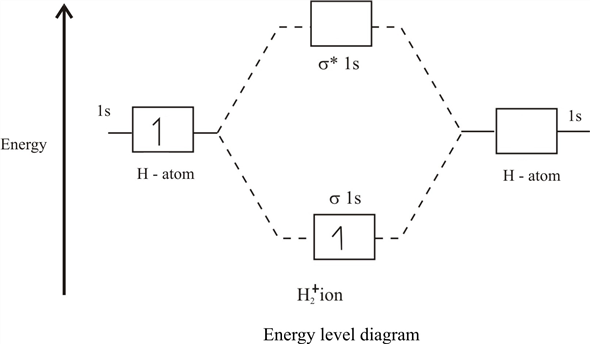
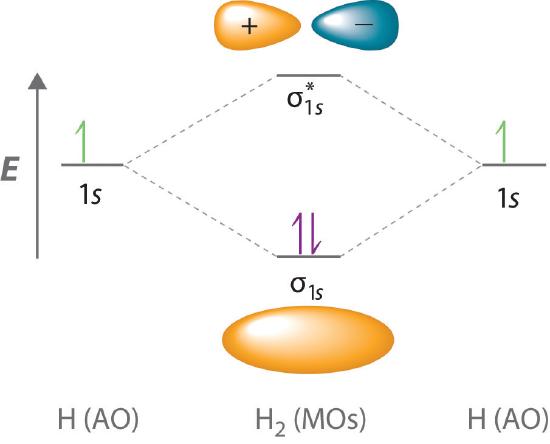
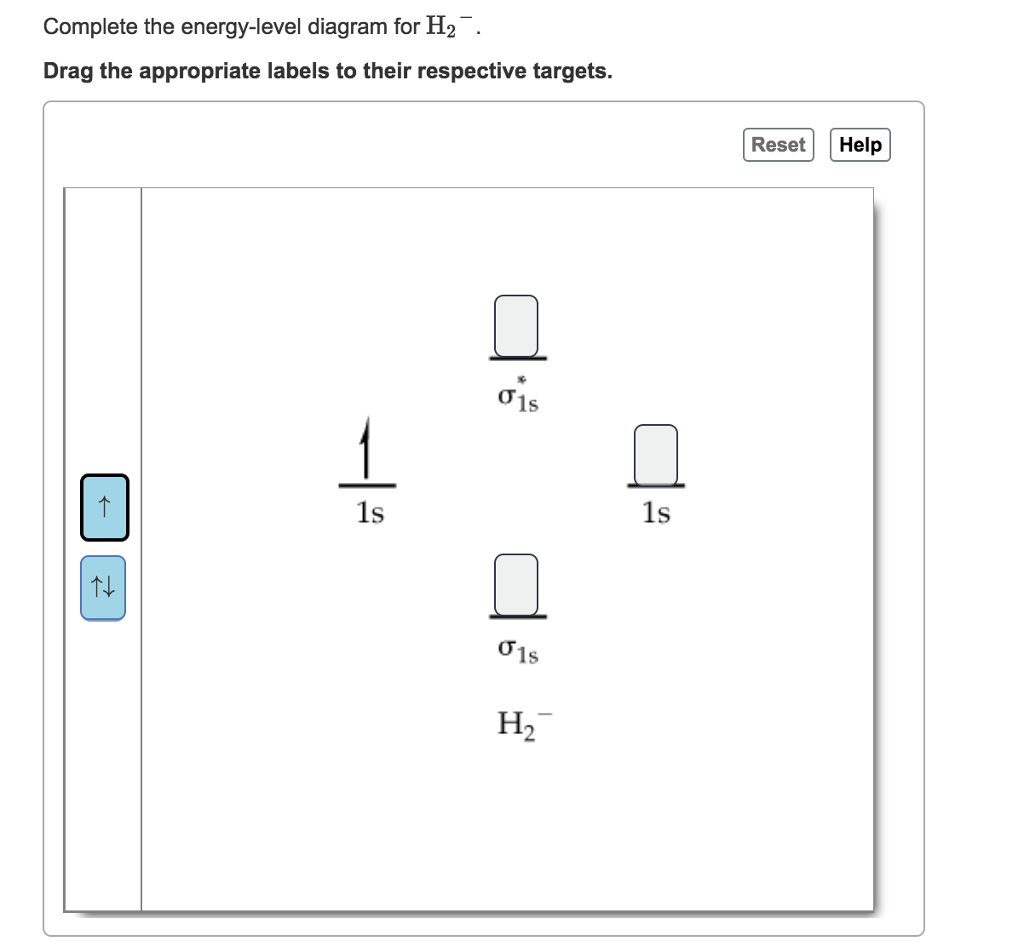
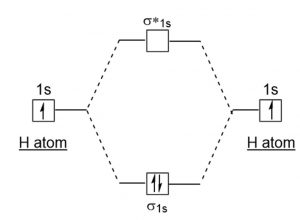
43 complete the energy-level diagram for h2−.
