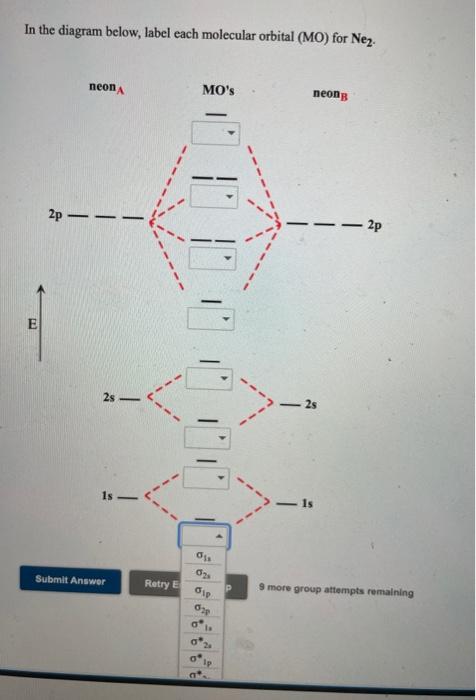
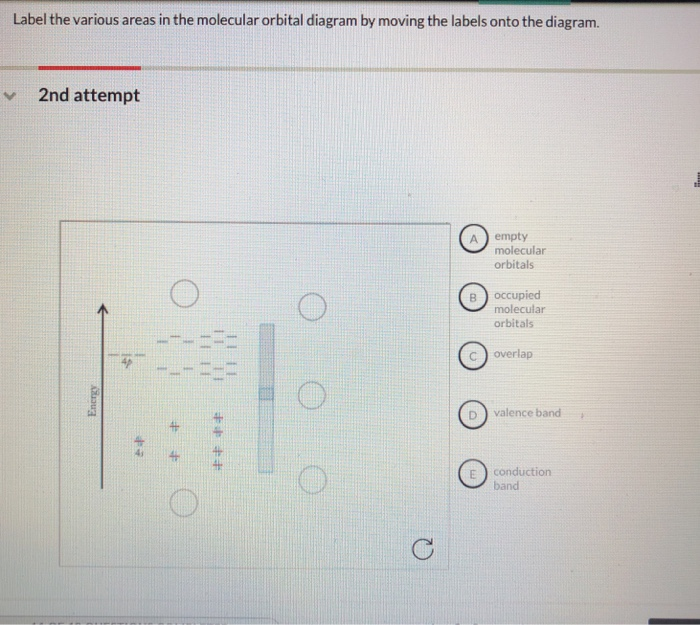
43 label the various areas in the molecular orbital diagram by moving the labels onto the diagram.
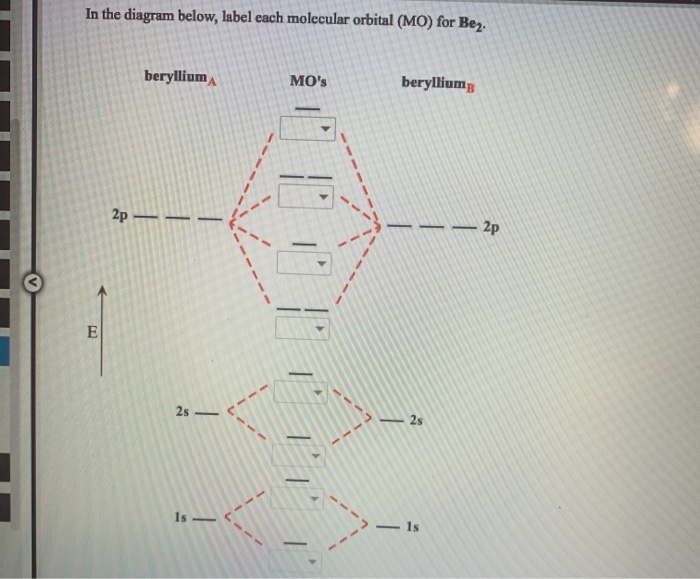
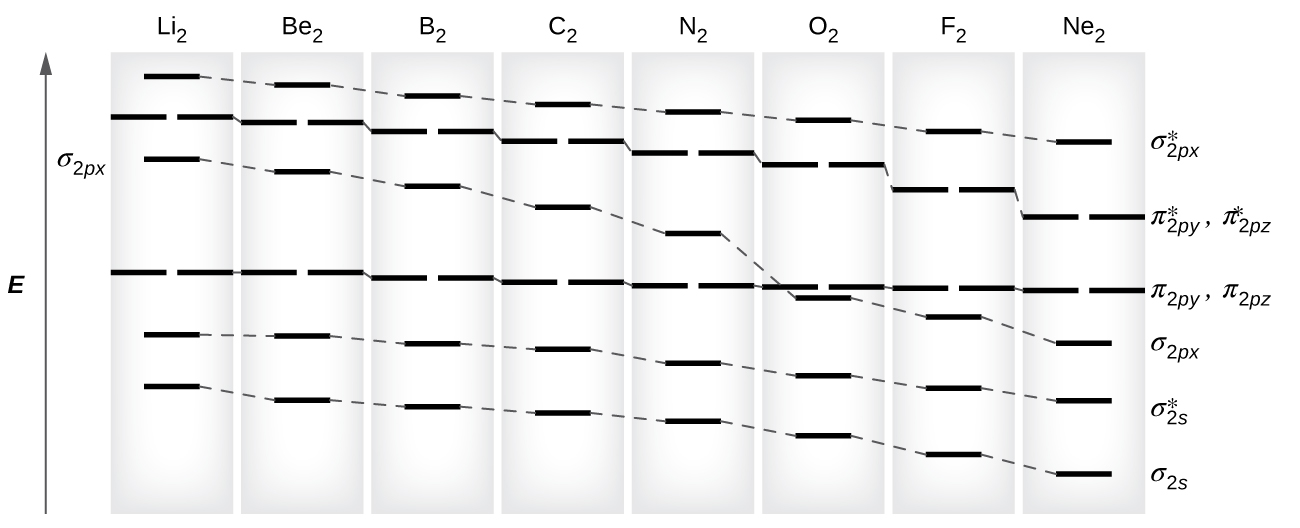
in the molecular orbital diagram. Moving across the period, as the electronegativity of atoms increases e.g, Oxygen and Fluorine, the Let's label the doubly occupied orbital as 2py. The double bond in O2 can be formed from the sigma overlap of the unhybridized 2pz orbital of each oxygen atom. Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. The video below describes how to generate molecular orbital diagrams for B₂ and other diatomic molecules from Row 2 elements of the...
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. Label the diagram by dragging the Molecular Orbital Mo Diagram Of N2. 8 2 Hybrid Atomic Orbitals Chemistry. Covalent Dye Attachment Influences The Dynamics And Conformational.
Label the various areas in the molecular orbital diagram by moving the labels onto the diagram.
Molecular Orbital theory (MO) is the most important quantum mechanical theory for describing bonding in molecules. The difference become more apparent when we look at MO in larger molecules. MO and Molecular Geometry. Why in the world would you ever do a molecular orbital calculation? Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on The energies involved in the molecule's various motions can then be broken down into three categories ...of molecular orbitals (LCAO), bonding / antibonding - Labelling of molecular orbitals (MOs) (σ, π and g, u) - Homonuclear diatomic MO diagrams • E.g. n=4.33 is not allowed - The wavefunction is not continuous. • The wave nature of electrons brings in the quantized nature of the orbital energies.
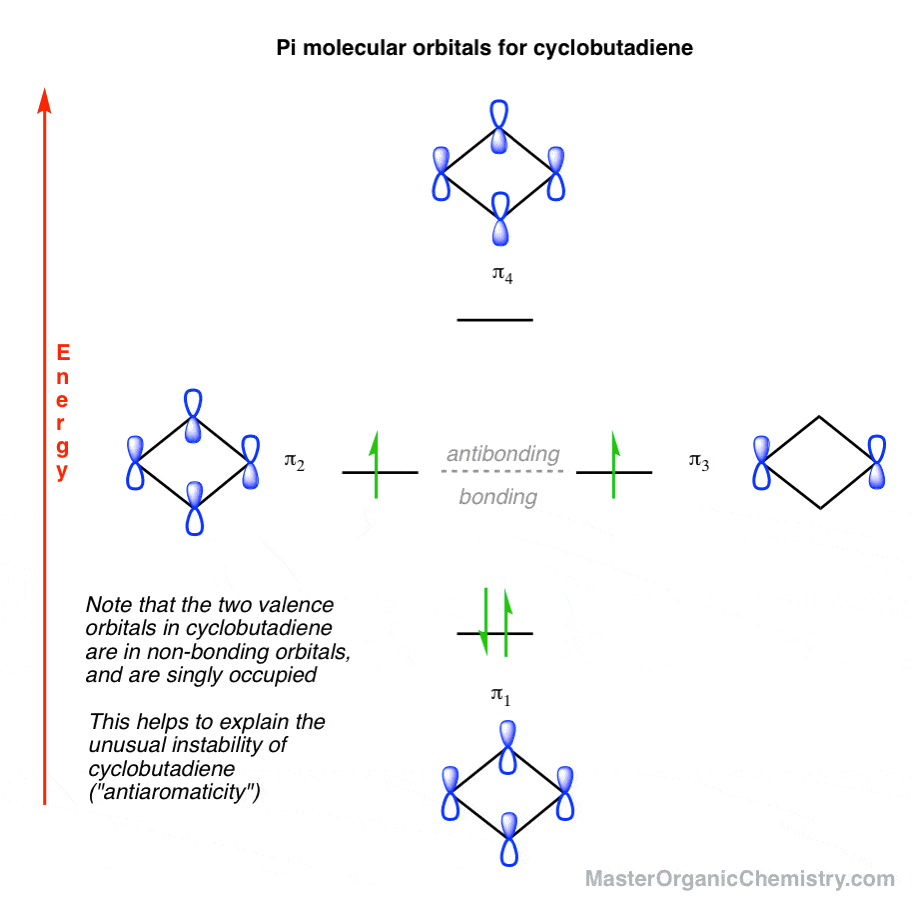
Label the various areas in the molecular orbital diagram by moving the labels onto the diagram.. Condenser focus knob - this is a knob that moves the condenser up or down thus controlling the focus of light on the specimen. A. Microscope is usually used for the study of microscopic algae, fungi, and biological specimens. Q. Diagrammatically, identify the various parts of a microscope. The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Cyclobutadiene Reveals Why Cyclobutadiene Is Extremely Unstable: It Has Unpaired Electrons Of Equal Energy. In the next post we'll cover a very convenient short-cut that will help us quickly draw molecular orbital diagrams in seconds (yes, really!) called... Energy levels: Molecular Orbital Theory - revision11:10. Molecular Orbital diagram for CO5:09. Here we have a molecular orbital diagram for the CO molecule. So again, it's drawn in the familiar pattern. Check Your Learning Label the