42 e1 reaction energy diagram
8.2 E1 Reaction. E1 Mechanism. Similar to substitutions, some elimination reactions show first-order kinetics. These reactions go through E1 mechanism, ... Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams Predicting the Products: Substitution versus Elimination Is Nuc/Base strong? no Unimolecular Reaction Bimolecular yes Reaction Is Nuc/Base bulky? E2 yes no What kind of substrate? methyl or 1° S N2 3° yes mostly E1* 2° no mostly S N1* What kind of substrate? 2°, 3°, or stabilized 1° 1° S N2 + E2 Is Nuc ...
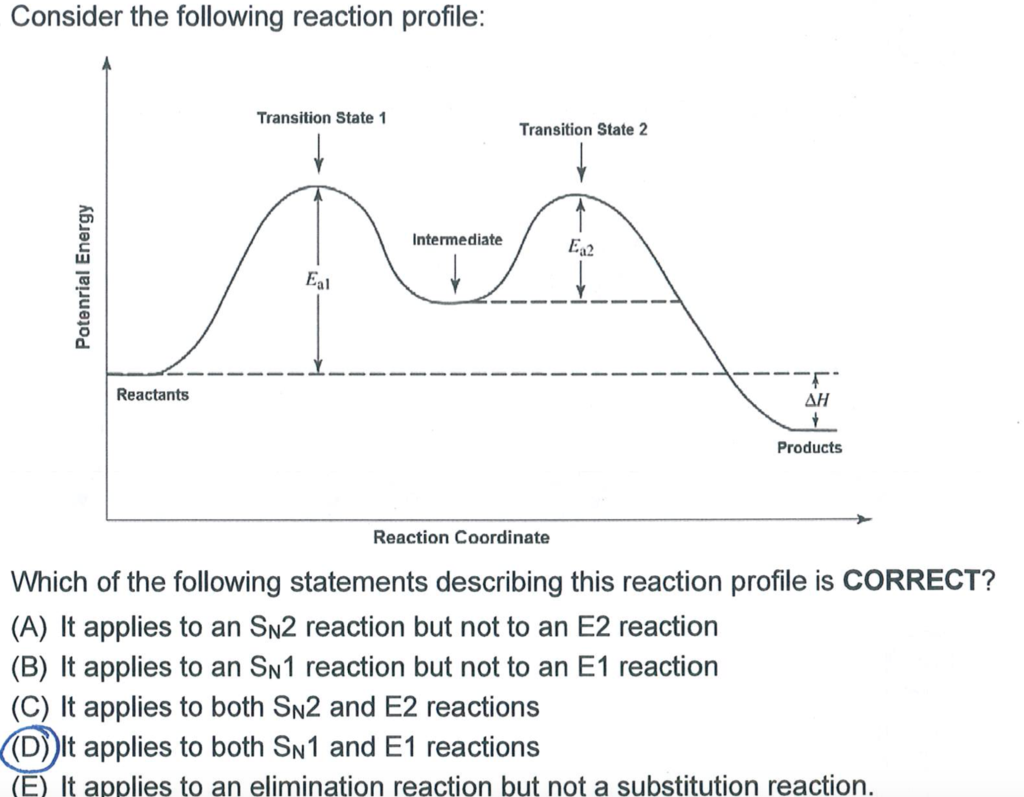
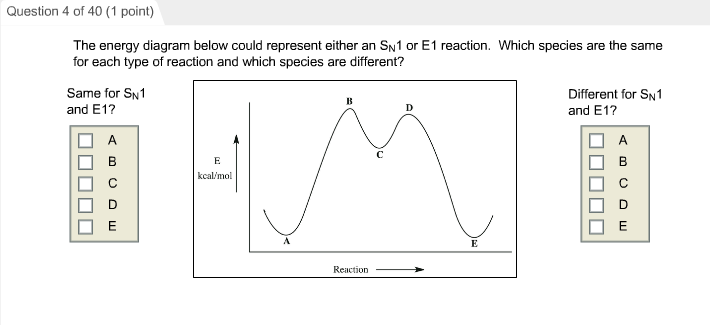
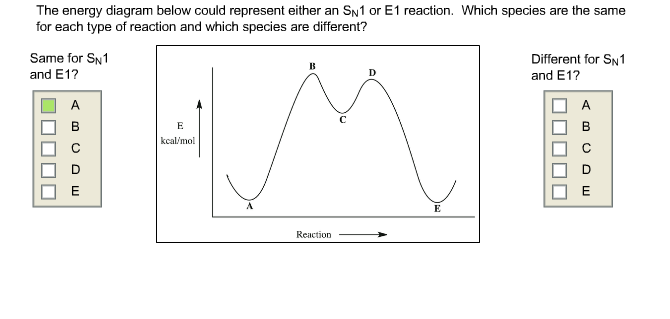
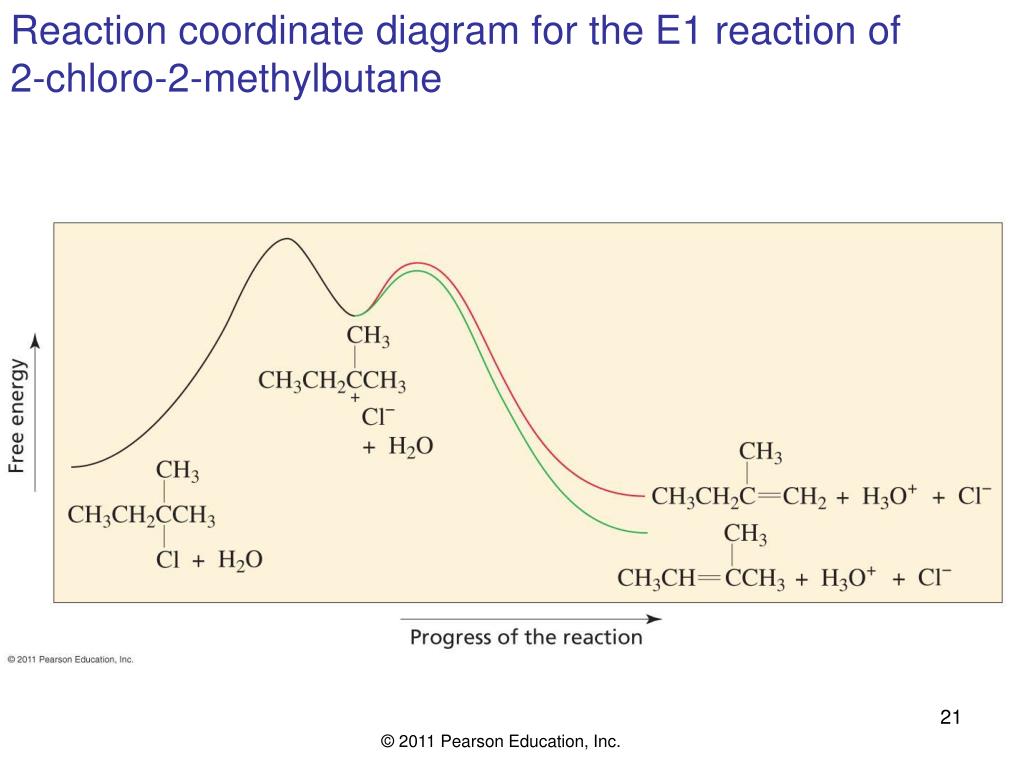
The E1 and S N 1 reactions always compete and a mixture of substitution and elimination products is obtained:. E1 - A Two-Step Mechanism. Let's break down the steps of the E1 reaction and characterize them on the energy diagram:

E1 reaction energy diagram
Elimination Reactions: E2 versus E1. Substrate: Alkene Stability Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams. The central carbon is sp 2 -hybridized, whereat the p orbital is used for the partial Fig Transition state and energy diagram of an S N 2 reaction: Chloroform. Transition state: highest point of an energy structure on a reaction profile graph for ... how many groups are lost in the E1 reaction and what are they. yes. does a mixture of products form for E1. the same as SN1, two hills, overall exothermic but first step has highest activation energy and is endothermic ... what does the energy diagram for E1 look like. E1. what reaction does Zaitsev's rule only apply to. more substituted. which ... For E1 elimination reaction intermediate with two t… View the full answer Transcribed image text : Based upon the energy diagram shown, is this reaction an E1 or an E2 elimination? free energy, kJ/mol reaction coordinate O E1 elimination O E2 elimination O It is impossible to determine from the diagram alone.