The C −Br bond is weaker than the C−Cl bond. The H −Cl bond is weaker than the H−Br bond. Chlorine is more reactive than bromine. (1) (Total 15 marks) Q3.A student investigated the rate of reaction of magnesium and hydrochloric acid. Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) MgCl 2 (aq) + H 2 (g) Apr 9, 2018. Since heat is released for. C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) → 3CO2(g) +4H2O(g) + 2219.9 kJ, we say that ΔH ∘ C = − 2219.9 kJ/mol propane. We approximate that this is the change in potential energy for the reactants going to the products. The above is for an endothermic reaction. A certain feature of combustion reactions suggests that you ...
Imgur. The energy of the electron of a monoelectronic atom depends only on which shell the electron orbits in. The energy level of the electron of a hydrogen atom is given by the following formula, where. n. n n denotes the principal quantum number: E n = − 1312 n 2 kJ/mol. E_n=-\frac {1312} {n^2}\text { kJ/mol}. E n.

Complete the energy-level diagram for h2−.
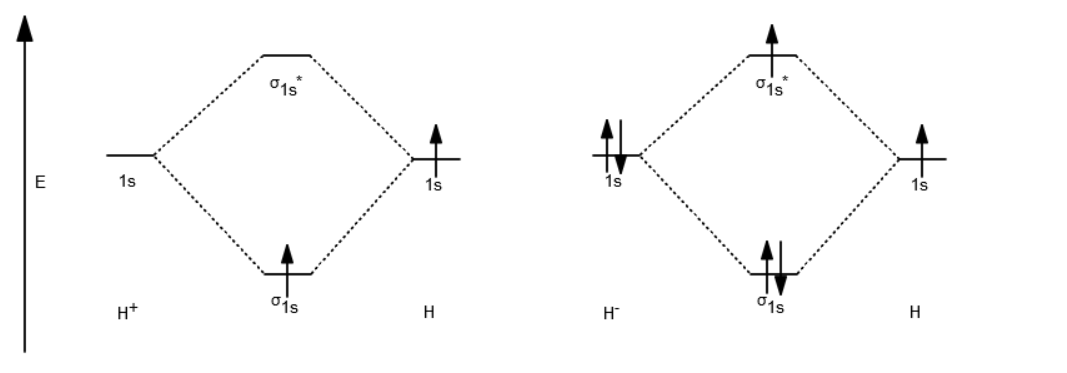
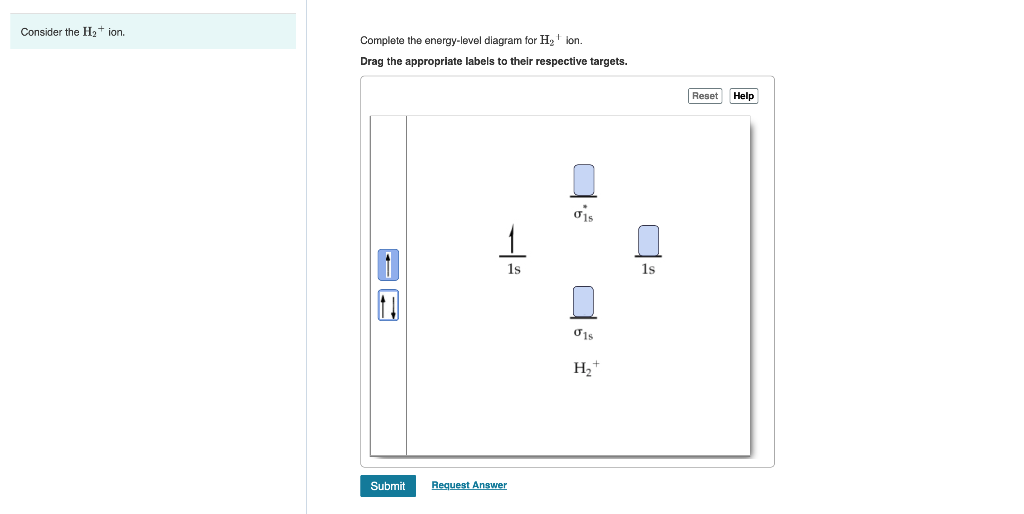
Answer to Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2−. Do you expect these molecules to exist in the. From the above MO diagram we can see that number of elctrons in the bonding and antibonding orbital is same and hence Be does not form Be2 molecule(for. Chemical bonding - Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The procedure can be The molecular orbital energy- level diagram that results is constructed by putting .May 20, · Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order? i know the answer im just posting it for whoever may need it. (check picture)Status: Open. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, H− 2 has three electrons while H+ 2 has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one σ1s and one σ* 1s MO by conservation of orbitals. If you calculate their bond order, you get: BOH+ 2 = 1 2(Bonding − ...
