41 beta decay feynman diagram
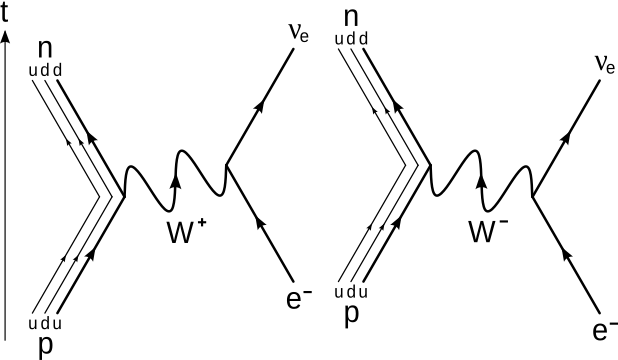
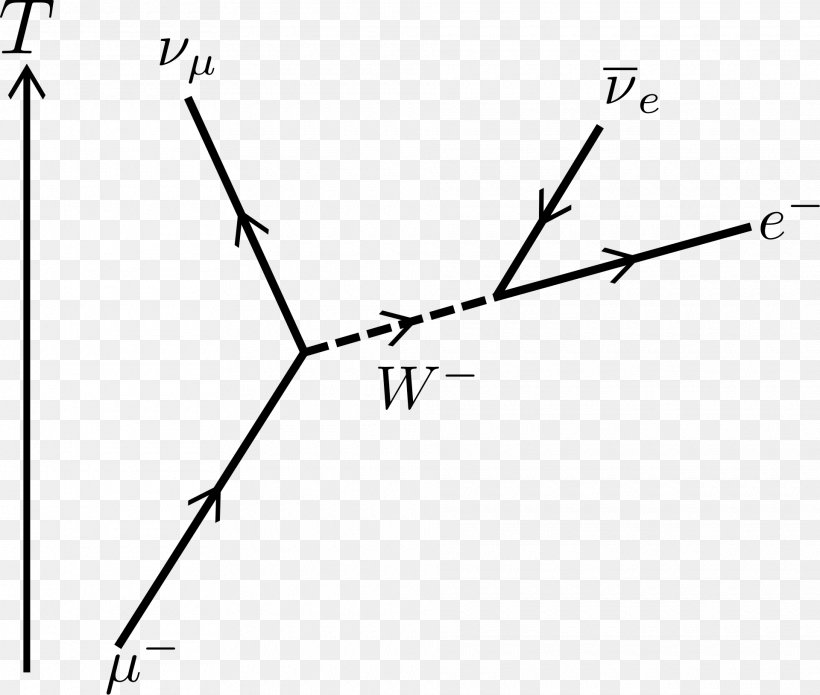
The Feynman diagram for the beta decay of a neutron into a proton, electron, and electron antineutrino via an intermediate heavy W-boson Before the structure of the nucleus was understood, this emission of negative particles was observed, and they were called "beta particles" or "beta rays".
Feynman diagram for beta decay in the Standard Model with three massive neutrinos (i = 1, 2, 3), mediated via left-handed currents. ... Figure 1: Feynman diagram ...
This weak force is believed to be carried by three fundamental particles: W-,W+ and Z bosons. Using the Feynman diagram, describe the beta-negative decay of a ...2 Nov 2019 · Uploaded by AK LECTURES
Beta decay feynman diagram
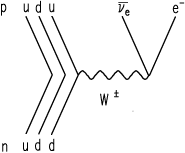
This is a list of common Feynman diagrams. Name or phenomenon Description Diagram Beta decay: beta particle is emitted from an atomic nucleus Compton scattering: scattering of a photon by a charged particle Neutrino-less double beta decay: If neutrinos are Majorana fermions (that is, their own antiparticle), Neutrino-less double beta decay is possible. Several experiments are searching for ...
