42 energy reaction coordinate diagram
For a chemical reaction or process an energy profile (or reaction coordinate diagram) is a theoretical representation of a single energetic pathway, along the reaction coordinate, as the reactants are transformed into products. Feb 26, · A solvolysis reaction.
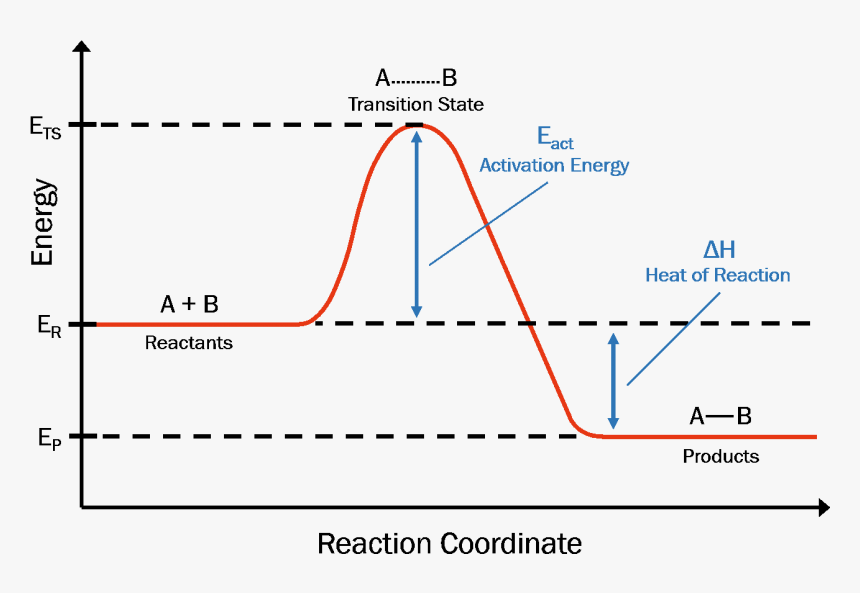
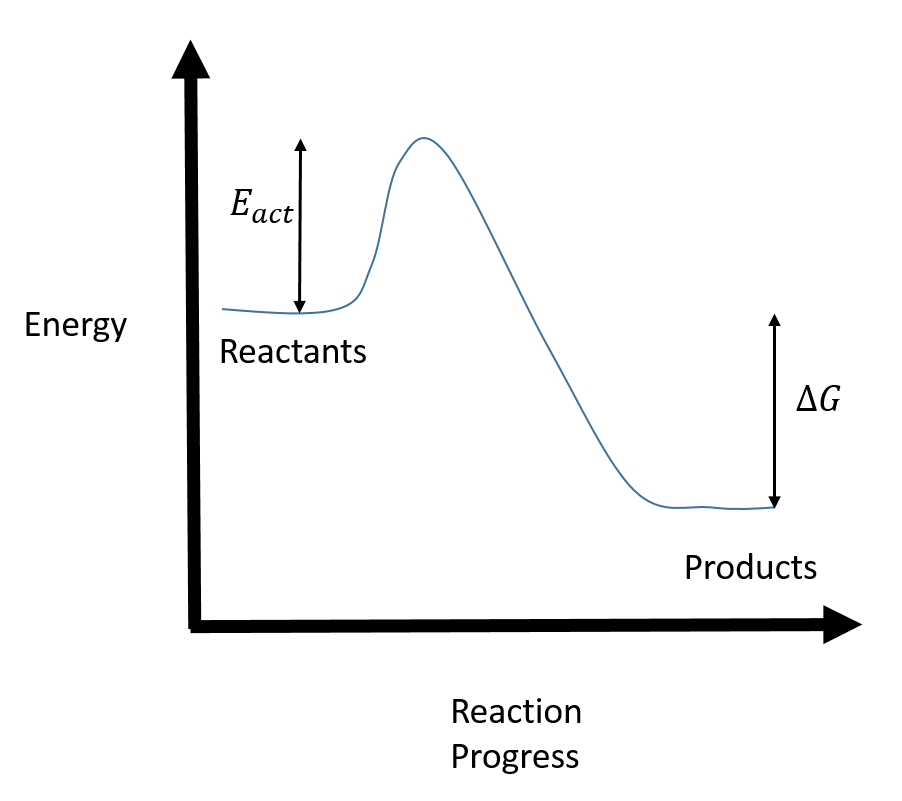
A general Reaction Coordinate Diagram relating the energy of a system to its geometry along one possible reaction pathway is given in the figure below. In the figure below, the Activation Energy, Ea is that critical minimum energy in a chemical reaction required by reactants to be converted into products. the quantities, Ea;
In an energy diagram, the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants, while the horizontal axis is the 'reaction coordinate', tracing from left to right the progress of the reaction from starting compounds to final products. The energy diagram for a typical one-step reaction might look like this:

Energy reaction coordinate diagram
Draw an energy vs reaction coordinate diagram to illustrate a reaction in which the free energy of the products is greater than the free energy of the reactants. Label all quantities as in Model 1. Products a(fwd) Reactants Reaction Coordinate Using your diagram from Exercise 3, identify which reaction (forward or reverse) has the larcer
A reaction energy diagram (Figure 1) is presented on the chalk board (complete with axes labeled: potential energy vs. reaction coordinate (or reaction progress)). The activation energy, Ea, (the change in energy from reactants to the top of the "hill") is labeled. The students are taught that the species at the top of