molecular orbital shown as σ or π, bonding or This interdisciplinary area of study uses biology (understanding diseases and how they operate) to identify specific In the molecular orbital model, an electron contributes to a bonding interaction if it occupies a bonding...
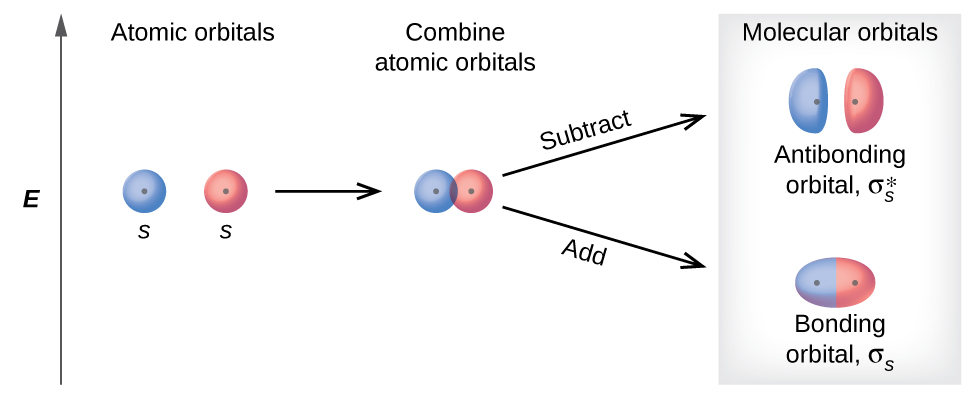
The molecular orbital diagram representing this order of energy levels is shown in fig. On the other hand, if there are unpaired electrons in the molecule, the substance is paramagnetic (attracted by the magnetic field). Let's take a question to understand it more clearly. Molecular orbital (MO) theory describes the behavior of electrons in a molecule in terms of combinations of the atomic wavefunctions. We predict the distribution of electrons in these molecular orbitals by filling the orbitals in the same way that we fill atomic orbitals, by the Aufbau principle. Simple molecular orbital diagrams. Dihydrogen and its ion H2+. Dihelium He2. As two H nuclei move toward each other, the 1s atomic orbitals of the isolated atoms gradually merge into a new molecular The in-phase, reinforcing interaction yields the bonding orbital that we just considered. ...the labels onto the diagram. v 2nd attempt A empty molecular orbitals B occupied molecular orbitals C overlap D valence band Econduction band. Who are the experts?Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the...
