the diagram below assume the system is in equilibrium. F 1 f 2 f 3 1 2 3 if 1 ˇ 3. The organic chemistry tutor 252691 views. Assume the system is in equilibrium.
Transcribed image text: 2. Thee forces act on a particle as given in the diagram below. Assume the system is in equilibrium. If θ,- , θ2 e, F-5N, ...
2 Dimensional Equilibrium! Calculate force of hand to keep a book sliding at constant speed (i.e. a = 0), if the mass of the book is 1 Kg, m s =.84 and m k =.75 We do exactly the same thing as before, except in both x and y directions! Step 1 - Draw! Step 2 - Forces! Step 3 - Newton's 2nd (F Net = ma)! Treat x and y independently ...

Consider The Diagram Below Of A Seesaw Of Length L With Two Blocks Fixed Onto It As Shown The Vertical Dashed Line Marks The Center Of The Seesaw As Well As The
Three forces, given by F1 = (−2.00i + 2.00j) N, F2 = (5.00i − 3.00j) N, ... the particle is in equilibrium, and 14 comes from combining 12 and 13.4 pages
A particle is said to be in equilibrium if it was originally at rest or moving along a straight line with constant velocity, and remains so. According to Newton's first law of motion, if a particle is in equilibrium, the resultant forces of all the force acting on it must be zero, expressed as the equation of equilibrium (of a particle), (5.1)
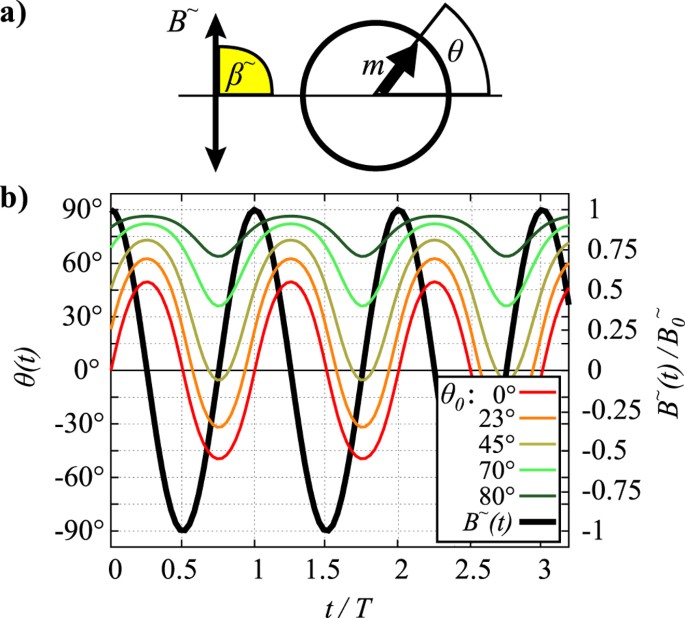
Rotational Friction Of Dipolar Colloids Measured By Driven Torsional Oscillations Scientific Reports

