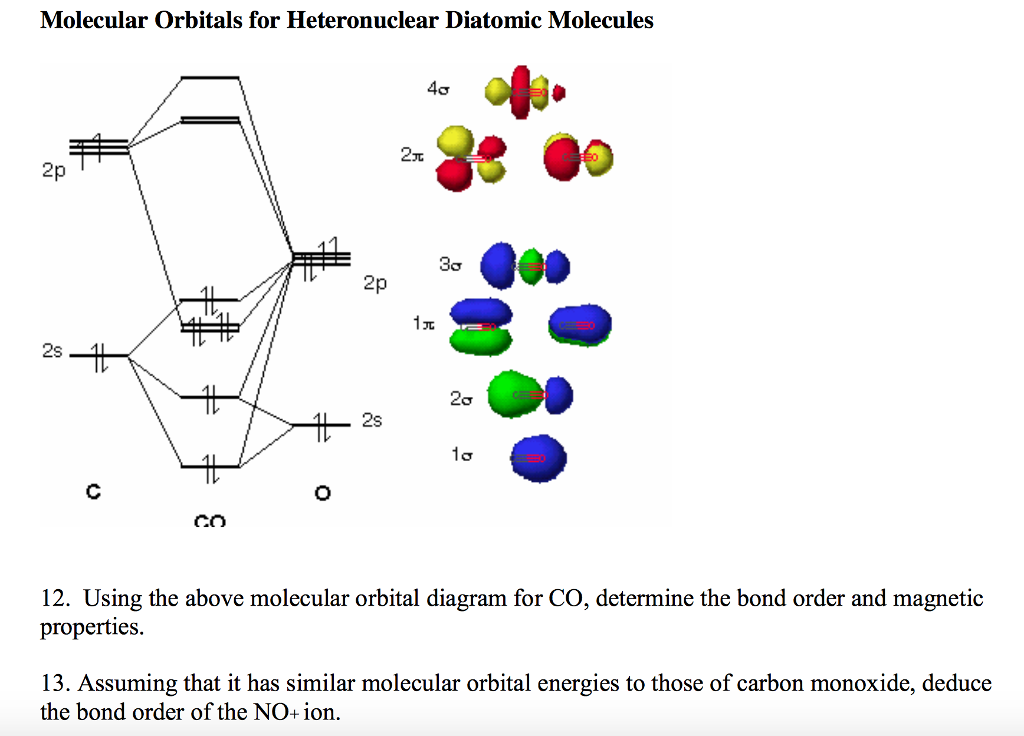
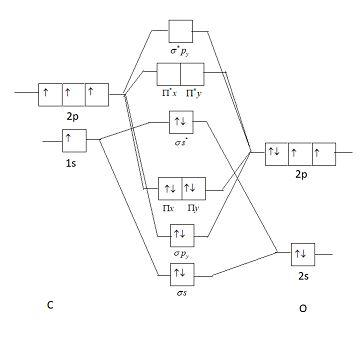
42 orbital diagram for co
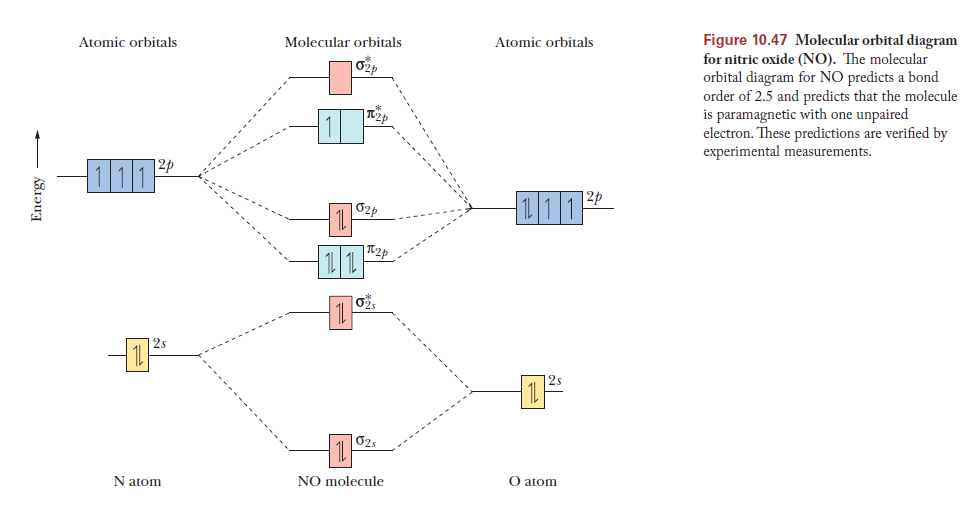
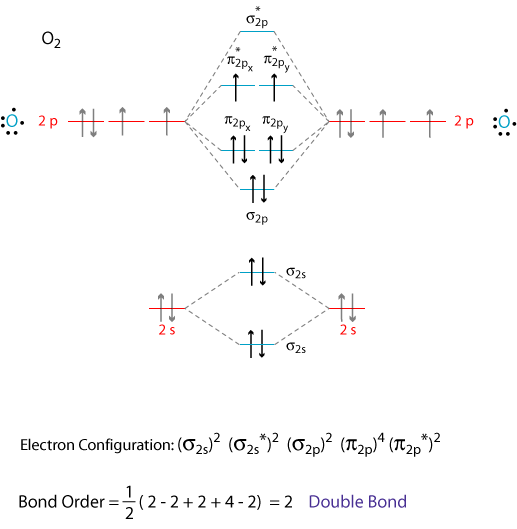
To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for \(\ce{O2}\), we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in Figure 9.10.1 . We again fill the orbitals according to Hund's rules and the Pauli principle, beginning with the orbital that is lowest in energy. Studying this comes after preparing the Lewis structure and can help with figuring out hybridization, polarity, and molecular orbital diagram of an atom. Carbonyl fluoride (COF2) is a tetra-atomic molecule where the bond angle between the participating atoms is 120° which makes the molecular geometry trigonal planar .
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air.Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom. It is the simplest molecule of the oxocarbon family. In coordination complexes the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl.It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry.
Orbital diagram for co
The orbital diagram of difluoromethane can be represented as: According to Bent's rule, if a central atom is bonded to multiple atoms then it will hybridize in such a way that hybrid orbitals with more s-character will point towards the more electropositive element and hybrid orbitals with more p-character will direct towards the more ... The orbital diagram is drawn as follows: the first 2 electrons will pair up in the 1s orbital; the next 2 electrons will pair up in the 2s orbital. That leaves 4 electrons, which must be placed in the 2p orbitals. According to Hund's Rule, all orbitals will be singly occupied before any is doubly occupied. Molecular orbital diagram of co. Find the point group of the molecule and assign cartesian coordinates so that z is the principle axis. To view a model click on a molecular orbital in the energy level correlation diagram shown the results displayed may be switched between those from a low level of calculation and those from a high level ...