Download scientific diagram | (Color Online) Molecular orbital diagram of MoS2. We show that neutral Er defects lead to localized defect states (LDS) in the band structure due to the f-orbital states of Er, which in turn give rise to sharp transitions in in-plane and out-of-plane optical absorption spectra... How do you label and identify the parts of the cell. Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the various chromosome structures. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. I really don't understand this or how to make/read the diagrams when asked to make one or how to determine something from it. I guess it would help to know about sp orbitals too. Books, professors, and everybody in the world really butchers molecular orbital theory. It makes me sad.
Molecular orbital diagrams provide qualitative information about the structure and stability of the electrons in a molecule. This article explains how to create molecular orbital diagrams in LaTeX by means of the package MOdiagram. For information about the more traditional molecular structure...
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. Specific titles may include: Computational Chemistry - This course will focus on using various computational engines to study chemical structure, molecular orbitals, spectroscopic...
A bare molecular orbital diagram is presented and you must drag the correct orbitals and labels onto the diagram. The diagram is then completed by filling the energy levels with the correct number of electrons. The following molecules are currently available
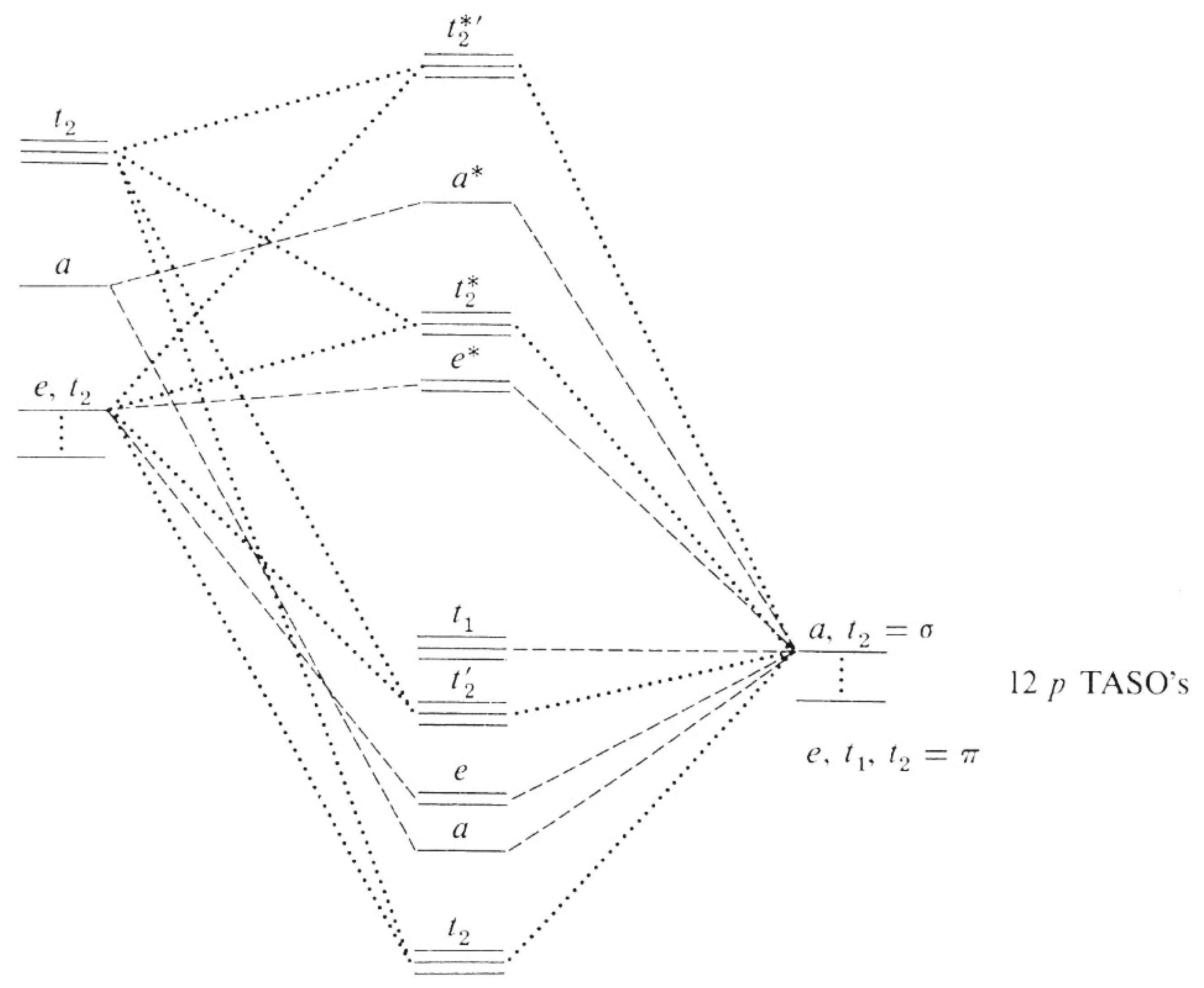
The procedure for working out a molecular orbital of a general diatomic molecule is quite simple. We then fill up the molecular orbitals, starting with the lowest in energy, until all the electrons in the species have been The central set of orbitals are the molecular orbitals, and are labeled for clarity.