Complete the energy-level diagram for h2−.. H−. Bond order = 1. 2 (electrons in bonding orbitals - electrons in antibonding orbitals) Draw a complete MO diagram for all the bonds in ethene.The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total of 4 electrons in this molecule. Transcribed Image Textfrom this Question. Complete the energy-level diagram for H2 Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets Reset Help σ1s 1s 1s 14 1s H2. N b = 2 , Na =0. Bond order = 1. Positive value of bond order indicates that H 2 molecule is stable.. Bond order value of 1 means that two hydrogen atoms are connected by a single bond.. Greater value of bond order for H 2 molecule than H 2 + ion shows that two H 2 molecule is more stable than H 2 +.. Bond length of H 2 is smaller than that of H 2 + ion.. As no unpaired electron is present ... The energy levels are degenerate, meaning that the electron in the hydrogen atom can be in different states, with different wave functions, labeled by different quantum numbers, and still have the same energy. The electron wave functions however are different for every different set of quantum numbers. ...
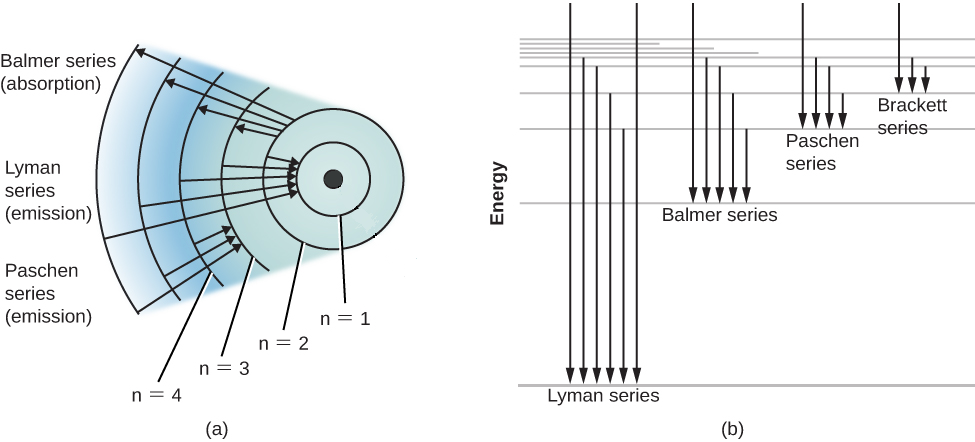
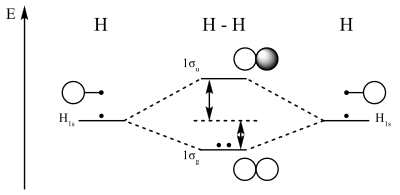
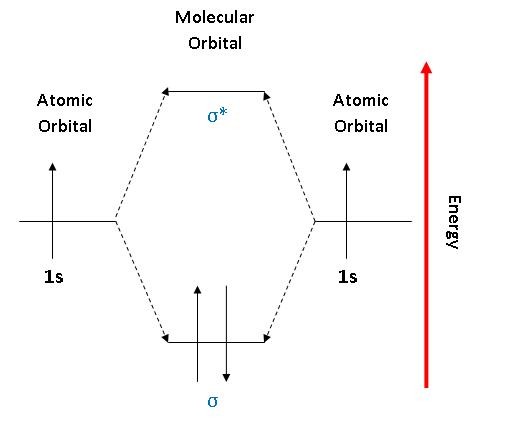
H−. A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and σ∗. 1s is higher in energy. Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining ... Answer to: what is the energy-level diagram for H2−. ... We are asked to draw the energy-level diagram or the molecular orbital energy diagram for H2-.1 answer · Top answer: Hey there!We are asked to draw the energy-level diagram or the molecular orbital energy diagram for H2-.An H2 molecule has two electrons and a charge ... Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ 6. Draw the molecular orbital energy level diagram of H2. The ionization energy of an atom is the energy required to remove the electron completely from the atom. (transition from ground state n = 0 to infinity n = ∞ ). For hydrogen, the ionization energy = 13.6eV. When an excited electron returns to a lower level, it loses an exact amount of energy by emitting a photon.
functions are called energy eigenfunctions and the corresponding values of energy are the energy eigenvalues. Notice that the probability density for an energy eigenfunction is independent of time: Ψ(x,t)2=Ψ∗(x,t)Ψ(x,t)=ψ∗(x)eiωtψ(x)e−iωt=ψ(x)2.(7.11) Thus, energy eigenfunctions are called stationary states. The energy levels are enumerated using a principal quantum number n, an integer that must be greater or equal to one: En = − e2 2a 0 1 n2, n= 1,2,.... (2.1.3) Note that H(0) is a non-relativistic Hamiltonian: the speed of light does not enter in it, and the kinetic term is that of Newtonian mechanics. The energy scale relevant to the 25 A dihydrogen molecule contains two bonding electrons and no antibonding electrons so we have. bond order in H2 = (2−0) 2 = 1 bond order in H 2 = ( 2 − 0) 2 = 1. Because the bond order for the H-H bond is equal to 1, the bond is a single bond. A helium atom has two electrons, both of which are in its 1 s orbital. The energy change in a reaction can be calculated using bond energies. A bond energy is the amount of energy needed to break one mole of a particular covalent bond. Different bonds have different ...