E1 reaction energy diagram. 1! Energy/Reaction Coordinate! Diagrams! Thermodynamics, Kinetics ! Dr. Ron Rusay" A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change (ΔGo) Enthalphy (ΔHo): the heat given off or absorbed during a reaction The elimination reaction consists of three fundamental events, and they are; Proton removal. C-C pi bond is formed. There is a breakage in the bond of the leaving group. Depending on the reaction kinetics, elimination reactions can occur mostly by two mechanisms namely E1 or E2 where E is referred to as elimination and the number represent the ... The 4 Components of Every Acid Base Reaction · The E1 Reaction · The Golden Rule ... The SN1 Mechanism · The SN2 Mechanism · The SN2 Reaction Energy Diagram ... E1 reactionOrganic Chemistry. ... E1 Mechanism and energy diagram. 1,919 views1.9K views. Sep 5, 2020 ... E1 reaction Organic Chemistry.
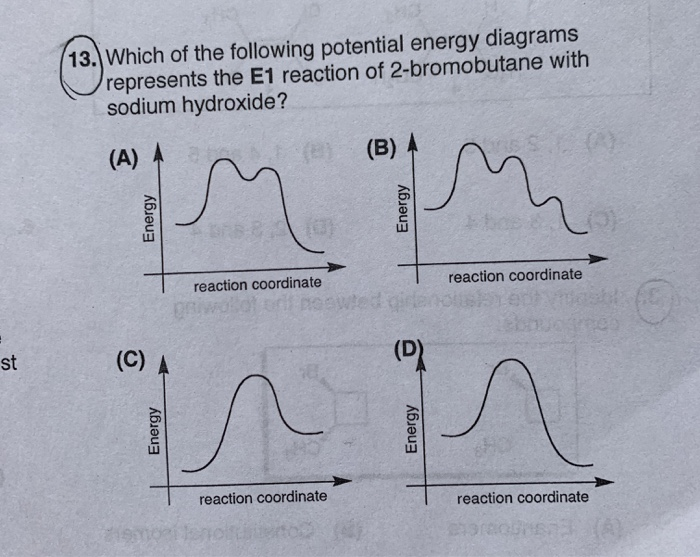
Considering the S N 1, S N 2, E1 and E2 mechanisms, the energy diagram shown below corresponds to. a) only the S N 1 mechanism. b) only the S N 2 mechanism. c) both the S N 1 and E1 mechanism. d) both the S N 2 and E2 mechanism. Learn this topic by watching SN1 SN2 E1 E2 Chart (Big Daddy Flowchart) Concept Videos. The E1 reaction occurs in either the complete absence of bases or in the presence of weak bases. E2 reactions occur in the presence of strong bases. Mechanism. The reaction mechanisms of E1 reactions are known as unimolecular eliminations. The reaction mechanisms of E2 reactions are known as bimolecular eliminations. Steps. See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. Organic chem - E1 and E2 Reactions: 1. Draw the mechanism for the reaction between 2-chloro-2-methylbutane and potassium hydroxide. 2. Draw the mechanism for the reaction between 2-methyl-2-butanol and sulfuric acid. Expert Answer. Acid catalyzed dehydration of secondary / tertiary alcohols. We'll take a look at a mechanism involving solvolysis during an E1 reaction of Propanol in Sulfuric Acid.. Step 1: The OH group on the pentanol is hydrated by H 2 SO 4.This allows the OH to become an H 2 O, which is a better leaving group.; Step 2: Once the OH has been hydrated, the H 2 O molecule leaves, taking its electrons with it.
