42 molecular orbital diagram of benzene
Molecular orbitals of benzene. Benzene (C 6 H 6) consists of 6 carbon atoms in a ring. A hydrogen atom is attached to each carbon atom. The carbon-carbon bond length is 1.40 Å and the carbon-hydrogen bond length is 1.10 Å. 31 models in this collection. The characteristics such as lewis structure, molecular geometry, hybridization, and molecular orbital diagram of benzene molecule make it a special molecule. Its structure displays such properties of benzene which are different than other ring structures.
Donate here: http://www.aklectures.com/donate.phpWebsite video link: http://www.aklectures.com/lecture/molecular-orbitals-of-benzeneFacebook link: https://ww...

Molecular orbital diagram of benzene
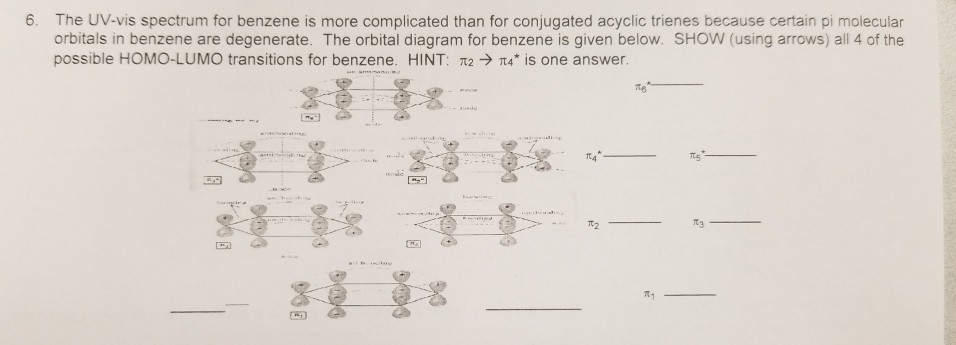
Molecular Orbital Diagram This is a molecular orbital energy level diagram for the p orbitals. Note that the σ bonding orbital is lowest in energy due to the greater overlap end-onend. σu πg 2p πu σg 2p ... A simplified example will be shown for the π bonding of benzene. The number of pi molecular orbitals in the pi-system equals the number of contributing atomic p orbitals. For butadiene (n=4) we saw that the energy levels of the pi system stacked like a four-story apartment building. Both hexatriene and benzene have six contributing p-orbitals (n = 6), so we should expect six pi orbitals for each. Note that, like in benzene, when there are multiple ways to represent a combination, one molecular orbital is usually represented to show both bonding and antibonding interactions. The other usually shows the net result, either just bonding or antibonding or, in the case of cyclobutadiene, no direct interaction between adjacent atoms because it ...
Molecular orbital diagram of benzene. In large part, the answer to this question lies in the fact that benzene is a cyclic molecule in which all of the ring atoms are sp2-hybridized. This allows the ... The orbital structure of benzene: All the carbon atoms in benzene are sp2 hybridised. The three sp2 hybrid orbitals are lying in one plane and oriented at ... Rating: 4.4 · 740 votes · Free · Android · Educational In benzene, the carbon atoms are sp2 hybridized. That means that each carbon's set of atomic orbitals is three sp2 orbitals and one p orbital. The sp2 orbitals are utilized to make sigma bonds to the adjacent carbons and hydrogens. The unhybridized p orbital contributes to the pi system. Aromaticity - π Molecular Orbitals of Benzene. 31 models in this collection. Use getProperty "modelInfo" or getProperty "auxiliaryInfo" to inspect them. Use "set autoLoadOrientation TRUE" before loading or "restore orientation DEFAULT" after loading to view this orientation. The calculated energy of the molecular orbital is shown in the left ...