https://Leah4sci.com/elimination presents: E1 Reaction Coordinate Energy Diagram with step by step mechanism, transition states and intermediates📺Watch Next...
Energy reaction coordinate diagram.
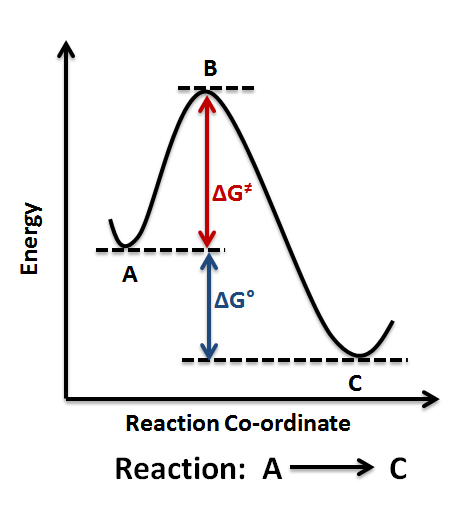
1! Energy/Reaction Coordinate! Diagrams! Thermodynamics, Kinetics ! Dr. Ron Rusay" A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change (ΔGo) Enthalphy (ΔHo): the heat given off or absorbed during a reaction
Reaction Coordinate Diagrams It is helpful to visualize energy changes throughout a process on a reaction coordinate diagram like this one for the rearrangement of methyl isonitrile. Reaction Coordinate Diagrams The diagram shows the energy of the reactants and products (and, therefore, E). The high point on the diagram is the transition state.
Energy Surfaces vs. Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Something that cannot be represented in the three dimensional energy surface below is the differentially populated vibrational modes of the molecules Reaction coordinate diagrams are used to simplify the situation, they represent a composite
In this video, Dr. Norris goes over practice problems in interpreting reaction energy coordinate diagrams.
Despite its apparent simplicity, this energy diagram conveys some very important ideas about the thermodynamics and kinetics of the reaction. Recall that when ...
For a chemical reaction or process an energy profile (or reaction coordinate diagram) is a theoretical representation of a single energetic pathway, along the reaction coordinate, as the reactants are transformed into products.