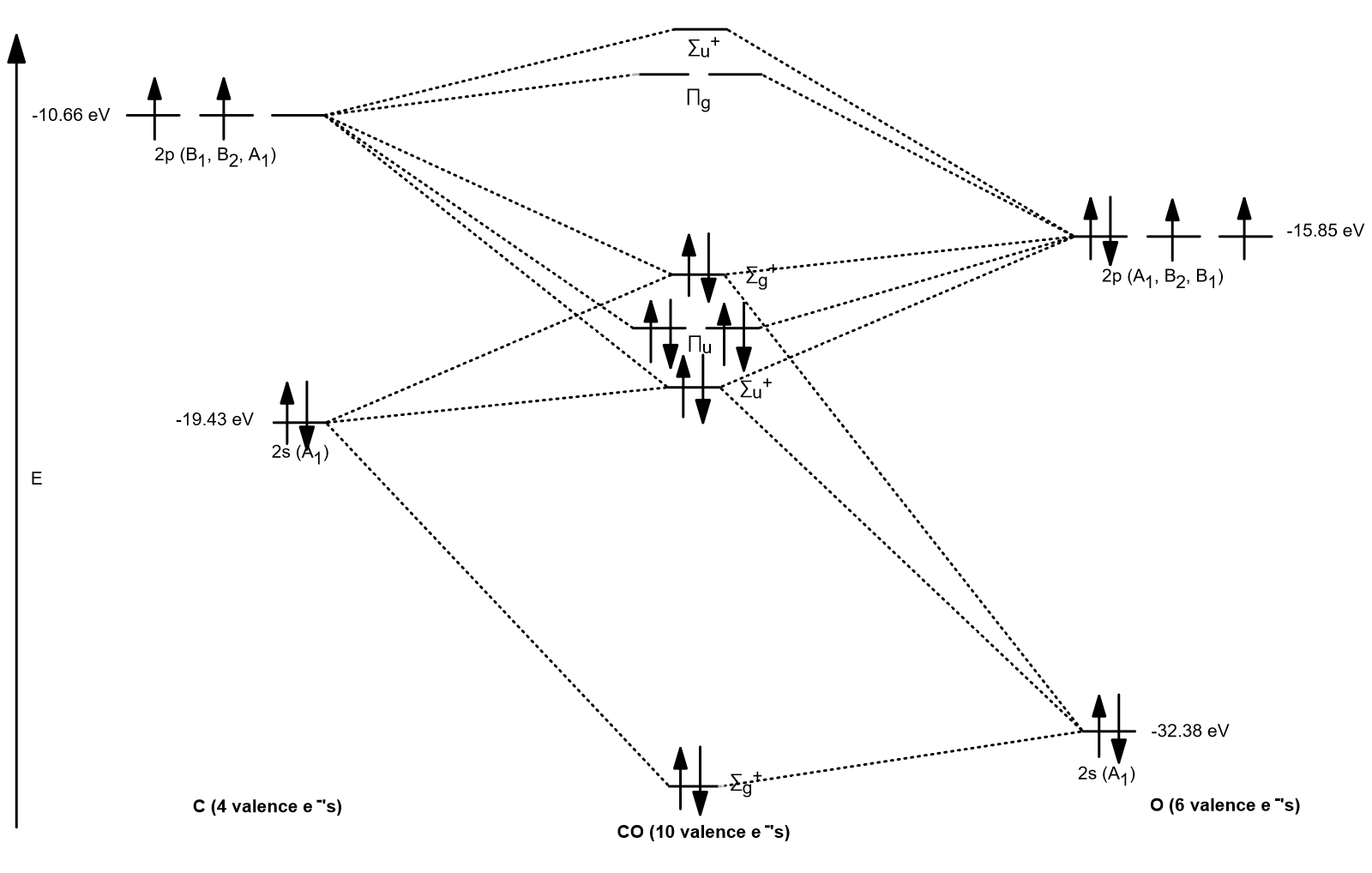
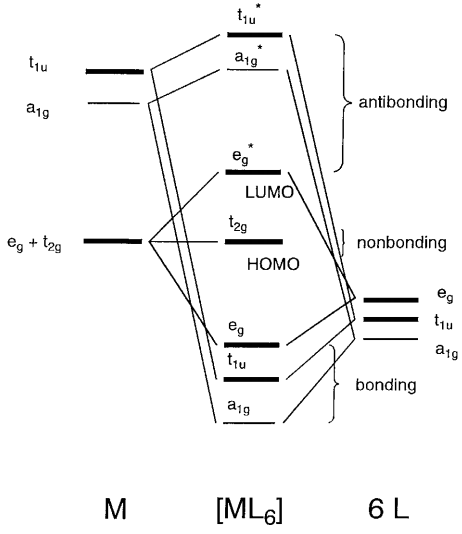
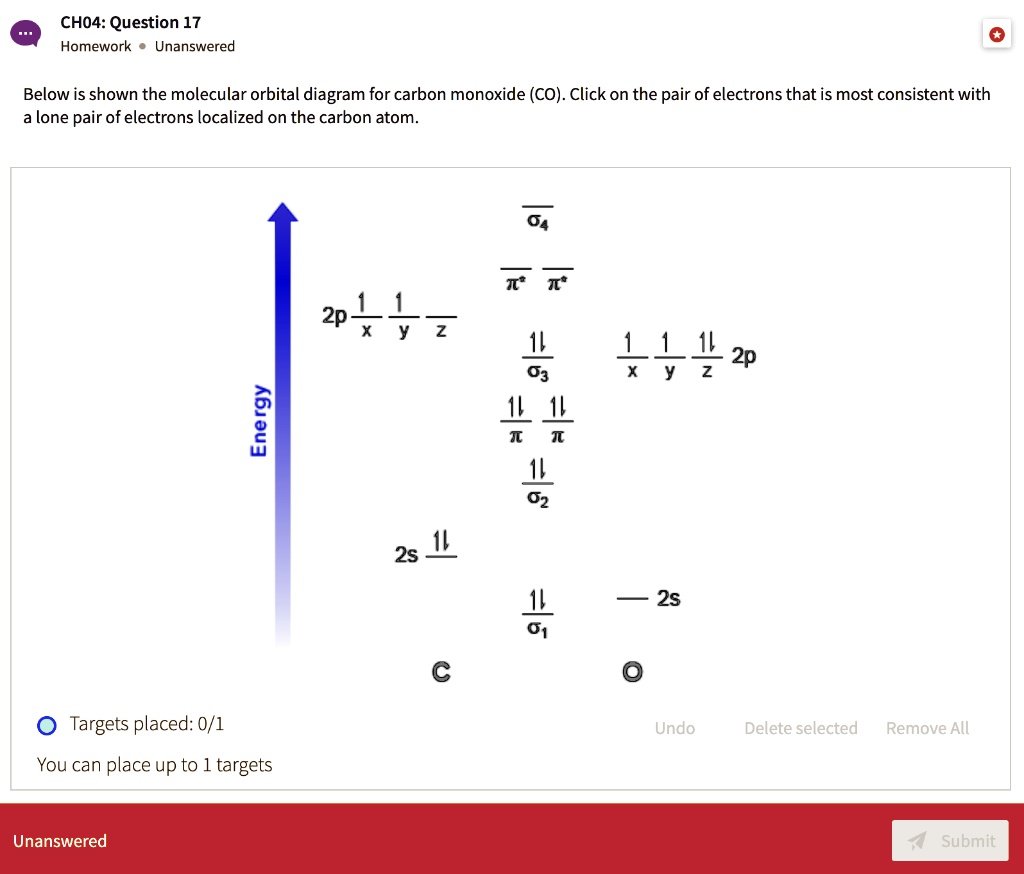
Orbital diagram for co. Molecular Orbital Theory and MO diagram of Dibromine (Br2) The MO diagram or Molecular Orbital diagram is an extension of the 3-dimensional molecular design and gives a better understanding of the structure of an atom. Molecular Diagram also reflects upon bond length, bond shape, bond energy, and the bond angle between 2 atoms. Molecular orbitals diagrams of [Co (NH3)6]3+. 1. M. O. diagram for [Co (NH3)6]3+ Dr. Mithil Fal Desai Shree Mallikarjun and Shri Chetan Manju Desai College Canacona Goa. 2. t* 1u a1g t2g, eg a1g, t1u, eg a1g t1u a* 1g e* g eg t1u Δo t2g Metal (Ti3+)orbitals Co3+→ [Ar] 3d6, 4s0 6e- Ligand group (NH3) orbitals 6 x 2 = 12 e- σ [Co (NH3)6]3 ... Describe the orbital diagram of an atom with 16 electrons. Explain how this orbital diagram demonstrates Hund's rule. (8 points) - 25463668 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Carbon Monoxide (CO) The above image shows energy levels for the molecular orbitals of the carbon monoxide (CO) The molecular orbital diagram is a diagrammatic representation of showing how chemical bonding is taking place within a molecule.