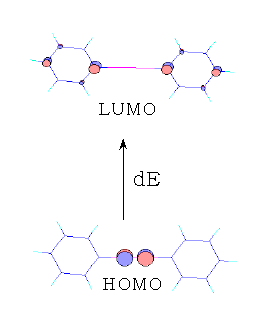
Hey everyone. I had hard time to understand molecular orbital theory. I understand the diagrams, sigma and pi bonds, HOMO and LUMO now but I have no idea why I need it. What is the purpose of drawing those diagrams besides found out if the molecule exists? For example, how can MO theory of benzene or any other molecule help me in the organic chemistry? Thanks. The orbital structure of benzene: All the carbon atoms in benzene are sp2 hybridised. The three sp2 hybrid orbitals are lying in one plane and oriented at an angle of 120°. The fourth unhybridized p-orbital having two lobes is lying perpendicular to the plane of the hybrid orbital. Two out of the three sp2 hybrid orbitals of each carbon atom overlap axially with sp2 hybrid orbitals of the ... Today, let's go through how to draw out the molecular orbitals of benzene.In the case of cyclic systems, the (n-1) rule fails.Instead of looking at these as ... The Molecular Orbitals of Benzene. A molecular orbital description of benzene provides a more satisfying and more general treatment of "aromaticity". We know that benzene has a planar hexagonal structure in which all the carbon atoms are sp 2 hybridized, and all the carbon-carbon bonds are equal in length. As shown below, the remaining cyclic ...
Remember: A molecular orbital is the region of space which contains a bonding pair of electrons. Warning! Be very careful how you phrase this in exams. You must never talk about the p orbitals on the carbons overlapping sideways to produce a delocalised pi bond. This upsets examiners because a pi bond can only hold 2 electrons - whereas in benzene there are 6 delocalised electrons. We