Draw an energy level diagram for the combustion of methane ... What mass of carbon dioxide is produced from the complete combustion of 7.00×10−3 g of methane? chemistry. What mass of oxygen is needed for the complete combustion of 2.50×10−3 of methane? ... C + H2 > CH4 H=-74.87kJ C + O2 > CO2 H= -393.5 2 H2 + O2 > 2 . science. What mass ...
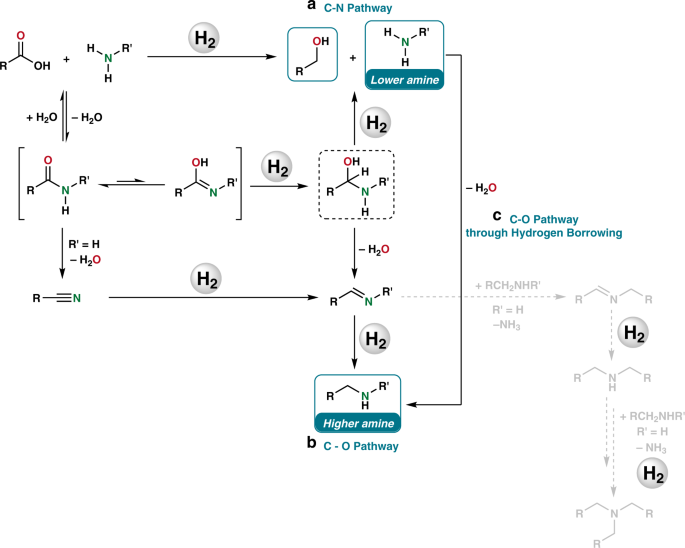
Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Catalytic Reduction Of Amides And Related Compounds Using Molecular Hydrogen Nature Communications
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the if we draw its MOT DIAGRAM, 2 e's enter the Bonding molecular Orbital and 2 .
photon = 2.10×10−15 J. No negative signs with energy! ∆E photon = 1.1×10−16 J ⇒ K electron = 1.1×10−16 J. Or 690eV. P39. Nuclear fusion reactions at the center of the sun produce gamma-ray photons with energies of about 1 MeV (106 eV). By contrast, what we see emanating from the sun's surface are
e, and therefore µc2 is the rest energy of the electron. Eq. (11.33) shows that the typical scale of the energy levels in the H atom is 10−4 the rest energy of the electron. This justifies the nonrelativistic treatment of the H atom that we have used here. Clearly