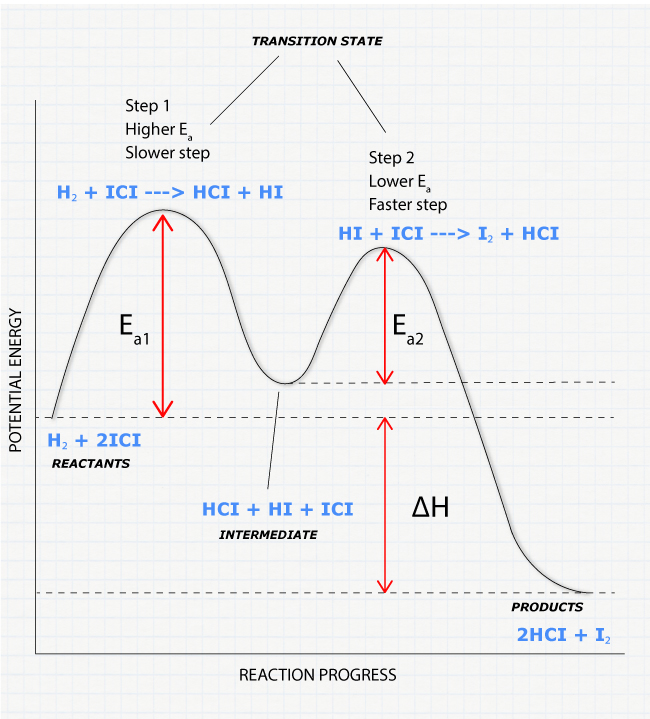
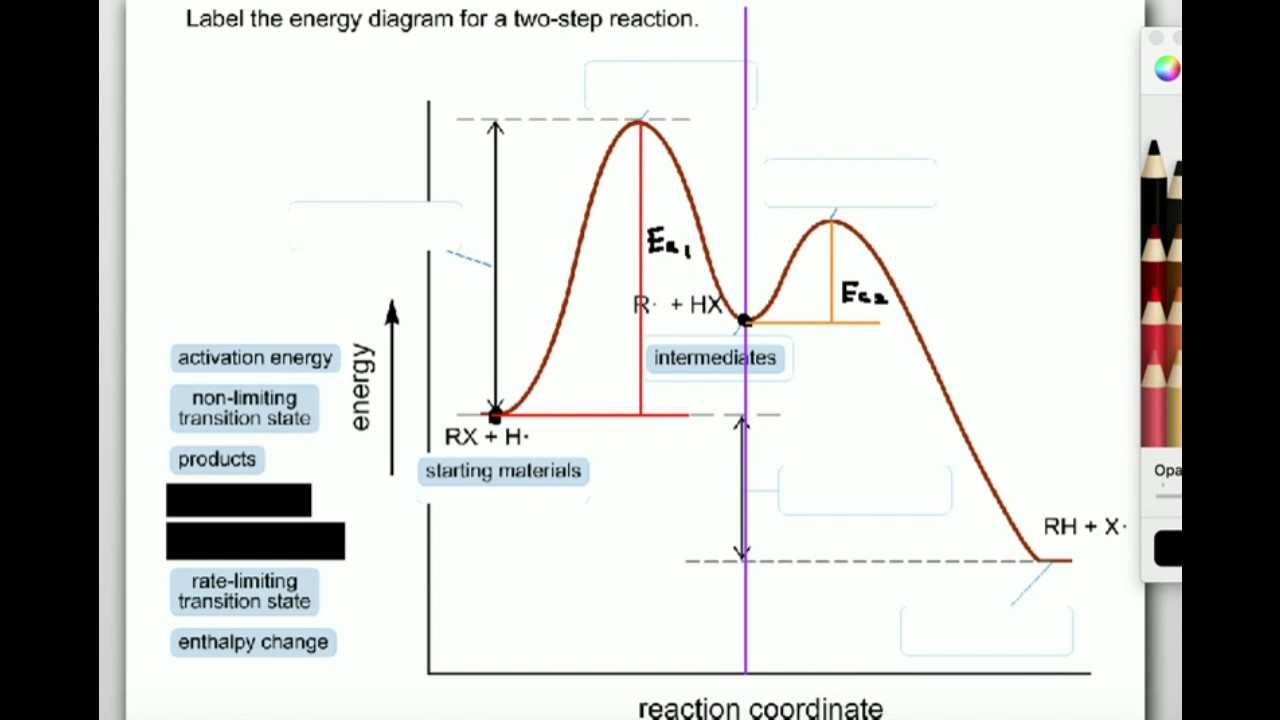
Potential Energy Diagram for E1 TS energy depends on carbocation rate-determining titi tt stability and leaving group quality. (Same as SN1.) H CH3 CH3 E transition state TS energy does not depend on the strength of the base. X H H a rate determining E - step reaction coordinate E1 and SN1 Frequently Occur Together (because they pass through a ...