know that benzene has a planar hexagonal structure in which all the carbon atoms are sp 2 hybridized, and all the carbon-carbon bonds are equal in length. As shown below, the remaining cyclic array of six p-orbitals ( one on each carbon) overlap to generate six molecular orbitals, three bonding and three antibonding. occupied molecular orbitals and N/2 unoccupied ones. For the ground state, we of course occupy the lowest energy orbitals. 5) Compute the energy. Being a very approximate form of MO theory, Hückel uses the noninteracting electron energy expression: ... benzene as an example. 1 2 orbitals. These four 2py orbitals can overlap to form π bonds. Once again, using the Hückel approximation we can determine the energies and shapes of these π molecular orbitals. As we can see in Figure 8, combining these four 2py atomic orbitals, we end up with four π molecular orbitals. Energy α - 1.618 β α - 0.618 β α α + 0.618 β
16.2a Pi Molecular Orbitals 1,3 Butadiene; 16.2b Pi Molecular Orbitals the Allyl System; 16.2c Pi Molecular Orbitals 1,3,5 Hexatriene; 16.3 UV Vis Spectroscopy; 16.4 Electrophilic Addition to Conjugated Dienes; 16.5 Diels Alder Reactions; 16.6 Cycloaddition Reactions; 16.7 Electrocyclic Reactions; 16.8 Sigmatropic Rearrangements
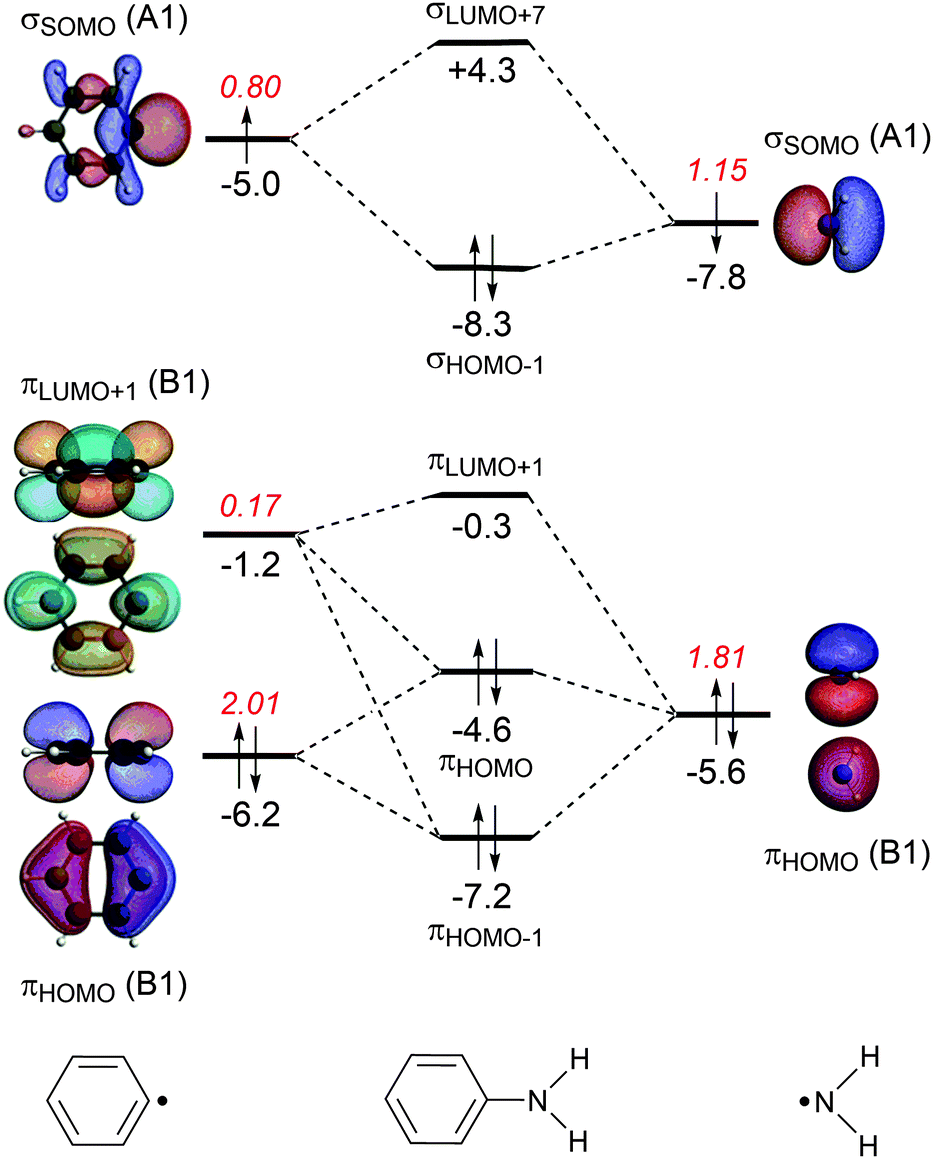
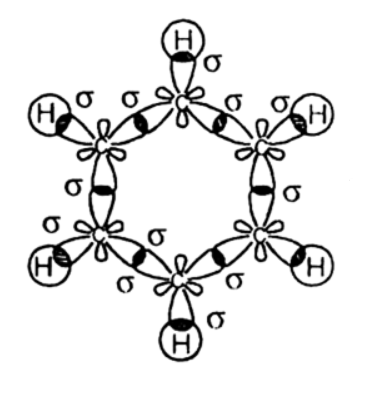
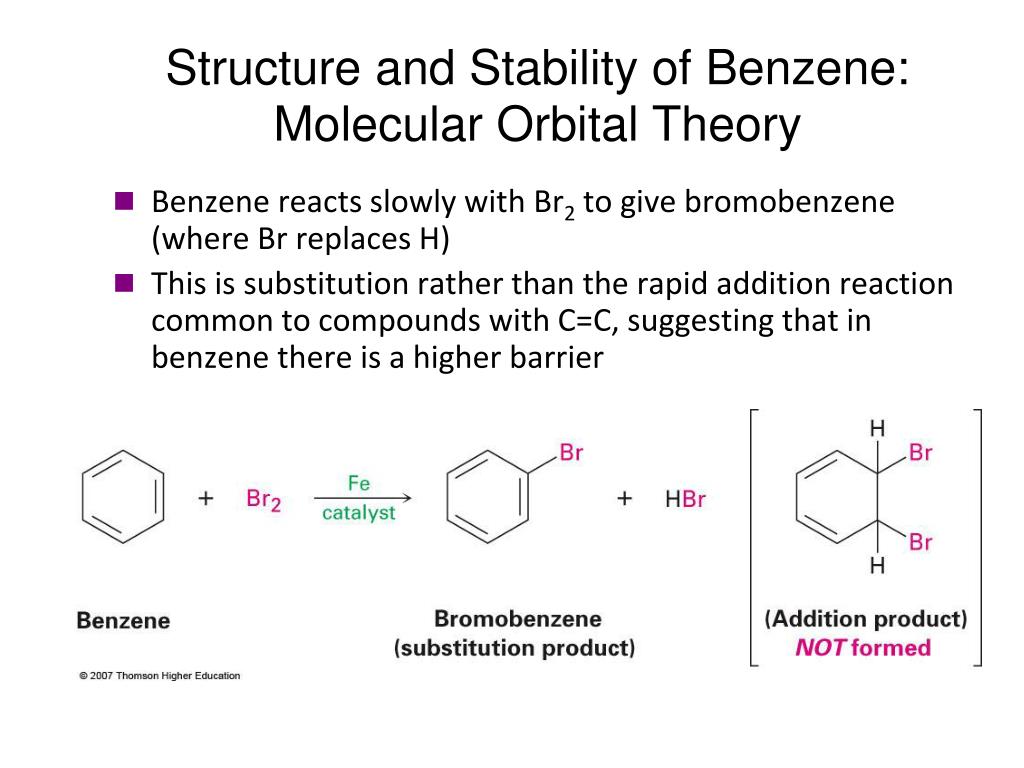
Benzene's extra stability cannot be explained by resonance alone, and so we must turn to Molecular Orbital theory for a fuller answer. Benzene has 6 planar sp2 carbons, and therefore each carbon has an unhybridized p orbital. These p orbitals are perfectly aligned for overlap (i.e. bonding, just like for a bond).