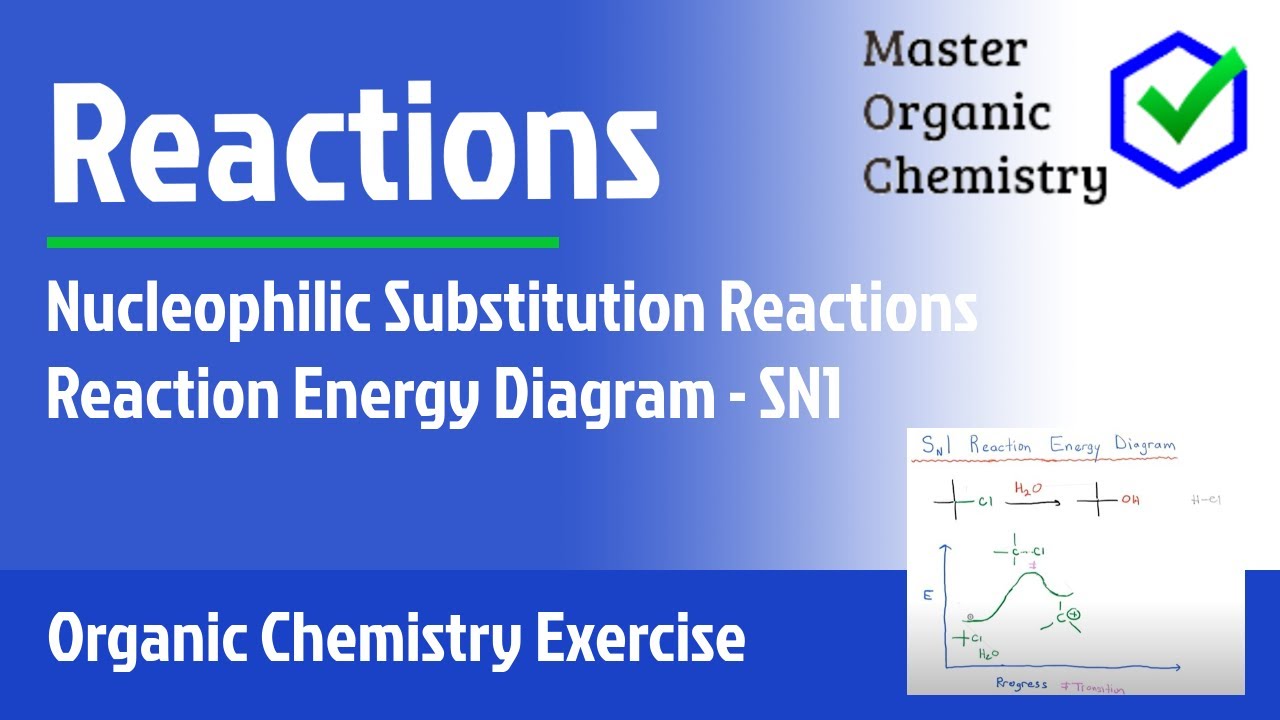
Figure 9.11 Reaction free-energy diagram for the S N1-E1 solvolysis reaction of (CH 3) 3CBr with ethanol.The rate-limiting step,ionization of the alkyl halide (red curve),has the transition state of highest standard free energy.The relative rates of the product-determining steps (blue curves) determine the relative amounts of substitution and b) Does the reaction proceed via S N 1 or S N 2 mechanism? c) Draw the products and complete mechanism of the reaction and identify the rate determining step. d) Is there an intermediate in this reaction? If yes, show its structure and position on the energy diagram. e) How many kJ is the activation energy of the rate determining step? Energy profile diagram of E1 reaction: Orientation and reactivity of E1 reaction: References; Elimination reaction. An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which a pair of atoms or group of atoms are removed from a organic molecule. Elimination reaction is the principal process by which saturated organic compounds (i.e ... The S N 1 reaction energy diagram illustrates the dominant part of the substrate with respect to the reaction rate. The rate-determining step is the formation of the . Substitution Reactions (SN2 versus SN1) SN1. Elimination Reactions: E2 versus E1. Substrate: Alkene Stability Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams.