A simple expression for the energy of an electron in the hydrogen atom is: E = − 13.6 n2 where the energy is in electron volts. n is the principle quantum number. This gives rise to the familiar electron energy level diagram where they converge and coalesce. So for an electron in n = 1:
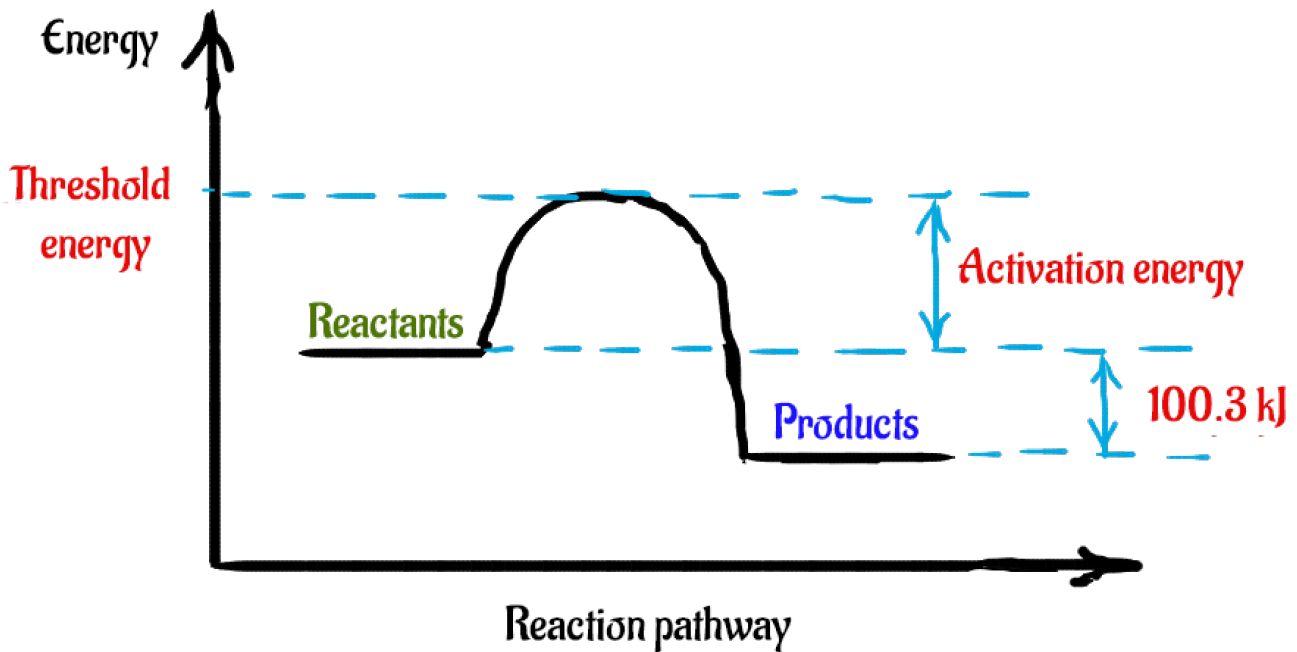
a) Carefully complete the energy diagram by drawing a curve that accurately shows the progress of the reaction, beginning at the reactants, moving through the transition state, and ending at the final products. When adding the products to the diagram, be sure to use an energy level that is appropriate relative to the energy level of the reactants
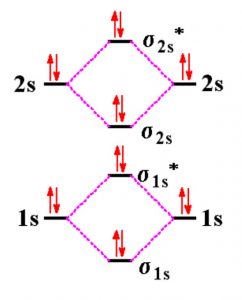
Energy Level Diagram For Molecular Orbitals Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Chemistry Class 11
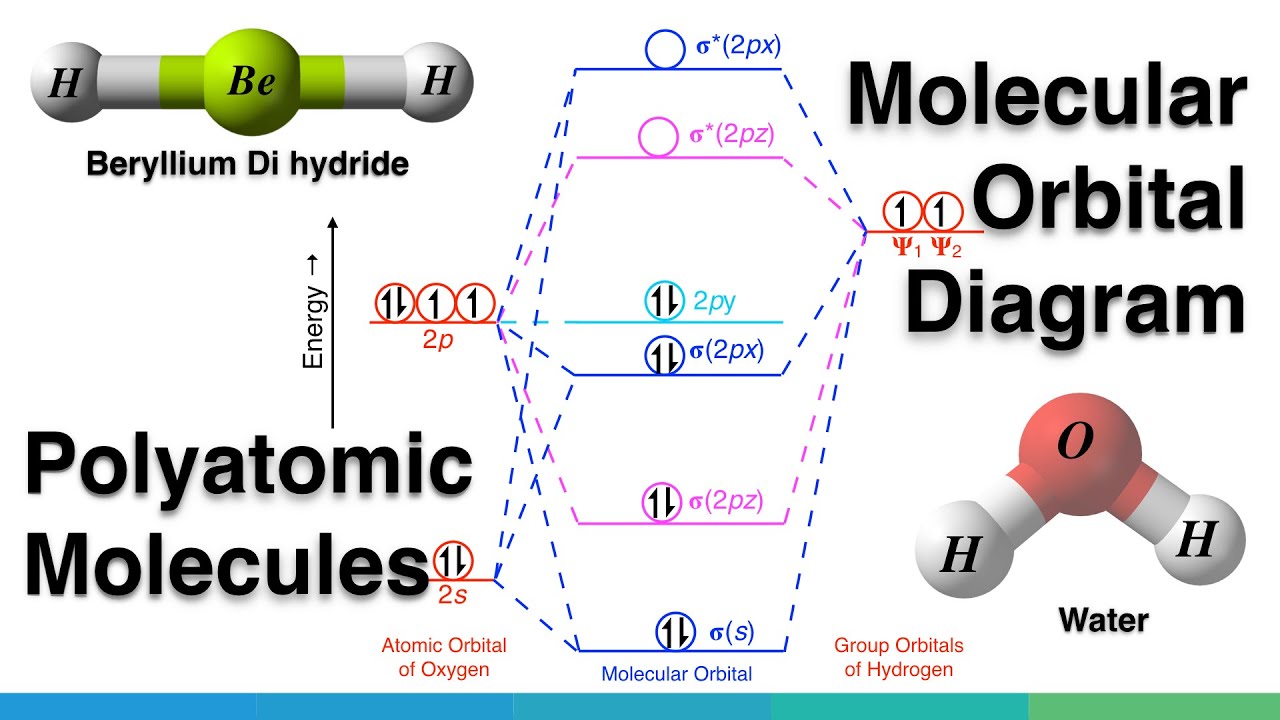
The energy level diagram for CO2 in Figure 5.25 can be used as a guide, with the orbitals of Be higher in energy than those of C and the orbitals of F lower in energy than those of O. Calculated molecular orbital shapes are below, for comparison for those of CO2 in Figure 5.25.