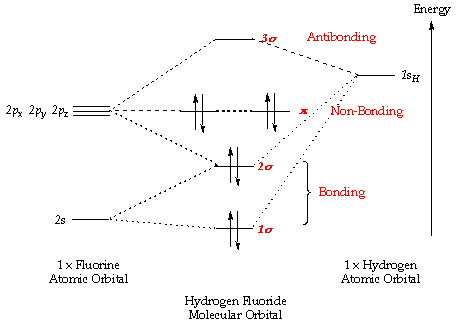
Label the molecular orbital shown as σ or π, bonding or antibonding and indicate where the node occurs. Figure 8.34 This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic. The molecular orbitals are filled in the same manner as atomic orbitals, using the Aufbau principle and...
Other articles where molecular orbital energy-level diagram is discussed: chemical bonding: Molecular orbitals of H2 and He2: The molecular orbital The molecular orbitals are labeled to reflect the atomic orbitals from which they are composed as well as their symmetry properties.
Chapter 6 - Molecular Structure. Introduction. A method for constructing Lewis structures of simple molecules and ions was presented in Chapter 5. In this Double and triple bonds each represent a single electron group because the electron pairs in the bonds are all restricted to the region of space...
Molecular Orbital Diagram for Carbon Dimer (C2).Fill from the bottom up, with 8 electrons total.Bonding Order is 2, and it is Diamagnetic.sigma2s(2),sigma2s...
Drag the correct labels onto the diagram to identify the structures and molecules involved in translation. Drag the labels to fill in the targets beneath each diagram of a cell. Look carefully at the diagrams depicting different stages in meiosis in a cell where 2n 6. Molecular Orbital Diagram Cn.
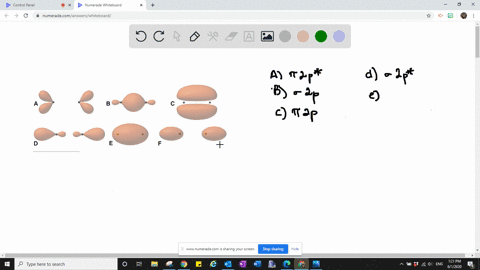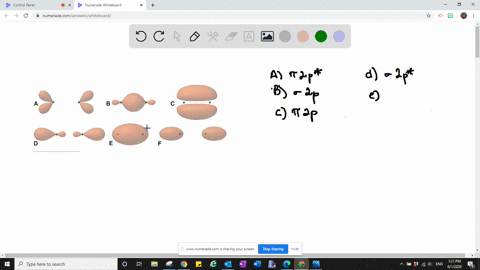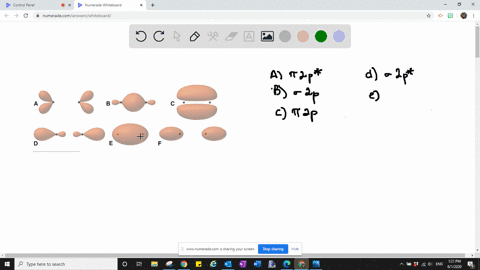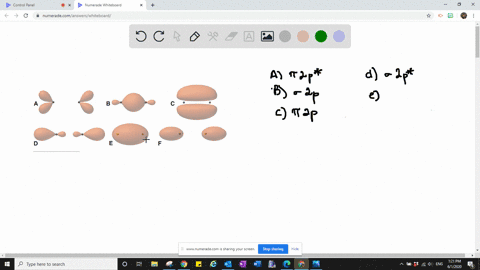
Solved The Following Is Part Of A Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram For Mos Constructed From 1s Atomic Orbitals A What Labels Do We Use For The Two Mos Shown B For Which Of
Molecular orbital theory was put forward by Hund and Mullikan in 1932. This theory is modern and more rational. This theory assume that in molecules, atomic orbitals (vii) The molecular orbitals are filled in the increasing order of their energies, starting with orbital of least energy. (Aufbau principle).
