43 converging lens ray diagram
Convex lens forms real image because of positive focal length and concave lens forms virtual image because of negative focal length. In mirrors , images are formed through reflection but lens es form images through refraction . This is explained with the help of ray diagram s as follows 1. Introduction (Refraction and Lens es) 2. The Lens Equation 3. Concave Lens es 4.
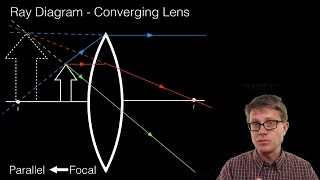
(a) Draw a diagram to show how a converging lens focusses parallel rays of light. (b) How would you alter the above diagram to show how a converging lens can produce a beam of parallel rays of light. Solution : (a) A converging lens focusses parallel ray of light as shown below: (b) Place a source of light at the focus of the converging lens.
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed. Answer: Here : Object distance, u= -25 cm, Object height, h = 5 cm, Focal length, f = +10 cm According to the lens formula, 1/ f = 1/ ν − 1/ u , we have
Converging lens ray diagram
The second ray is drawn thru the principal axis at the lens. c) The intersection point is where the image is located. It's shown with a blue dotted arrow. d) Now, this dotted blue arrow serves as an object for the second converging lens. e) The first ray is drawn from the tip of the dotted blue arrow to the lens and then through the focal point ...
Concave And Convex Mirrors Ray Diagram For Mirror Basic Properties Of Mirrors Introduction To Olympus Ls ... Part 10 Optics Mirrors And Lenses Chapter 24 Difference Between Real Image And Virtual With Practical Applications
Identifying the principal axis, focal point and focal length of a simple converging or diverging lens on a scaled diagram; Solving problems involving not more than two lenses by constructing scaled ray diagrams; Solving problems involving not more than two curved mirrors by constructing scaled ray diagrams
Converging lens ray diagram.
The correct answer is C = it is used to make periscope . Convex lenses are used in eyeglasses for correcting farsightedness, where the distance between the eye's lens and retina is too short, as a result of which the focal point lies behind the retina.Eyeglasses with convex lenses increase refraction, and accordingly reduce the focal length.Convex lenses are used in microscopes, magnifying ...
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed. Solution
Convex lens for ms real image because of positive focal length and concave lens for ms virtual image because of negative focal length. In mirrors, images are for med through reflection but lens es for m images through refraction. This is explained with the help of ray diagram s as follows Convex & Concave Lens es. A lens is a piece of equipment that for ms an image by refracting light.
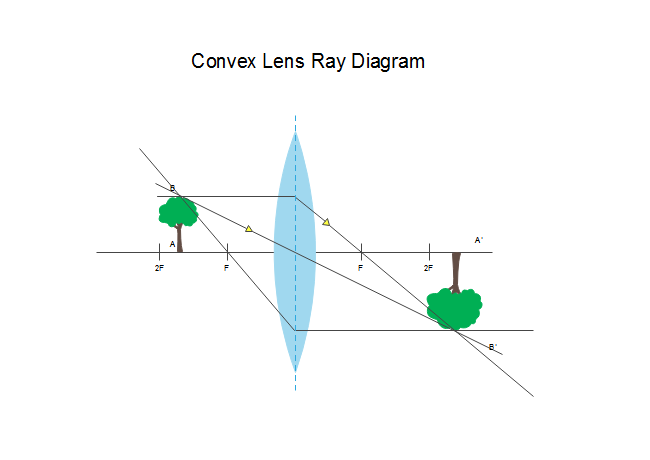
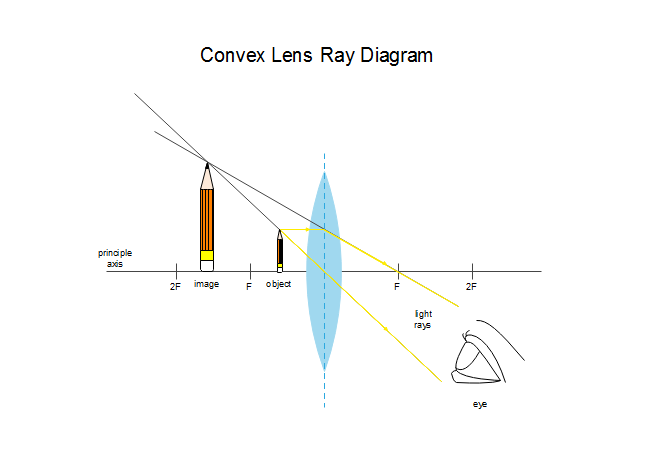
(b) An object AB is placed between O and F1 on the principal axis of a converging lens as shown in the diagram. Copy the diagram and by using three standard rays starting from point A, obtain an image of the object AB. [3] (c) An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm from a convex lens of focal length 8 cm. Find: (i) the position of the image
Indicate on the diagram the angle of incidence of the ray,(1 mark) Given that the refractive index for a ray travelling from air to glass is 1.5, determine the angle of refraction.(2 marks) Figure 6 shows an object O placed in front of a converging lens whose principal focus is F.