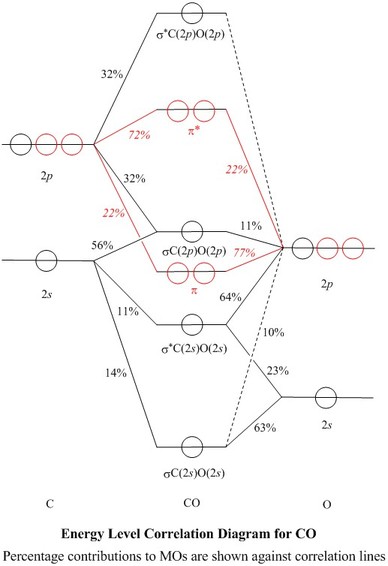
Molecular orbitals diagrams of [Co (NH3)6]3+. 1. M. O. diagram for [Co (NH3)6]3+ Dr. Mithil Fal Desai Shree Mallikarjun and Shri Chetan Manju Desai College Canacona Goa. 2. t* 1u a1g t2g, eg a1g, t1u, eg a1g t1u a* 1g e* g eg t1u Δo t2g Metal (Ti3+)orbitals Co3+→ [Ar] 3d6, 4s0 6e- Ligand group (NH3) orbitals 6 x 2 = 12 e- σ [Co (NH3)6]3 ... Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B_2^2+, B2, C_2^2-, B_2^2- and N_2^2+ b. ... Use the drawing of MO energy diagram of CO to predict the ... The initial diagram represents the ground state. Then, one electron of 2s orbital shifts to vacant 2p orbital. Hybridization occurs between the s and the two p orbitals giving us 3 sp2 hybrid orbitals. The remaining p orbital is therefore unhybridized. Sigma bond (𝛔) corresponds to a single bond formation. Figure 7.1.21 Molecular orbital diagram for the CO ligand. Orange, red, green and blue colors of MOs refer to the use of colors in the Lewis dot structure of Fig. 7.1.19 To construct a molecular orbital diagram we must consider that O is considerably more electronegative than C, and therefore, the 2s orbital of O is lower in energy compared to ...
The molecular orbital diagram of CO2 is as below. A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon. Molecular Orbital Diagram of Carbon Monoxide (CO) The above image shows energy levels for the molecular orbitals of the carbon monoxide (CO) The molecular orbital diagram is a diagrammatic representation of showing how chemical bonding is taking place within a molecule. Co orbital diagram. Cobalt has a total of 27 electrons which are contained in 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s and 3d sub. Controls click on the co molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. So you have the carbon two s orbital and you have the carbon two p orbitals. The diagram showing orbital overlapping in the ammonia (NH3) molecule. The orbitals of NH3 participating in the bond formation to undergo sp3 hybridization . Molecular orbital diagram of ammonia (NH3) molecule. The molecular orbital diagram is a diagrammatic representation of how chemical bonding is taking place within the molecules.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is non bond ing. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine MOLECULAR ORBITAL APPROACH Basis of VB approach: overlap orbital s in each bond separately.
(SHOW WORK, DRAW THE ORBITAL DIAGRAM) O 0 0 1 04 O 3 7 O 6 O 5 02 QUEST ION 15 Which of the following is diamagnetic? (SHOW WORK, DRAW THE NOBLE GAS ORBITAL DIAGRAM S) O 37Rb O 15P 13A1 0 24Cr O 48Cd QUEST ION 16 Answer Draw the orbital diagram of the element. Explain the two rules applied in arranging the electrons in the orbital s. 8Q: 2p ...
Molecular orbital diagram of co. Find the point group of the molecule and assign cartesian coordinates so that z is the principle axis. To view a model click on a molecular orbital in the energy level correlation diagram shown the results displayed may be switched between those from a low level of calculation and those from a high level ...
The orbital diagram is drawn as follows: the first 2 electrons will pair up in the 1s orbital; the next 2 electrons will pair up in the 2s orbital. That leaves 4 electrons, which must be placed in the 2p orbitals. According to Hund's Rule, all orbitals will be singly occupied before any is doubly occupied.
The orbital diagram of difluoromethane can be represented as: According to Bent's rule, if a central atom is bonded to multiple atoms then it will hybridize in such a way that hybrid orbitals with more s-character will point towards the more electropositive element and hybrid orbitals with more p-character will direct towards the more ...