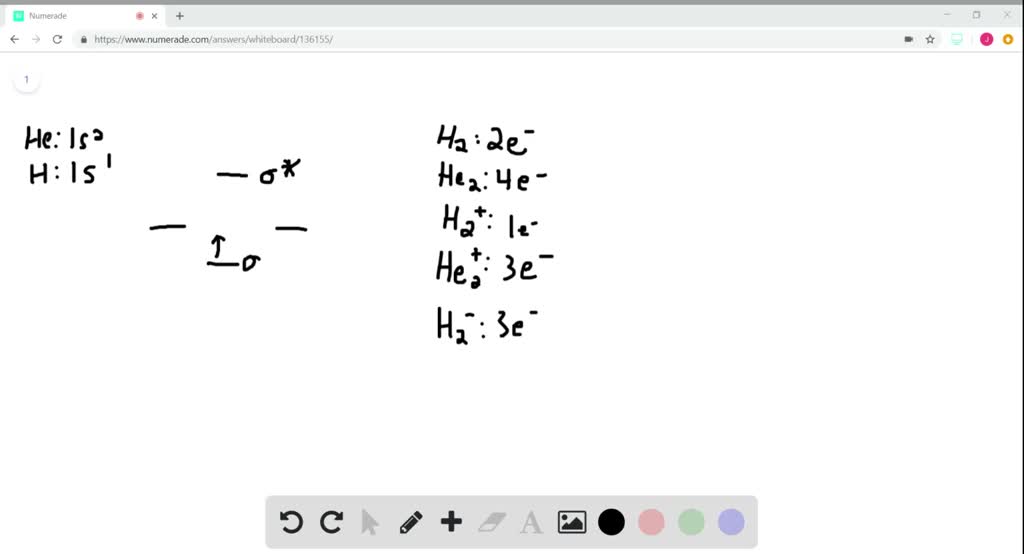
Solved The Following Is Part Of A Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagram For Mos Constructed From 1s Atomic Orbitals A What Labels Do We Use For The Two Mos Shown B For Which Of
Valence bond (VB) theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding, which was useful for predicting the shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations accurately because it ignores the wave nature of the electrons.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the stages of the cell cycle. Drag the terms on the left to the appropriate blanks on the right to complete the sentences. Which of the following statements correctly describes the timing of DNA synthesis? DNA is synthesized in the S phase of interphase.
...of molecular orbitals (LCAO), bonding / antibonding - Labelling of molecular orbitals (MOs) (σ, π and g, u) - Homonuclear diatomic MO diagrams • E.g. n=4.33 is not allowed - The wavefunction is not continuous. • The wave nature of electrons brings in the quantized nature of the orbital energies.
Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on The energies involved in the molecule's various motions can then be broken down into three categories