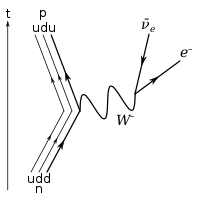
Download scientific diagram | 1: Feynman diagram of Inverse Beta Decay (IBD) process. from publication: Neutrino Physics in Present and Future Kamioka Water-Cherenkov Detectors with Neutron ...
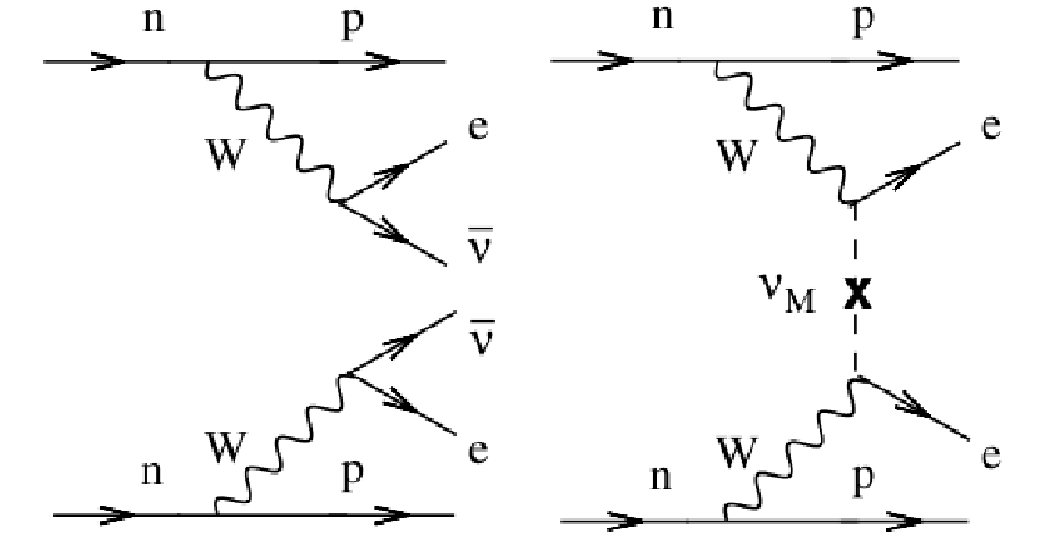
The explanation is the same as the one above. Positron has a lepton number equal to − 1 (because its an antilepton) and neutrino has + 1, so that the total lepton number on the RHS is equal to the total lepton number on the LHS. The second Feynman diagram is wrong. W + should decay into a positron-neutrino pair: W + → e + ν e.
Beta decay feynman diagram.
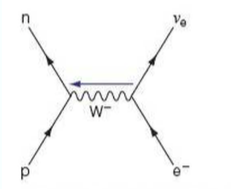
Answer (1 of 2): Why is an antineutrino emitted in a beta minus decay and not a neutrino? Just for those playing along at home, in a beta minus decay a neutron decays into a proton and emits an electron and an antineutrino (actually an anti-electron neutrino). It has to be an antineutrino becau...
Explains examples of electron repulsion, Beta decay and positron decay. Feynman Diagrams Richard Feynman, born in 1918, was an American theoretical physicist, who played a major role in the field of quantum electrodynamics(QED) with a significant contribution.
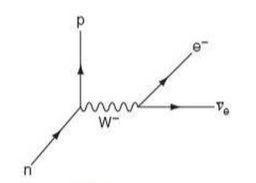
The weak interaction visualized in the Feynman diagram below is responsible for the decay of the neutron and for beta decay. The charged W bosons participate in the transformation of quarks in which the flavor of the quark is changed. The neutral Z boson does not participate in changing the flavor of quarks, so its interactions are harder to ...
A Feynman diagram is a representation of quantum field theory processes in terms of particle interactions. The particles are represented by the lines of the diagram, which can be squiggly or straight, with an arrow or without, depending on the type of particle.