In chemical reactions one often considers so called "reaction coordinate" diagrams like this: Is it possible to interpret the abstract "reaction coordinate" just as a simple time axis? ... Additionally, being explicit that the energy diagram is a two dimensional depiction of the energy of the molecules as a function of the structure (Anslyn and ...
Sn1 Reaction Coordinate Diagram. SN1 reaction is a two step reaction as mentioned below: 1. Leaving group leaves first being solvolysed by solvent creating a carbocation intermediate. This is. whose proposed mechanism and free energy diagram are depicted Figures 1 and 2. Figure 2: Reaction coordinate diagram for an SN1 reaction1. 1. Identify the .
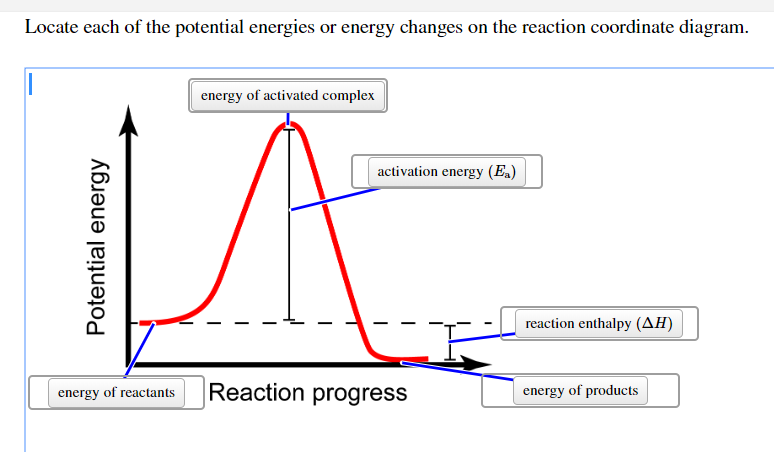
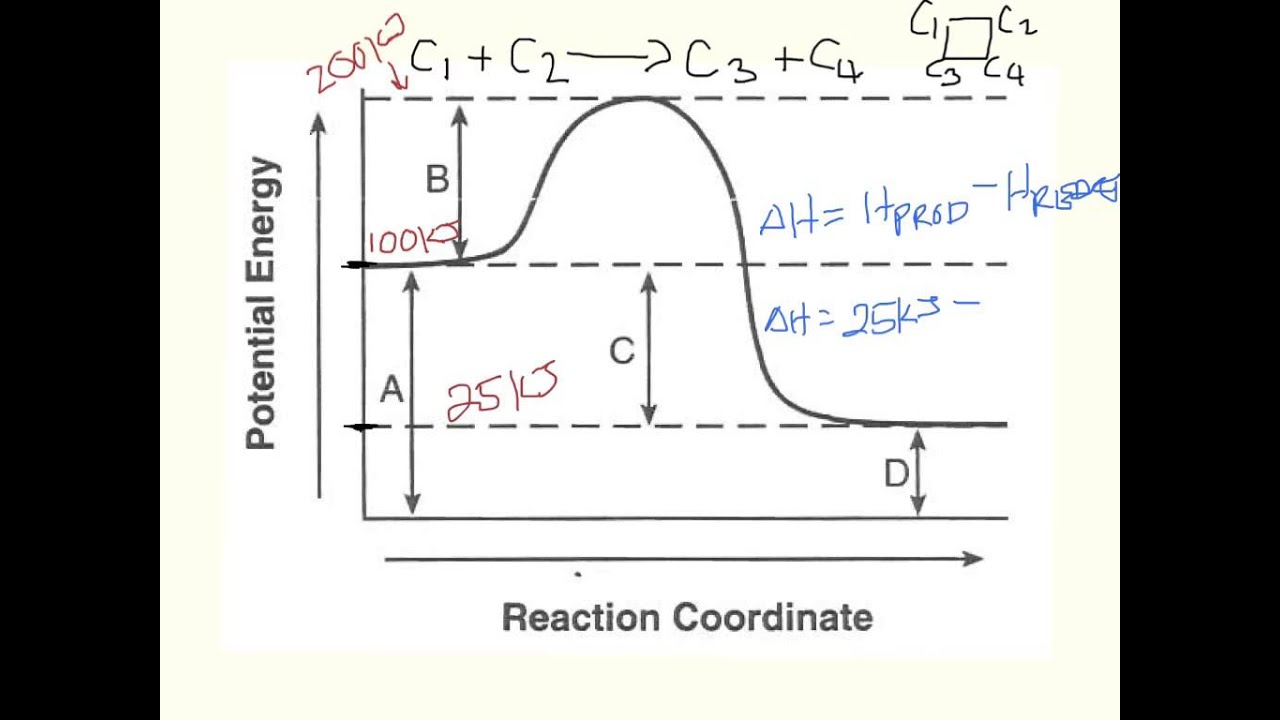
The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a chemical reaction. In this example, B is at a lower total energy than A. This is an exothermic reaction(heat is given off) and should be favorable from an energy standpoint. The energy difference between A and B is E in the diagram.
SN2 reaction coordinate diagram. In this diagram, there are really only three parts: the reagents, the transition state, and the products. The transition state is the point in the reaction with the highest energy level, and the difference in energy between the reagents and transition state is called the activation energy (often abbreviated as Ea).