An energy diagram for the single-step bimolecular E2 mechanism is shown below. We should be aware that the E2 transition state is less well defined than is that of S N 2 reactions. More bonds are being broken and formed, with the possibility of a continuum of states in which the extent of C-H and C-X bond-breaking and C=C bond-making varies.
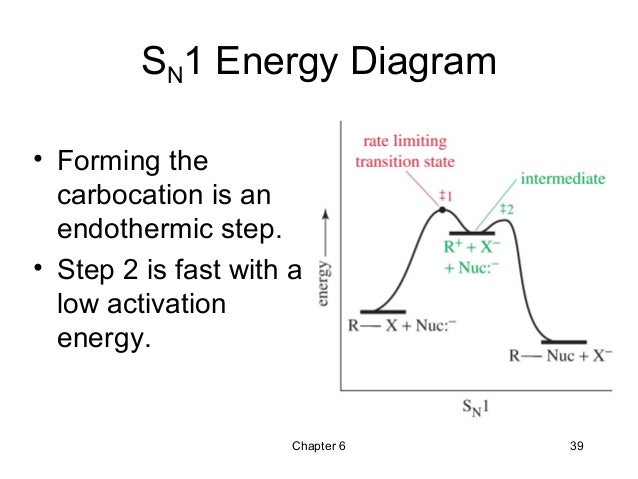
7.4 SN1 Reaction Mechanism, Energy Diagram and Stereochemistry. The reaction between tert -butylbromide and water proceeds via the SN1 mechanism. Unlike S N 2 that is a single-step reaction, S N 1 reaction involves multiple steps. Reaction: (CH 3) 3 CBr + H 2 O → (CH 3) 3 COH + HBr. In step 1, C—Br bond breaks and Br departs with the ...
the slow step of the reaction) and a weak electron pair donor in SN1/E1 reactions (that's why they don't participate in the slow step of the reaction). This leads to differences in reaction mechanisms, which show up in the kinetics of ... energy diagram below. gas phase reactions polar solvent phase reactions Carbocations are more stable ...
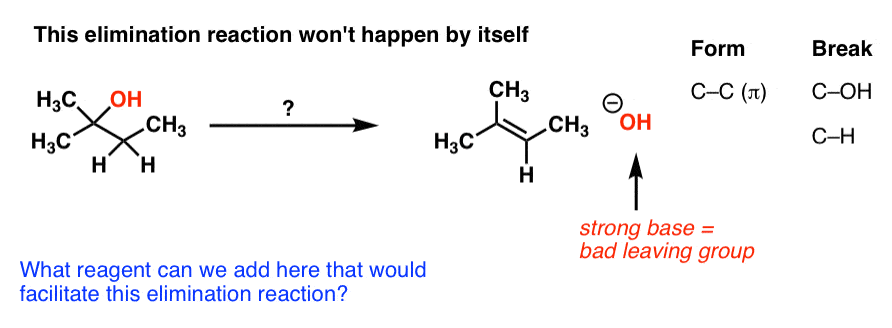
First of all, an elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one or two-step mechanism.. The one-step mechanism is known as the E2 reaction; The two-step mechanism is known as the E1 reaction. Note: The numbers do not have to do with the number of steps in the mechanism, but rather the kinetics of the reaction ...