The Feynman diagram shows a neutron undergoing beta decay. What particle is represented by 𝑋 in the diagram? A 𝛽 B 𝑒 C 𝑊 D 𝛾 E 𝑊 Q4: The Feynman diagram is supposed to show the annihilation of an electron and a positron to produce a gamma-ray photon and then the pair production of an electron and a positron by that same photon.
⇒ Feynman Diagrams are pictorial representations of the interactions of subatomic particles ⇒ For example, this shows a Feynman Diagram of beta (β-) decay (see our notes on nuclear equations if you have not done so already): ⇒ Usually, Feynman Diagrams are read from left to right ⇒ So, here, we can see a neutron decaying into a proton and a W-exchange particle, which subsequently ...
Feynman diagrams for all the ones mentioned above can be found in google images ( I don't know how to draw it out on here). The gauge bosons which show up in the diagrams are fixed for that diagram. Beta plus/minus decay occur through the weak interaction so have a W + and W - gauge boson respectively.
The Feynman diagram for neutrinoless double-beta decay. M AJORANA is an experiment to search for neutrinoless double-beta decay (0νββ). Neutrinos are fundamental particles that play key roles in the early universe, cosmology and astrophysics, and nuclear and particle physics.
Like muon decay, the theory of neutron beta decay based on the Feynman diagram of gure 3 is still a V-A theory and produces surprisingly good results. However, a more 6. sophisticated theory will take into consideration the observed generational mixing of quarks associated with the weak interaction. Moreover, since a neutron is composite particle, the presence of spectator quarks must also be ...
Drawing Feynman Diagrams A Feynman diagram is a pictorial representation of the matrix element describing particle decay or interaction a !b + c + ::: a + b !c + d To draw a Feynman diagram and determine whether a process is allowed, follow the vebasic steps below: 1 Write down the initial and nal state particles and antiparticles and note
22 Apr 2014 — The Feynman diagram below shows how it really works—and why the name of intermediate vector bosons for these three strange 'particles' (W+, W–, ...
A Feynman diagram represents all possible time orderings of the possible vertices, so the positions of the vertices within the graph are arbitrary. Consider the following two diagrams for e+ + e ! + + : e+ e + e+ e + In the left diagram it appears that the incoming particles annihilated to form a virtual photon, which then split to produce the outgoing particles. On the right diagram it ...
With a twist of the Feynman diagram above, one can arrive at the interaction responsible for the decay of the muon, so the structures obtained from the primitive vertices can be used to build up a family of interactions. The transformation between the two Feynman diagrams can also be seen as an example of crossing symmetry.
If you Google 'feynman diagram beta decay' you'll see that, for the beta minus decay, on some the anti-electron neutrino's arrow is pointed away from the W-, and in others it's pointed towards. Which way should it be? Does it matter? 0. reply. Not what you're looking for? Try… Feynman diagram feynman diagrams Beta Radiation W Bosons lerjj Badges: 13. Rep:? #2 Report 7 years ago #2 I think it ...
The corresponding Feynman diagram will be: This is a weak decay of the strange quark. It is an allowed diagonal change between quark generations. The Feynman diagram for the s to u transition is a combination of two quark-W vertices. The pion is derived from a same generation quark weak vertex. Return to top of page
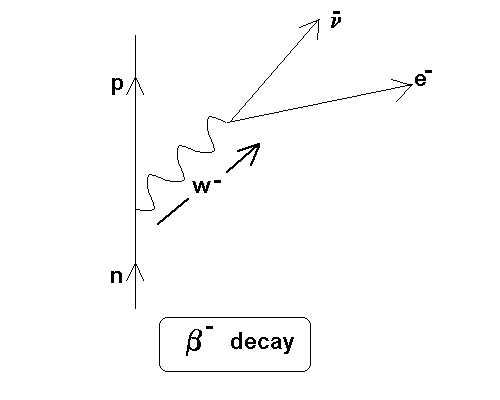
In beta minus decay, a neutron decays into a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino. In beta plus decay, a proton decays into a neutron, a positron, and a neutrino. β- decay: n ⇒ p + e- +ū e β + decay: p ⇒ n + e + + u e. Let's see the Feynman diagram for a β- decay:
In nuclear physics, beta decay (β-decay) is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (fast energetic electron or positron) is emitted from an atomic nucleus, transforming the original nuclide to an isobar of that nuclide. For example, beta decay of a neutron transforms it into a proton by the emission of an electron accompanied by an antineutrino; or, conversely a proton is ...