Typically, we envision reactions proceeding left to right along the reaction coordinate, so often, the activation energy is only noted for the forward reaction. The activation energy on the diagram below shows the barrier to be 102.6 kJ mol -1. Barriers are measured in energy per mole (typically kJ mol -1 ). Arrhenius Law and Temperature Dependence
Graphs that show the change in energy as a function of the progress of the reaction are known as reaction coordinate diagrams or reaction profiles.
1i. Draw an energy vs reaction coordinate diagram to illustrate a reaction in which the energy of the products is greater than the energy of the reactants. Label all quantities as per Fig. 1. See diagram (3) in sample exercise 14.10 on pg 595 of Brown and LeMay, 11th ed.
For this quiz, you must be able to: Understand endothermic and exothermic reactions. Identify which points on sample reaction coordinate diagrams represent the activation energy and the change in ...
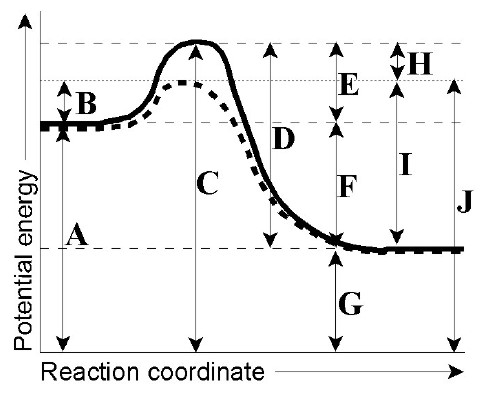
Chemistry questions and answers. Label the following reaction coordinate diagram. Energy Reactant (s) Transition State Product (s) Activation Energy (forward) Transition State Activation Energy (forward) Energy Enthalpy of Enthalpy of Reaction Product (s) Reaction AHrxn Reactant (s) Reaction Coordinate Reaction Coordinate Reset Zoom.