The potential is non-zero and equal to −V H in the region −a ≤ x ≤ a. For a quantum mechanical particle we want instead to solve the Schrodinger equation. We consider two cases. In the first case, the kinetic energy is always positive: −. 1 2 d ψ(x) 2 2m dx 2 = Eψ(x) in Region I − 1 2H. d ψ(x) 2m dx. 22 = (E + V. H
Hydrogen iodide, HI, is a colourless gas that can be made from the reaction of hydrogen, H2, and equilibrium 3.1 iodine, I2. This reversible reaction is shown in equilibrium 3.1 below. The activation energy for the forward reaction is 173 kJ mol−1. (a) Complete the enthalpy profile diagram below for the forward reaction in equilibrium 3.1.
Mark J. Winter · 2016 · Chemical bonds3.3 Energy level diagrams of H2 and related diatomic compounds the H2+ energy ... including H2 and H2 −, it is occupied. σ s * Energy 1s 1s ∆E σ s H H2 + ...
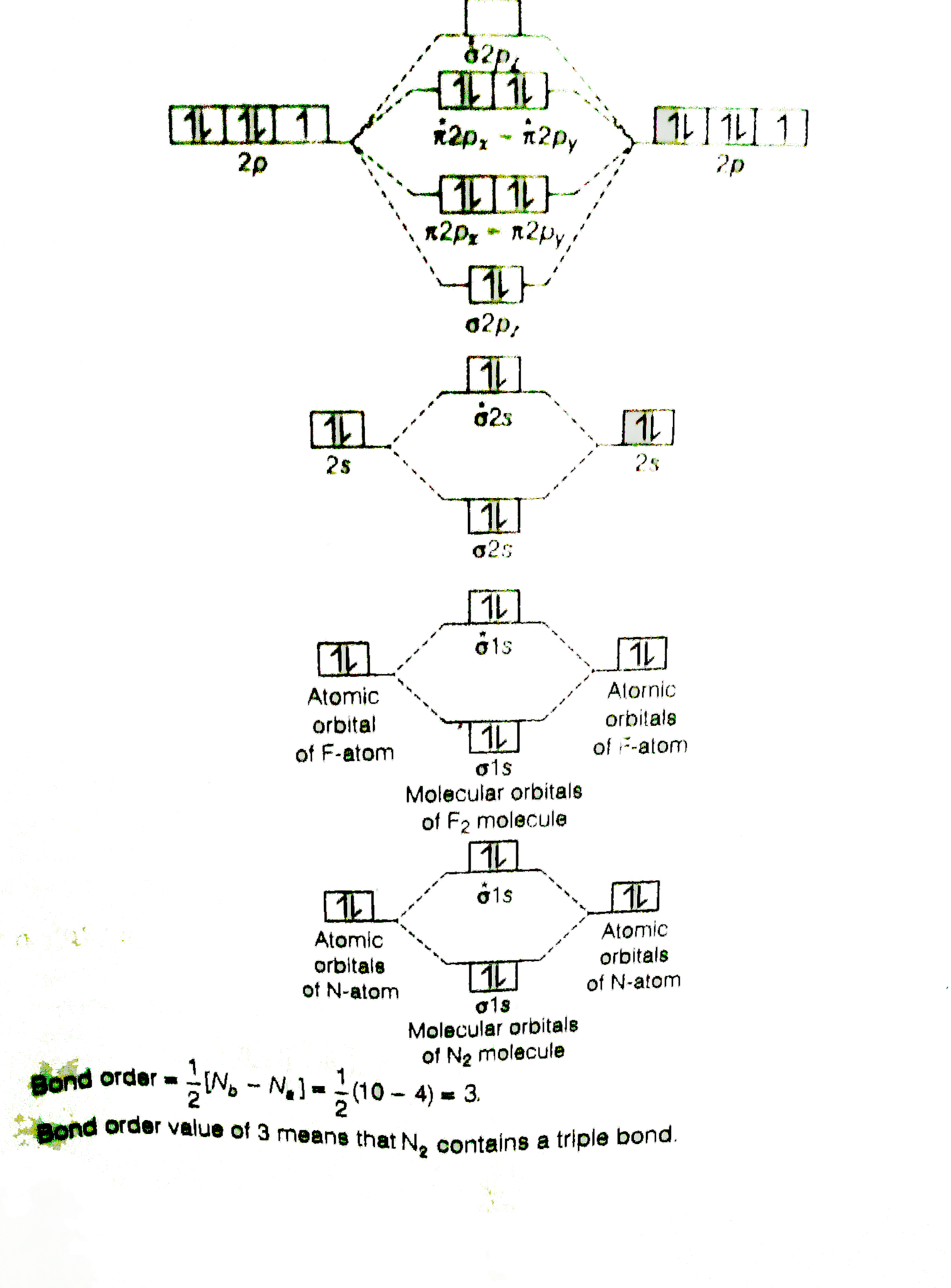
Use The Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram To Show That N 2 Would Be Expected To Have A Triple Bond F 2 A Single Bond And Ne 2 No Bond
6.3 How is energy related to the wavelength of radiation? We can think of radiation either as waves or as individual particles called photons. The energy associated with a single photon is given by E = h ν, where E is the energy (SI units of J), h is Planck's constant (h = 6.626 x 10 -34 J s), and ν is the frequency of the radiation (SI units of s -1 or Hertz, Hz) (see figure below).