By Taking Torques About O Derive An Equation That Gives The Angle Theta In Terms Of The Parameters Given Above Study Com
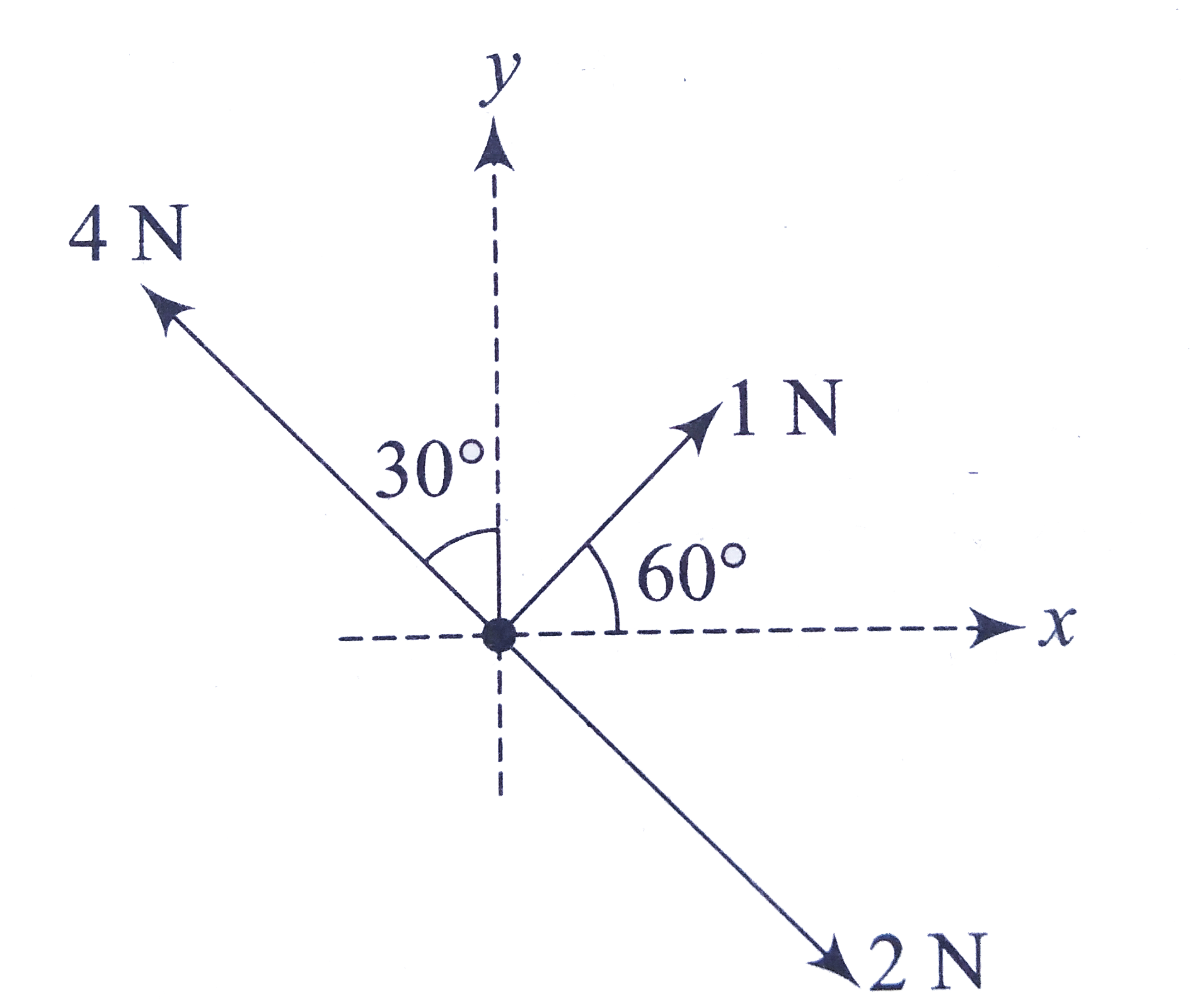
Three Forces Are Acting On A Particle As Shown In The Figure To Have The Resultant Force Only Along The Y Direction The Magnitude Of The Maximum Additional Force Needed Is Img Src Https D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images

Force Measurements Between Particles And The Air Water Interface Implications For Particle Mobilization In Unsaturated Porous Media Shang 2009 Water Resources Research Wiley Online Library