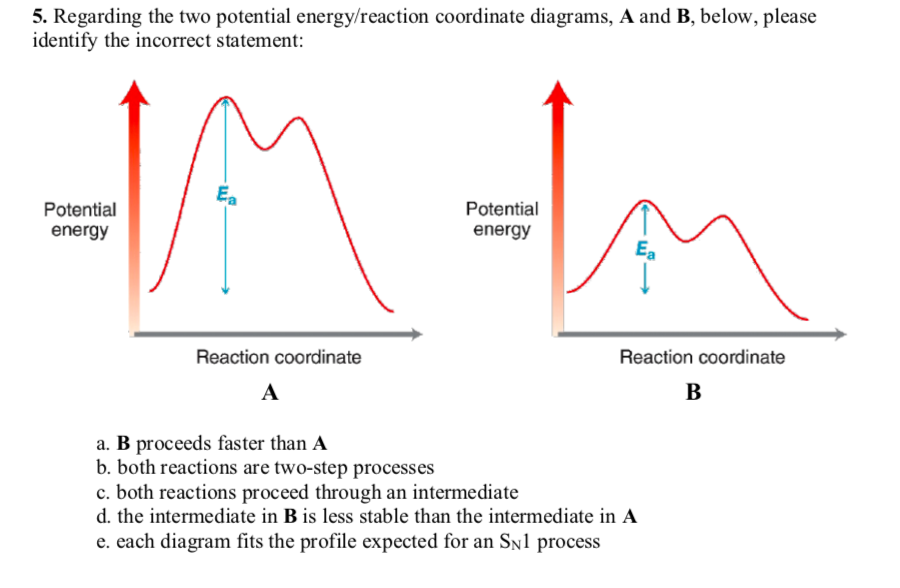
21) Which of the following statements about the Free Energy-Reaction Coordinate diagram is incorrect? A AG+ B AG+ Free Energy Reaction coordinate a) The diagram could represent different Sn1 reactions. Plot A represents the tertiary alkyl halide and plot B an allylic alkyl halide. b) The diagram could represent the addition of HCl to propene.
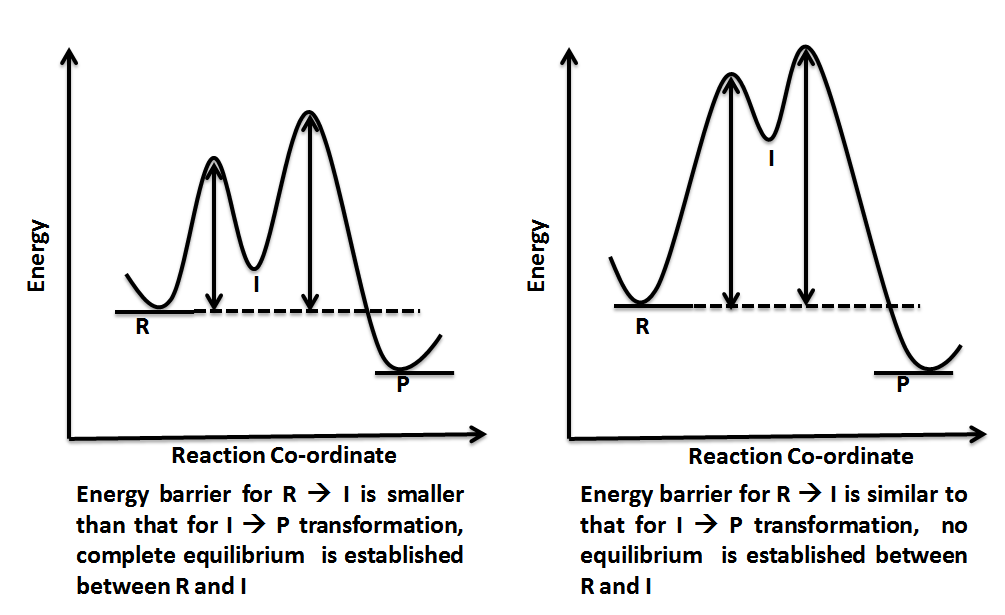
by JM Scholey · 2013 · Cited by 6 — Reaction coordinate diagrams are used to relate the free energy changes that occur during the progress of chemical processes to the rate and equilibrium ...