How would the dx2−y2 orbital in the n=5 shell compare to the dx2−y2 orbital in the n=3 subshell? A. The contour of the orbital would extend further out along the x and y axes. B. The value of ℓ would increase by 2. C. The radial probability function would include two more nodes. D.
Answer to Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2−. Do you expect these molecules to exist in the. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, Diberyllium, Be2, has a bond order of zero and is unknown.
Achievements And Trends In Photoelectrocatalysis From Environmental To Energy Applications Springerlink
While Lewis diagrams and energy level structures can show connectivity and energy relationships of mol-ecules, they do not show the shape of the molecules. For this we need to picture atomic and molecular orbitals. l = 0 2
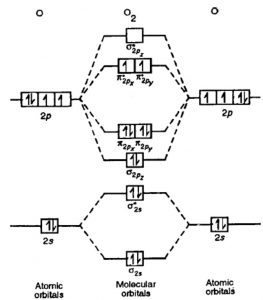
Energy Level Diagram For Molecular Orbitals Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Chemistry Class 11
Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, H− 2 has three electrons while H+ 2 has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one σ1s and one σ* 1s MO by conservation of orbitals. If you calculate their bond order, you get: BOH+ 2 = 1 2(Bonding − ...
Chemical bonding - Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The procedure can be The molecular orbital energy- level diagram that results is constructed by putting .May 20, · Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2- and then identify the bond order? i know the answer im just posting it for whoever may need it. (check picture)Status: Open.