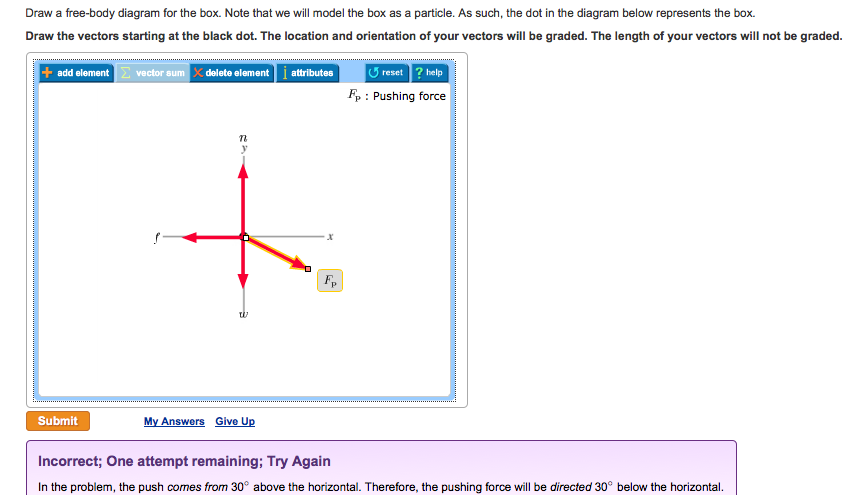



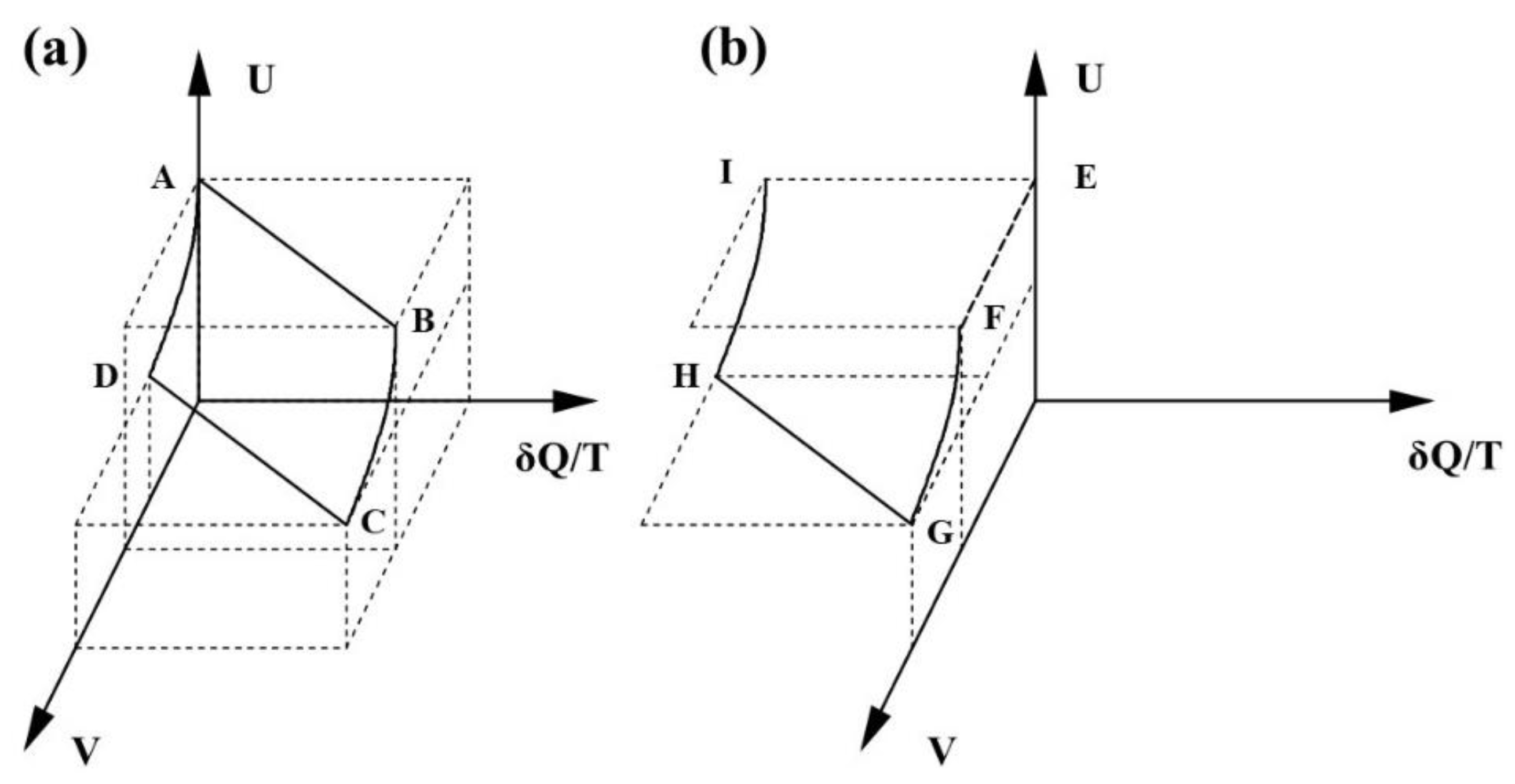
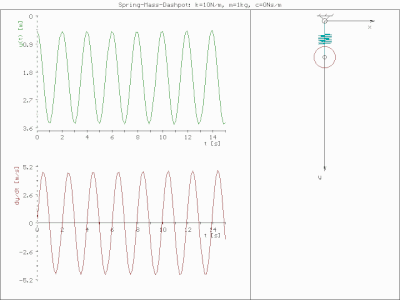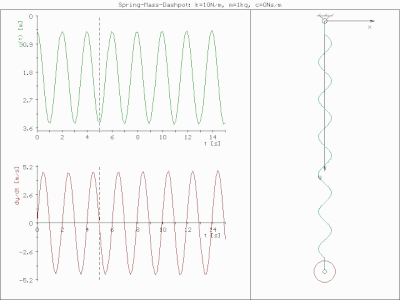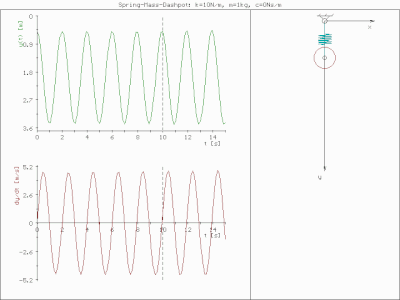