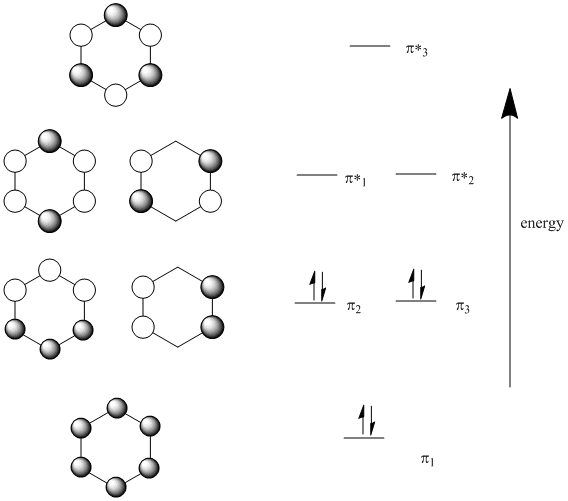
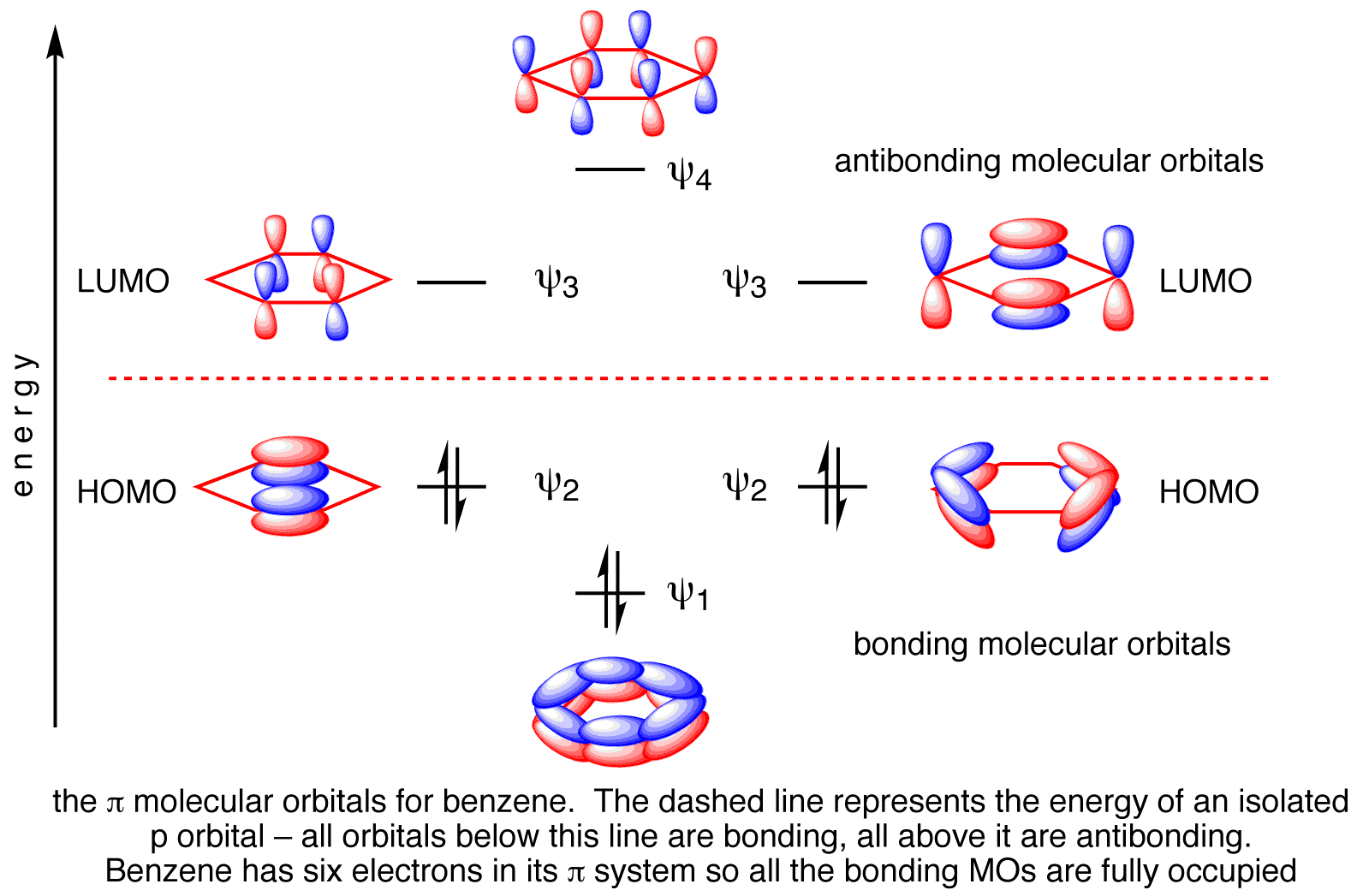
Benzene has 6 molecular π orbitals. Of these, three are bonding and three are antibonding. The six π electrons go into the three bonding orbitals. π BO = ½(B - A) = ½(6 - 0) = 3. This is the π bond order for 6 C-C bonds. For one C-C π bond, BO = 3/6 = 0.5. For a single C-C bond in benzene, the total BO = σ + π = 1 + 0.5 = 1.5.
From the cyclic polyene diagram it can be seen that benzene has six p-molecular orbitals, (which contain the six p-electrons), three bonding and three anti-bonding. The upper bonding degenerate pair of orbitals are the HOMO's of benzene.
There are 15 bonding orbitals in benzene.. The valence bond (Lewis) structure of benzene is. There are 6 C-C σ bonds, 6 C-H σ bonds, and 3 C=C π