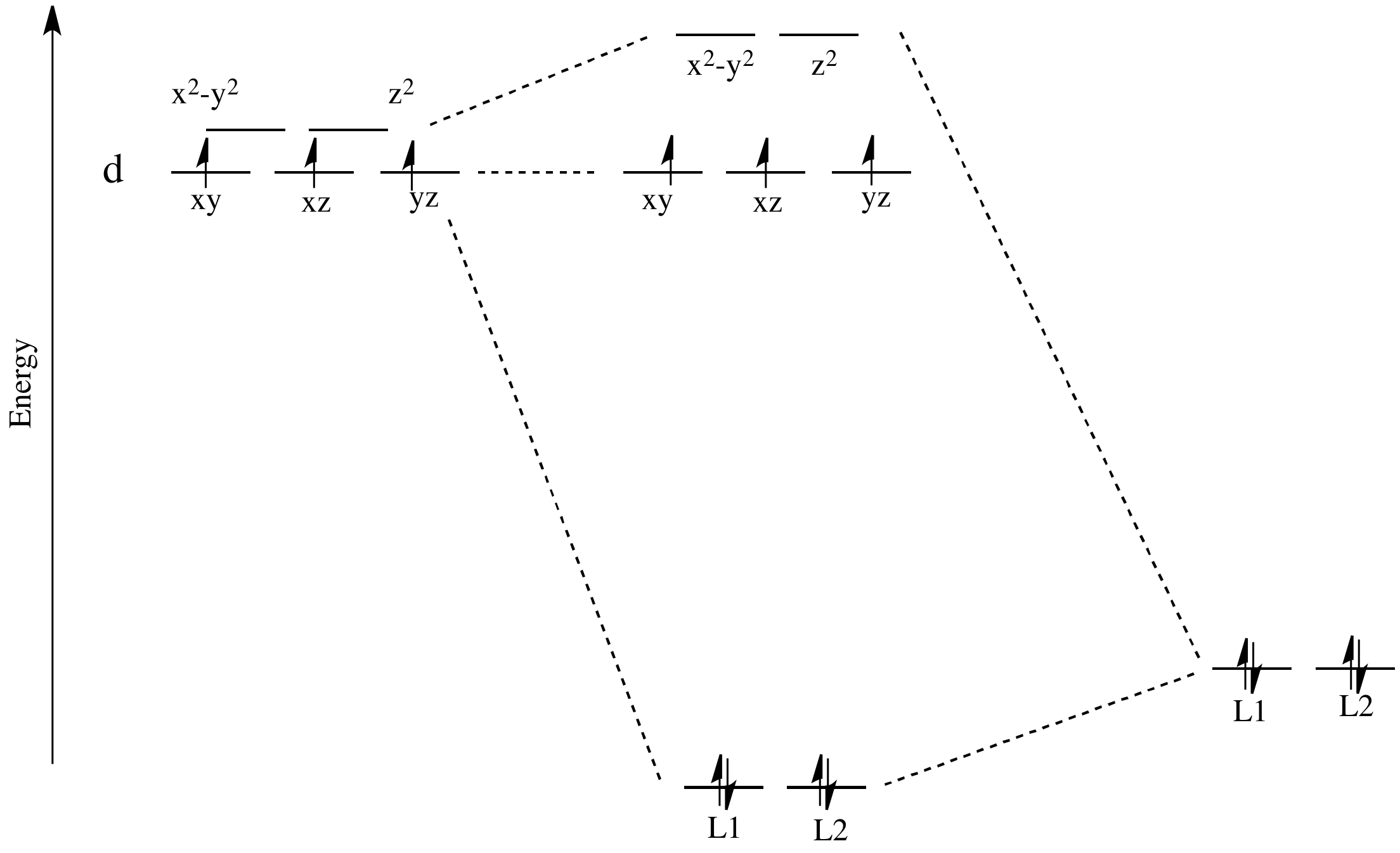


0 Response to "42 orbital diagram for co"
Post a Comment