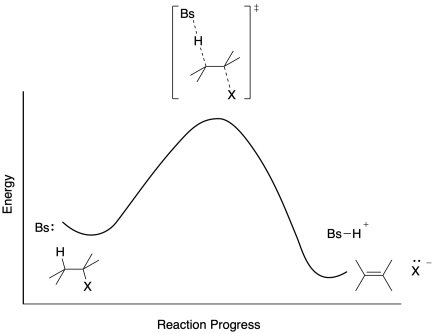
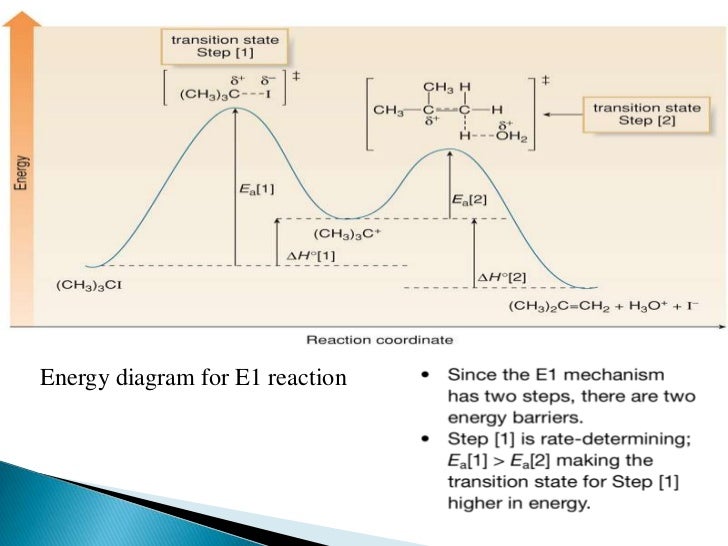
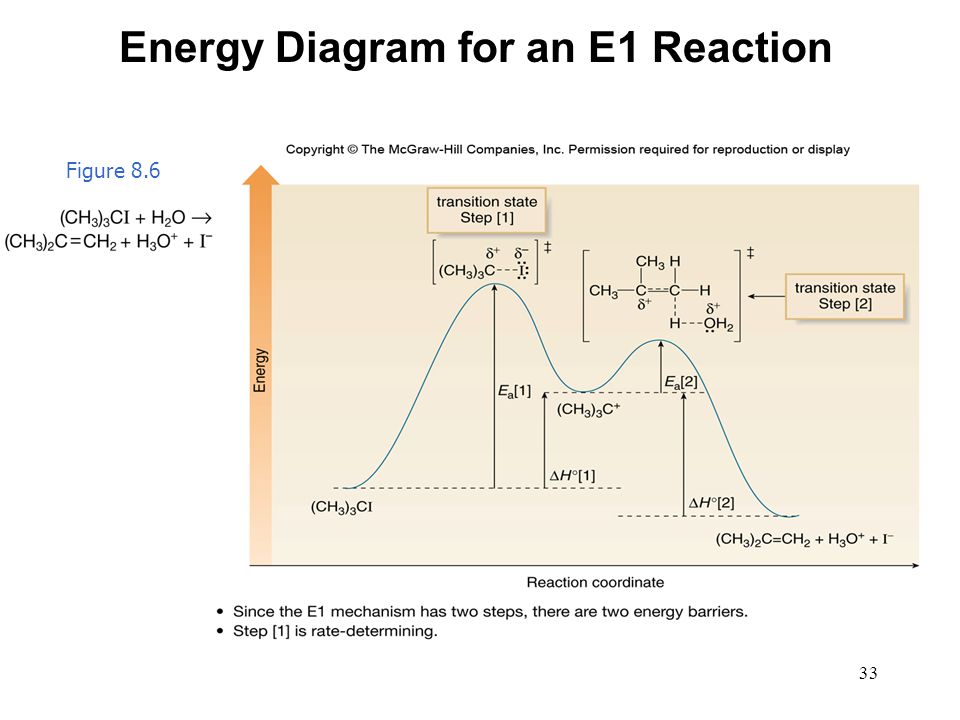
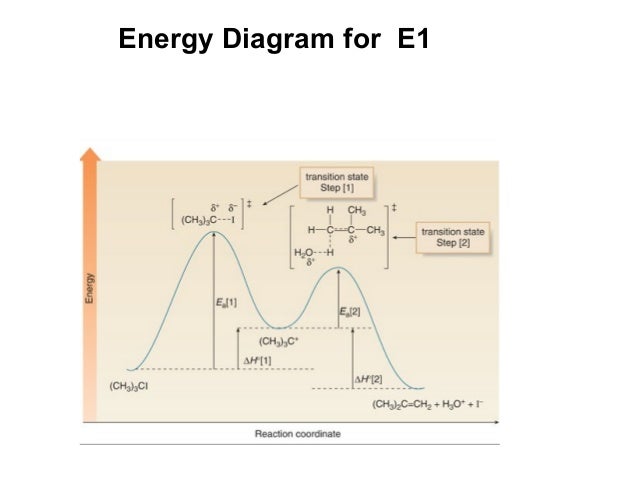
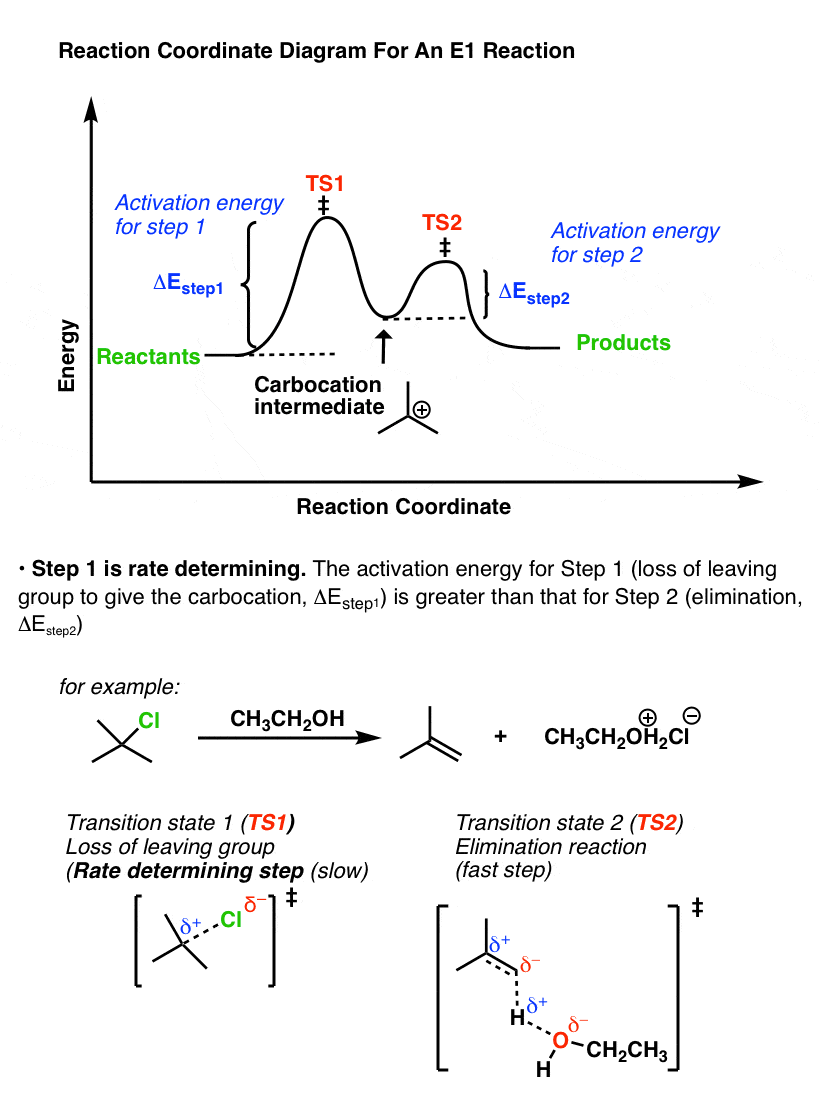
The E1 reaction proceeds via a two-step mechanism: the bond to the leaving group breaks first before the π bond is formed. The slow step is unimolecular, involving only the alkyl halide. 7. The dehydrohalogenation of (CH3)3CI with H2O to form (CH3)2C=CH2 can be used to illustrate the E1 mechanism. 8. Energy diagram for E1 reaction 9. 1.