bonds. This makes 16 bonding orbitals. According to molecular orbital theory, the σ molecular orbitals form from the three sp² orbitals on each carbon atom and the 1s orbitals on each hydrogen atom.. These 24 atomic orbitals mix to form 24 ...
According to MO theory, the pi electrons of benzene occupy three molecular orbitals, y1, y2, and y3, all of which are lower in energy than an electron in an ...
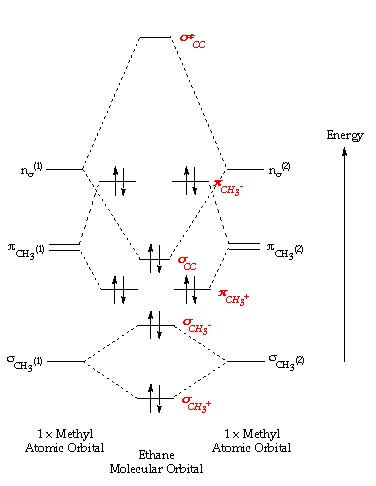
ethane thermophysical properties the phase diagram of ethane is shown below the table chemical physical and thermal properties of ethane c 2 h 6 values at 25 o c 77 o f 298 k and. benzene molecular orbitals chemtube3d university of liverpool is an internationally renowned seat of learning and research in the united kingdom uk. butat ne orbitals.