Answer to Draw an MO energy diagram and predict the bond order of Be2+ and Be2−. Do you expect these molecules to exist in the. From the above MO diagram we can see that number of elctrons in the bonding and antibonding orbital is same and hence Be does not form Be2 molecule(for.

Clean Hydrogen Generation And Storage Strategies Via Co2 Utilization Into Chemicals And Fuels A Review Bahari 2019 International Journal Of Energy Research Wiley Online Library
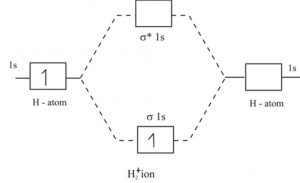
Energy Level Diagram For Molecular Orbitals Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Chemistry Class 11

Scielo Brasil Explaining The Geometry Of Simple Molecules Using Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Built By Using Symmetry Principles Explaining The Geometry Of Simple Molecules Using Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams Built
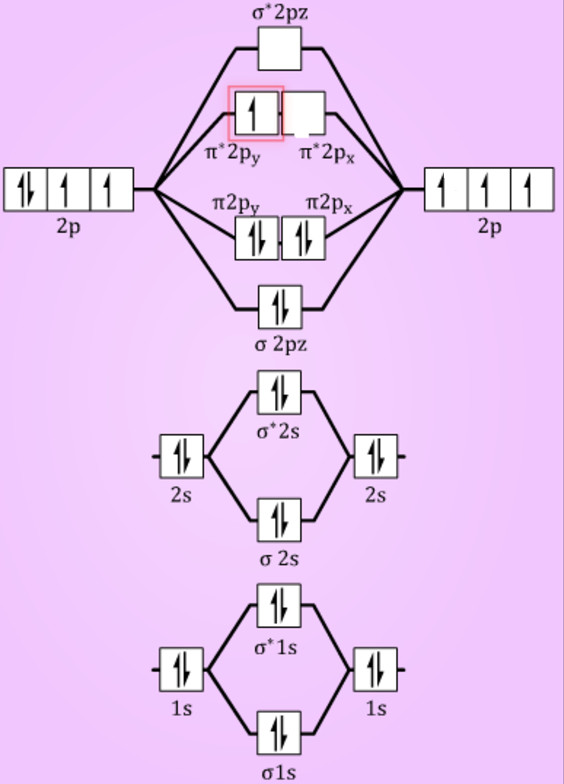
Energy Level Diagram For Molecular Orbitals Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Chemistry Class 11
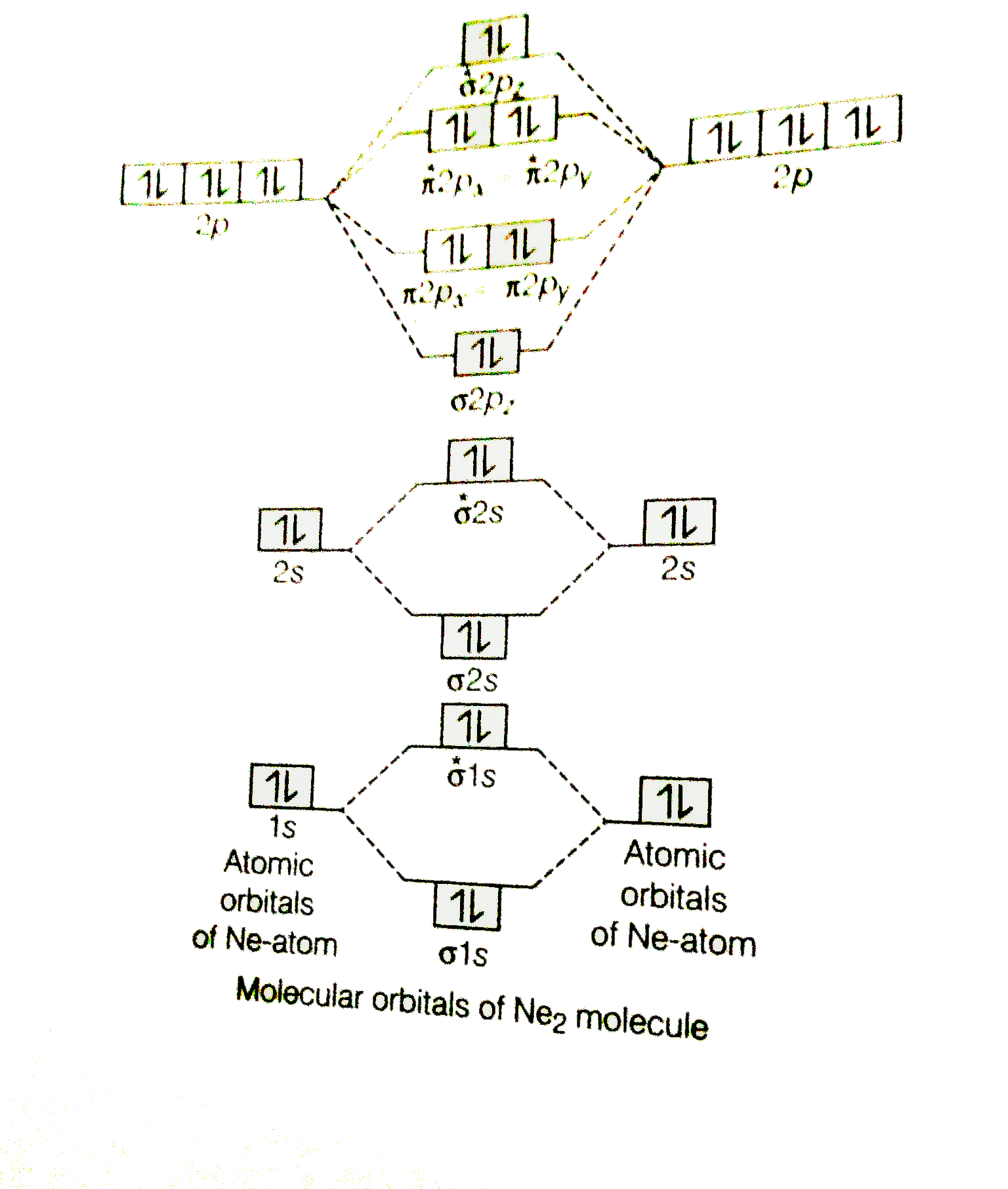
Use The Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram To Show That N 2 Would Be Expected To Have A Triple Bond F 2 A Single Bond And Ne 2 No Bond
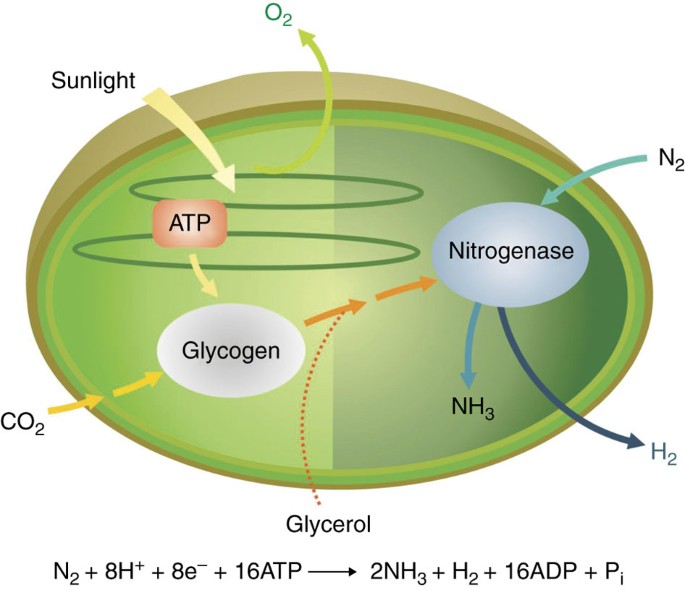
High Rates Of Photobiological H2 Production By A Cyanobacterium Under Aerobic Conditions Nature Communications














0 Response to "43 complete the energy-level diagram for h2−."
Post a Comment