The fully filled in reaction coordinate diagram is displayed below. The arrow marked in the question represents the activation energy, which is the energy barrier that must be overcome in order for the reactants to form products. This reaction is also exothermic because the energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants. Report an Error
Reactants Products + Energy. Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction as above but add the activation energy, E a, for the catalyzed reaction on the appropriate curve in this diagram and label it. This is a bit more subtle since .Types of catalysts (article) | Kinetics | Khan AcademySection The Rate of a Reaction ...
reaction coordinate diagram shows that the energy of activation for the reverse reaction is lowered by the catalyst as well. Enzymatic catalysis The ability of enzymes to catalyze reactions depends on their ability to interact directly and specifically with
All reactions require energy, from the simplest - such as boiling water to turn liquid water into gaseous water - to the complex, such as electrochemical reactions. We can see what is happening to...
An energy diagram for an endergonic or nonspontaneous reaction is shown to the right. The energy level of the products is higher than the energy level of the. Reaction coordinate diagrams of exergonic and endergonic reactions. Exergonic and endergonic reactions are characterized by changes in. Exergonic and endergonic qualifications only apply ...
FIGURE 1: Reaction coordinate diagram for chemical reactions. (A) Equation for an S N2 (substitution nucleophilic second order) reaction between a nucleophilic hydroxide ion and methyl chloride. (B) The reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction plots the changes in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) during the conversion of reactants
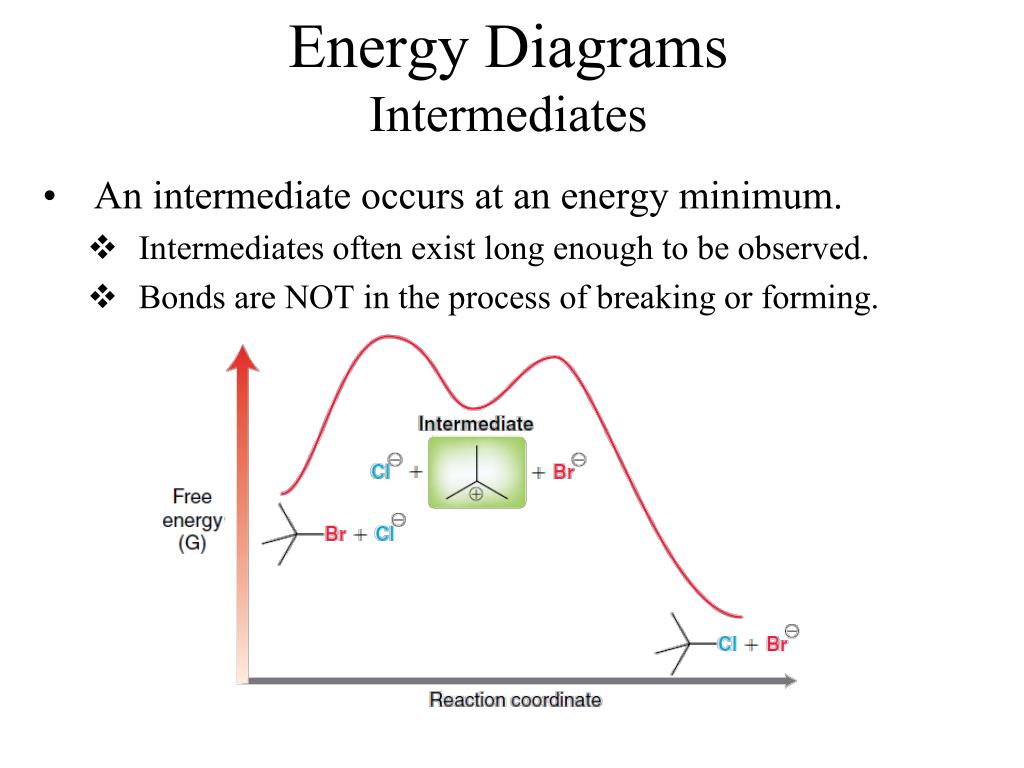
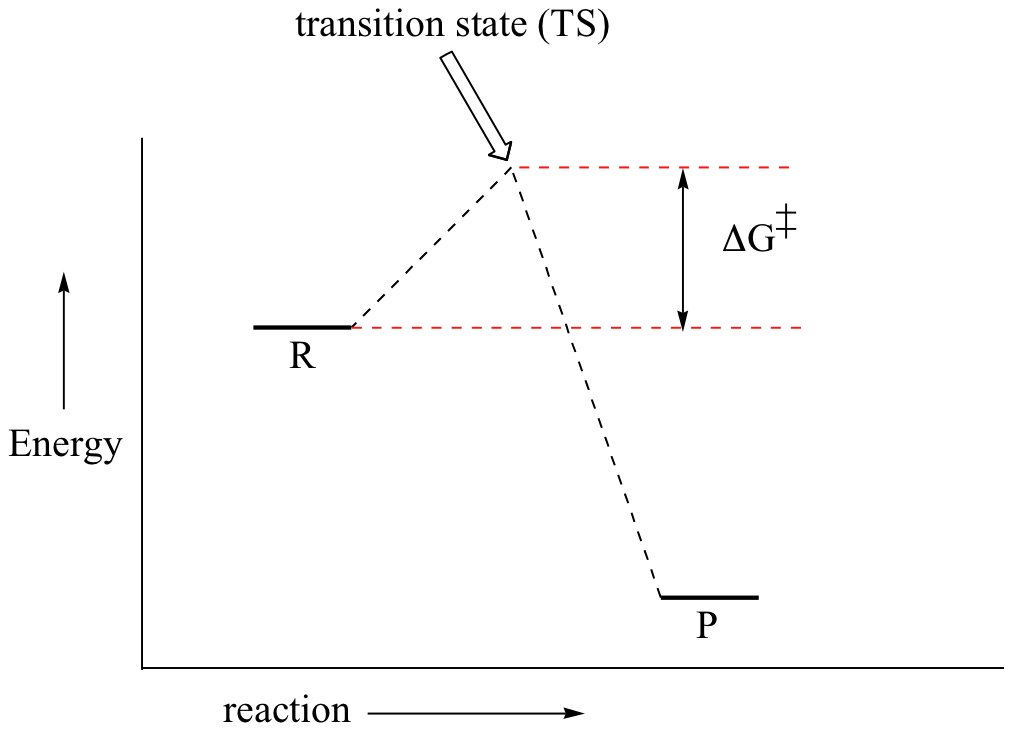
positions of atoms during a reaction. Reaction coordinate Energy Energy Diagrams 6 • Transition state ‡: - An unstable species of maximum energy formed during the course of a reaction. - A maximum on an energy diagram. • Activation Energy, ∆G‡: The difference in Gibbs free energy between reactants and a transition state.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Diagram of a catalytic reaction, showing the energy niveau depending on the reaction coordinate. For a catalysed reaction, the activation energy is lower. In chemistry, a reaction coordinate is an abstract one-dimensional coordinate which represents progress along a reaction pathway.

Which reaction coordinate diagram represents a reaction in which the activation energy, ea, is 50 kj•mol –1 and the δhrxn is –15 kj•mol –1?





















0 Response to "42 energy reaction coordinate diagram"
Post a Comment