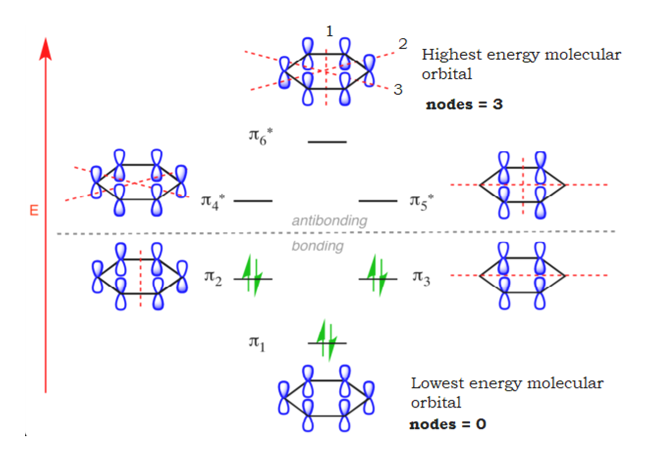
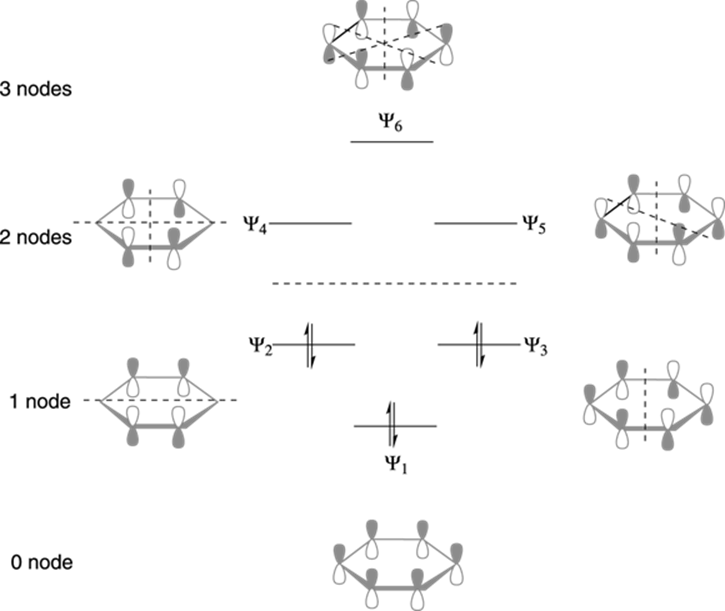
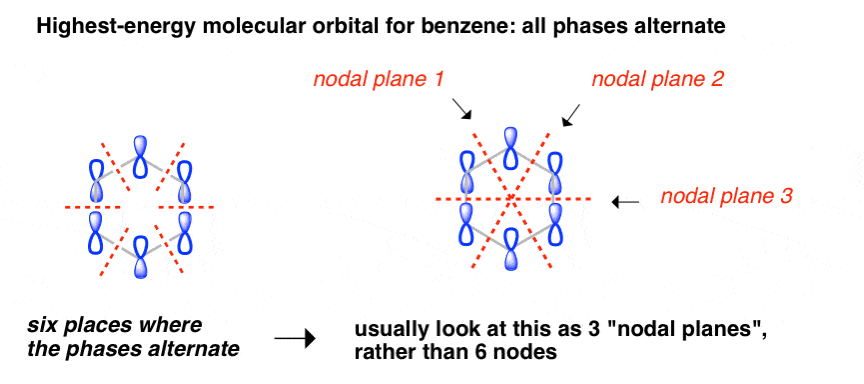
15.4: Molecular orbitals of benzenes: (figure 15.3)! 1!2! 3!4 5!6 six p-orbitals Ψ 1: zero nodes Ψ 2 and Ψ 3: one node Ψ 4 and Ψ 5: two nodes Ψ 6: three node Degenerate orbitals: orbitals that have the same energy Bonding Anti-bonding six AO's = six MO's
The Pi Molecular Orbitals of Benzene (D 6h Symmetry) Note: due to the size of the orbital files, it may take several seconds for the orbitals to appear. Note that only the total electron density is shown for each orbital (i.e., the phases for each orbital are not shown). 6 (b 2g) 4 (e 2u)
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.
p-type Molecular Orbitals - benzene 9 gy p 6 * p 1 p 2 p 3 p 4 * p 5 * Six atomic p orbitals create six molecular porbitals. p 2 and p 3 are degenerate (equal in energy) and have one node. p 4 * and p 5 * are degenerate and have two nodes. This delocalized psystem of three stabilizing molecular orbitals is the source of benzene's aromatic ...
benzene. C C C C C C ORBITALS AND MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION 17. To which we have now added the pi orbitals above the ring. Benzene carbon orbitals viewed from the side. Adding the hydrogen atoms to picture 16 we view benzene from above, complete. Benzene from the side, complete with hydrogen atoms.