Example 6: Beta Decay. Feynman diagram showing the process of beta decay. Notice that a W-boson is involved here. This implies that this interaction occurs through the weak nuclear interaction. This is one of the most important interaction we're going to consider in part 3 and is described briefly below.
Feynman’s Diagram for - Decay The force responsible for - decay is the weak force. So, the exchange particle is the W-. Draw Feynman’s diagram for this reaction. After p e- e W n Before The neutron decays into a proton releasing a W particle which very quickly decays into an -particle and an anti-neutrino.
Feynman diagrams can be adapted to describe the interactions of the weak force. Animations briefly explaining the Feynman diagrams for beta minus and beta plus decay. 'Adding up' all the possible diagrams for a particular decay (e.g. beta minus) tells us about the probability of the decay. Beta plus decay
The Feynman diagram for this process is below. The neutron ejects a W-boson, which then immediately decays to an electron and antineutrino. The neutron becomes a proton. Feynman Diagram - Beta Decay If the neutron consists of both a W+boson and a W-boson, it is validated in the decay process. Upon decay, it loses the W-boson.
1. Which Feynman diagram shows beta-plus (β) decay? Markscheme A Examiners report [N/A] + 2. The average binding energy per nucleon of the nucleus is 7.5 MeV. What is the total energy required to separate the nucleons of one nucleus of ? A. 53 MeV B. 60 MeV C. 113 MeV D. 173 MeV Markscheme C Examiners report [N/A] 15 8O 15 8O
Donate here: http://www.aklectures.com/donate.phpWebsite video link: http://www.aklectures.com/lecture/weak-charges-and-feynman-diagram-for-beta-decayFaceboo...
Beta Decay | Physics Forums. Feb 28, 2012. #1. Sagan369963. 4. 0. From what I understand, which is kind of limited, the neutron (939Mev) decays into a proton (938Mev) giving off a HUGELY massive particle called a W boson (80,000Mev). The W boson exists for 3*10^-25 seconds then gets transformed into an electron (.511Mev) and an electron anti ...
Video 3 of the Half-Life series of short animations about nuclear physics. Shows the equations and Feynman diagrams that describe beta minus and beta plus d...
Like electrical circuit diagrams, every line in the diagram has a strict mathematical interpretation. For details of Feynman diagram calculation, take a Advanced Quantum or 880.02 course see Griffiths (e.g. sections 6.3, 6.6, and 7.5) Bjorken & Drell (Relativistic Quantum Mechanics). Feynman Diagrams µ decay € e+e−→µ+µ− scattering
Feynman diagrams are graphical ways to represent exchange forces. Each point at which the lines come together is called a vertex, and at each vertex we must conserve charge, baryon number and lepton number. They were developed by Richard Feynman to decribe the interactions in quantum electrodynamics (QED).
1. Which Feynman diagram shows beta-plus (β+) decay? 2. The average binding energy per nucleon of the nucleus is 7.5 MeV. What is the total energy required to separate the nucleons of one nucleus of ? A. 53 MeV B. 60 MeV C. 113 MeV D. 173 MeV 15 8O 15 8O 3. Two pure samples of radioactive nuclides X and Y have the same initial number of atoms.





















![Beta Decay Equations and Feynman Diagrams [Half-life, video 03]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/j9IMw2eUHp4/maxresdefault.jpg)




0 Response to "41 beta decay feynman diagram"
Post a Comment