The reactions energy diagrams shown above are for single step reactions. In a single reaction step there is only one barrier (hump) in the diagram. Likewise in a two step reaction there are two humps or activation barriers. In multi-step reactions the species in between both steps is an called an intermediate.
Energy Diagram for E1 Reactions. 1,070 views1K views. Feb 7, 2018. 1. Dislike. Share. Save. Description. LearningChemistryOnline.
A) E1, SN1 B) E1, SN2 C) E2, SN1 D) E2, SN2. Predict the organic product (s) for the following reaction. Be sure to indicate stereochemistry when appropriate. If stereoisomers are produced draw one and label the relationship between the stereoisomers. (enantiomers, diastereomers, etc.). Draw the major organic product for the following reaction.
0 energy points. Science ... The bromide has already left so hopefully you see why this is called an E1 reaction. It's elimination. E for elimination and the rate-determining step only involves one of the reactants right here. It didn't involve in this case the weak base. Now that the bromide has left, let's think about whether this weak base ...
Free energy diagrams are first introduced in the acid/base chapter alongside a thorough discussion of charge stability. Students are shown how stability affects acid or base strength and are encouraged to use these diagrams to predict equilibrium outcomes of acid/base reactions. This is a useful aid in teaching a student to understand why one ...
Potential Energy Diagram for E1 TS energy depends on carbocation rate-determining titi tt stability and leaving group quality. (Same as SN1.) H CH3 CH3 E transition state TS energy does not depend on the strength of the base. X H H a rate determining E - step reaction coordinate E1 and SN1 Frequently Occur Together (because they pass through a ...
https://Leah4sci.com/elimination presents: E1 Reaction Coordinate Energy Diagram with step by step mechanism, transition states and intermediates📺Watch Next...
Energy Diagram For Sn2. It starts with the kinetics of SN2 reaction and covers the energy diagrams including questions on activation energy, enthalpy, the order of reaction and curved. SN2 Reaction follows second order rate kinetics. It forms a product via one transition state. Transition state is the state at which it posses.
energy! Reaction Coordinate! S N 1! Potential energy! Reaction Coordinate! E1! S N 1 and E1 Reactions Have Identical Energy Diagrams for Rate Determining Step! Cl H CH3 3C H3C Cl H CH3 3C H3C CH3 H3C CH3 CH3 H3C CH3 OCH3 H CH3 3C H3C H2C CH3 CH3 B CH3OH Rate = k [substrate]! Rate = k [substrate]!
Factors Affectin g the Rate of an E1 Reaction The rate of an E1 reaction increases as the number of R groups on the carbon with the leaving group increases. Increasing rate of E1 reaction RCH 2 XR 2CH XR 3C X 1° 2° 3° + + + I i bili f b i RCH 2 R 2CH R 3C 1° 2° 3° ncreas ng sta ty o car ocat ons The strength of the base usually determines ...
For E1 elimination reaction intermediate with two t… View the full answer Transcribed image text : Based upon the energy diagram shown, is this reaction an E1 or an E2 elimination? free energy, kJ/mol reaction coordinate O E1 elimination O E2 elimination O It is impossible to determine from the diagram alone.
how many groups are lost in the E1 reaction and what are they. yes. does a mixture of products form for E1. the same as SN1, two hills, overall exothermic but first step has highest activation energy and is endothermic ... what does the energy diagram for E1 look like. E1. what reaction does Zaitsev's rule only apply to. more substituted. which ...
Elimination Reactions: E2 versus E1. Substrate: Alkene Stability Generic Reaction-Energy Diagrams. The central carbon is sp 2 -hybridized, whereat the p orbital is used for the partial Fig Transition state and energy diagram of an S N 2 reaction: Chloroform. Transition state: highest point of an energy structure on a reaction profile graph for ...
























0 Response to "42 e1 reaction energy diagram"
Post a Comment