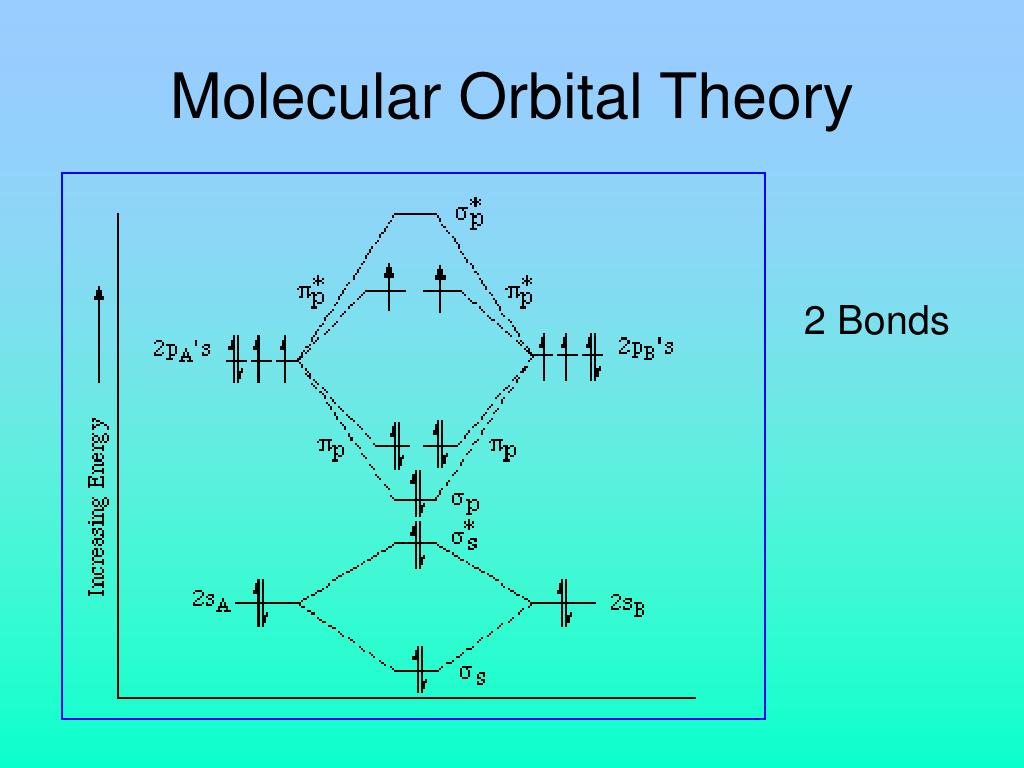
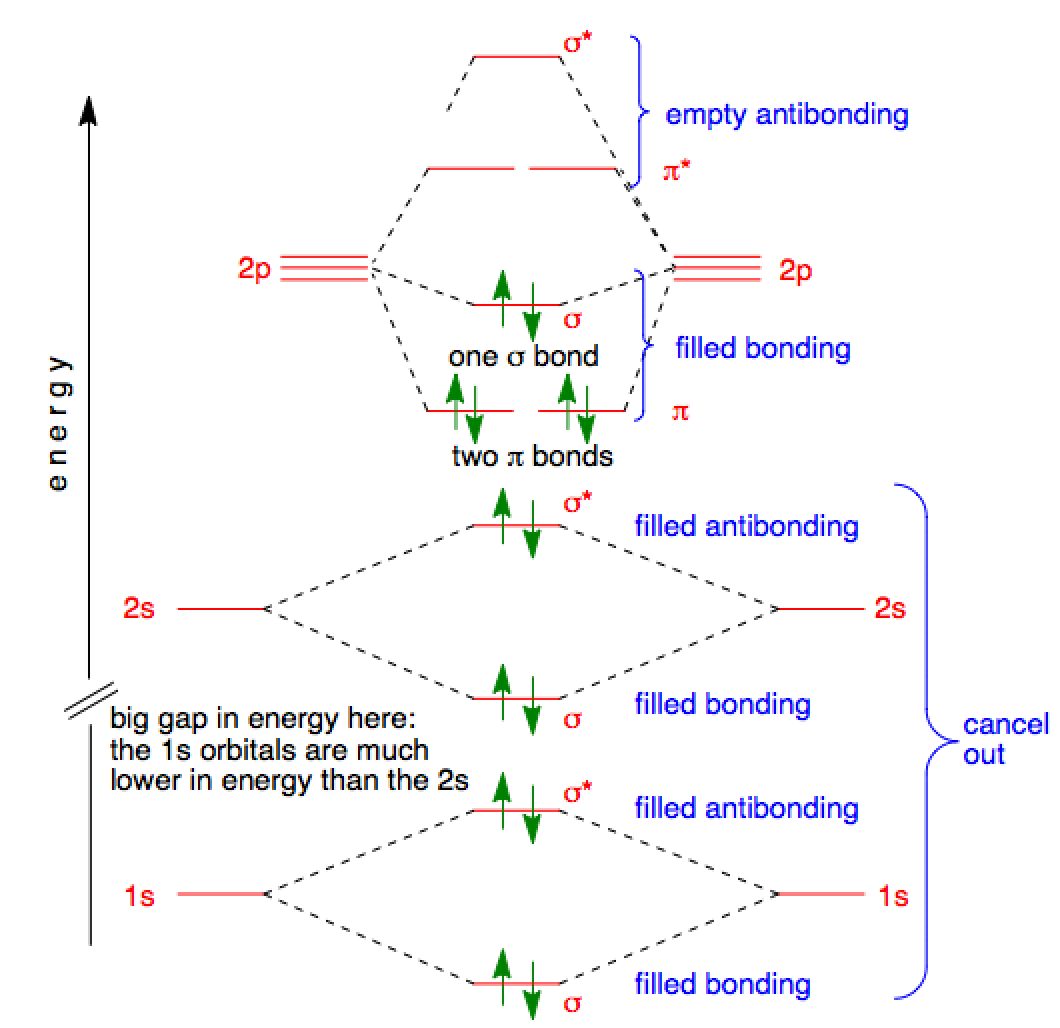
Molecular Orbital Theory • For example, when two hydrogen atoms bond, a σ1s (bonding) molecular orbital is formed as well as a σ1s* (antibonding) molecular orbital. • The following slide illustrates the relative energies of the molecular orbitals compared to the original atomic orbitals. • Because the energy of the two electrons is lower
The other molecular orbitals are almost never drawn. Benzene ( C 6 H 6) is a planar molecule containing a ring of six carbon atoms, each with a hydrogen atom attached. The six carbon atoms form a perfectly regular hexagon. All of the carbon-carbon bonds have exactly the same lengths - somewhere between single and double bonds.
The Molecular Orbitals of Benzene. To examine a model of the p-orbital components of these benzene orbitals. To examine the benzene pi-molecular orbitals . Fused Benzene Ring Compounds. Benzene rings may be joined together (fused) to give larger polycyclic aromatic compounds. A few examples are drawn below, together with the approved numbering ...
Molecular Orbital Structure for Benzene. X-ray diffraction studies shows that benzene consists of a hexagonal planar ring of six carbon atoms.2 pages
Note that, like in benzene, when there are multiple ways to represent a combination, one molecular orbital is usually represented to show both bonding and antibonding interactions. The other usually shows the net result, either just bonding or antibonding or, in the case of cyclobutadiene, no direct interaction between adjacent atoms because it ...
The number of pi molecular orbitals in the pi-system equals the number of contributing atomic p orbitals. For butadiene (n=4) we saw that the energy levels of the pi system stacked like a four-story apartment building. Both hexatriene and benzene have six contributing p-orbitals (n = 6), so we should expect six pi orbitals for each.
Molecular Orbital Diagram This is a molecular orbital energy level diagram for the p orbitals. Note that the σ bonding orbital is lowest in energy due to the greater overlap end-onend. σu πg 2p πu σg 2p ... A simplified example will be shown for the π bonding of benzene.




















0 Response to "42 molecular orbital diagram of benzene"
Post a Comment