Molecular Orbital theory (MO) is the most important quantum mechanical theory for describing bonding in molecules. The difference become more apparent when we look at MO in larger molecules. MO and Molecular Geometry. Why in the world would you ever do a molecular orbital calculation?
32 Label The Various Areas In The Molecular Orbital Diagram By Moving The Labels Onto The Diagram Labels For Your Ideas

33 Label The Various Areas In The Molecular Orbital Diagram By Moving The Labels Onto The Diagram Labels Design Ideas 2020
Molecules Free Full Text On The Origins Of Some Spectroscopic Properties Of Purple Iron The Tetraoxoferrate Vi Ion And Its Pourbaix Safe Space Html

4 On The Basis Of Molecular Orbitals And Molecular Orbital Diagrams Predict Which Molecule In Each Homeworklib
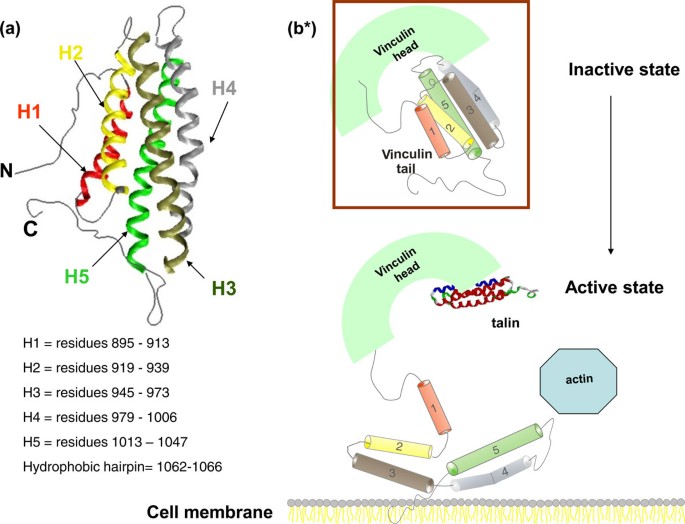
How Far In Silico Computing Meets Real Experiments A Study On The Structure And Dynamics Of Spin Labeled Vinculin Tail Protein By Molecular Dynamics Simulations And Epr Spectroscopy Bmc Genomics Full

4 On The Basis Of Molecular Orbitals And Molecular Orbital Diagrams Predict Which Molecule In Each Homeworklib
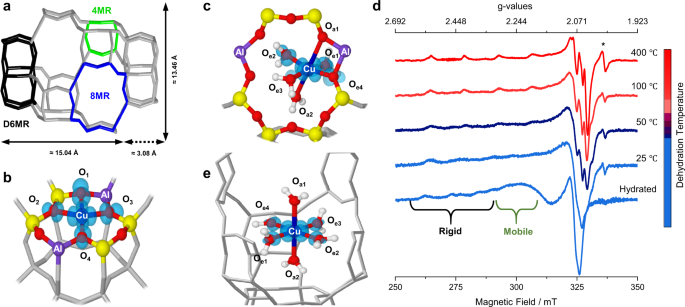