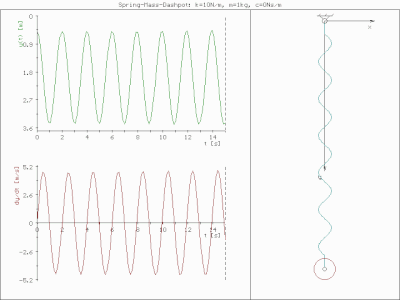

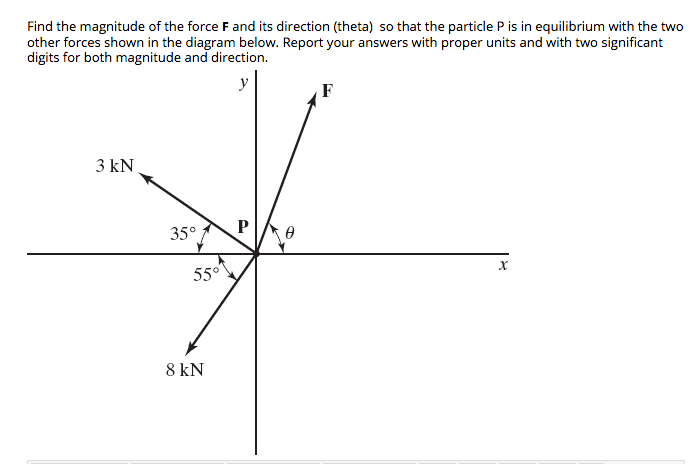



0 Response to "40 thee forces act on a particle as given in the diagram below. assume the system is in equilibrium."
Post a Comment