17o Epr Determination Of The Structure And Dynamics Of Copper Single Metal Sites In Zeolites Nature Communications
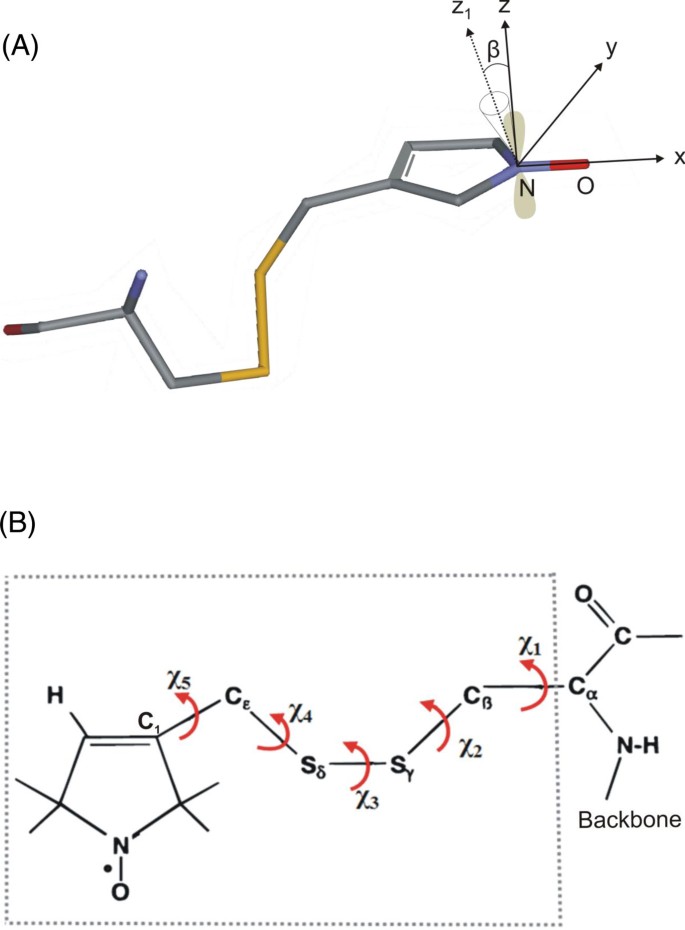
How Far In Silico Computing Meets Real Experiments A Study On The Structure And Dynamics Of Spin Labeled Vinculin Tail Protein By Molecular Dynamics Simulations And Epr Spectroscopy Bmc Genomics Full

33 Label The Various Areas In The Molecular Orbital Diagram By Moving The Labels Onto The Diagram Labels Design Ideas 2020

Single Reference Coupled Cluster Methods For Computing Excitation Energies In Large Molecules The Efficiency And Accuracy Of Approximations Izsak 2020 Wires Computational Molecular Science Wiley Online Library
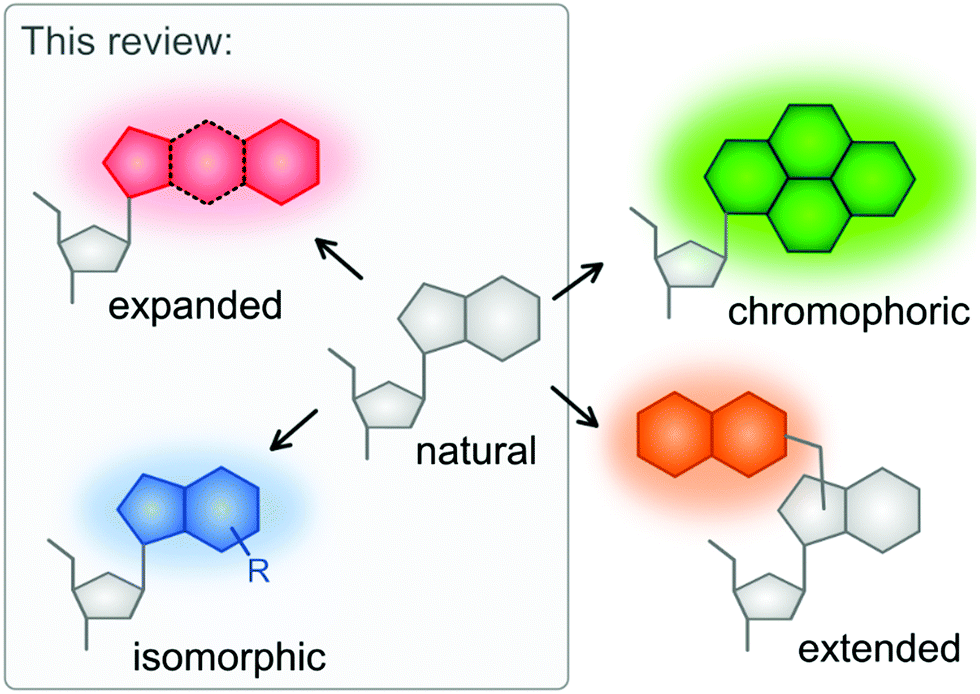
Fundamental Photophysics Of Isomorphic And Expanded Fluorescent Nucleoside Analogues Chemical Society Reviews Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D1cs00194a
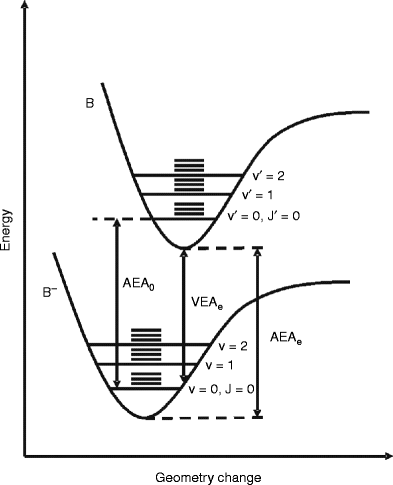
33 Label The Various Areas In The Molecular Orbital Diagram By Moving The Labels Onto The Diagram Labels Design Ideas 2020
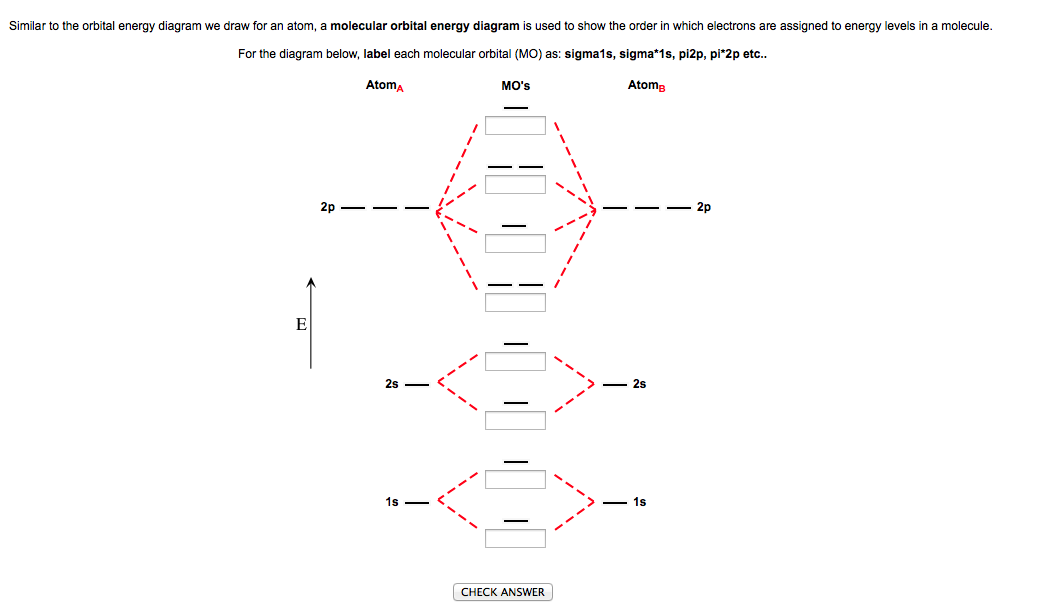







0 Response to "43 label the various areas in the molecular orbital diagram by moving the labels onto the diagram."
Post a Comment