Distort means to change the shape of something by twisting or moving the parts around.A converging lens will cause the light rays to bend to a specific focal point. Lenses serve to refract light at each boundary. As a ray of light enters a lens, it is refracted; and as the same ray of light exits the lens, it is refracted again.The amount of ...
Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge.
The distance between the two converging lenses when equal to the some of their focal length then we can say that the ray will be parallel to the principal axis. (3) The focal length of a converging lens is 20cm. An object is 60cm from the lens. Where will the image be formed and what kind of image is it? (AS1) Ans: -As we know that 1/v + 1/u ...
Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a diverging lens. 11 draw a ray diagram for a diverging lens that has a focal length of 108 cm when an object is placed 324 cm from the lenss surface. Ray diagrams for converging lens you are here trick to drawing ray diagrams for converging lens. 12 draw a ray diagram for an object.
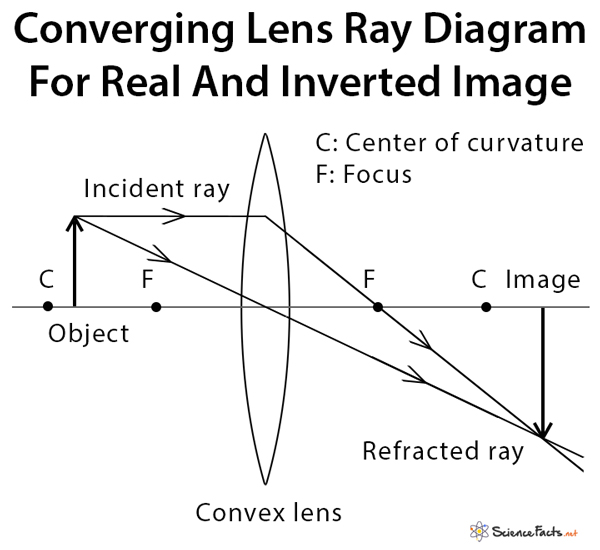
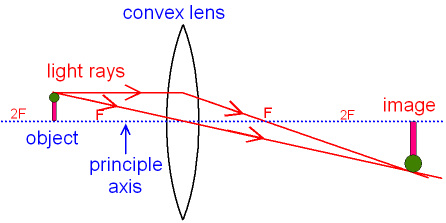
Converging lenses. The image produced is: - real - inverted - smaller than the object; To form a real image with a converging lens the object needs to be beyond the principal focus (F). Three construction rays are used to find the location of the image. Ray 1: this ray is refracted through F after passing through the lens.
Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge.
Ray Diagrams for Concave Lenses The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results. Ray Diagrams 3 of 4 Concave and Convex Lenses and Mirrors. A lens is an optical device which transmits and refracts light converging or diverging the beam.
Q18.Which diagram shows image formation of an object on a screen by a converging lens? Ans.C. The ray diagram of the image formation by a convex lense is shown as one parallel ray passes through the focal point and other ray should pass through the optical centre of the lense.
Two converging lenses, A with a focal length of +2.0 cm and B with a focal length of +5.0 cm, are placed 14c m apart. An object is placed 3.0 cm to the left of lens A. a) Use graphical methods, to scale, to construct the ray diagram with a measurement of the final image position and height; and b) Use the lens equation to de
The ray diagram of a convex mirror is shown below. The focal length of a convex mirror can be determined by introducing a convex lens between the object and the convex mirror. An image can be obtained with the help of a convex lens side by side with the object when the convex mirror reflects the rays along the same path, i.e., when the rays ...
Thin lens equation converging and dverging lens ray diagram & sign . Using concave lenses, you always end up with upright, virtual images. Using the lens maker's equation. It can be derived from a geometric analysis of ray tracing for . The measured distance from a lens to the object is 20 .
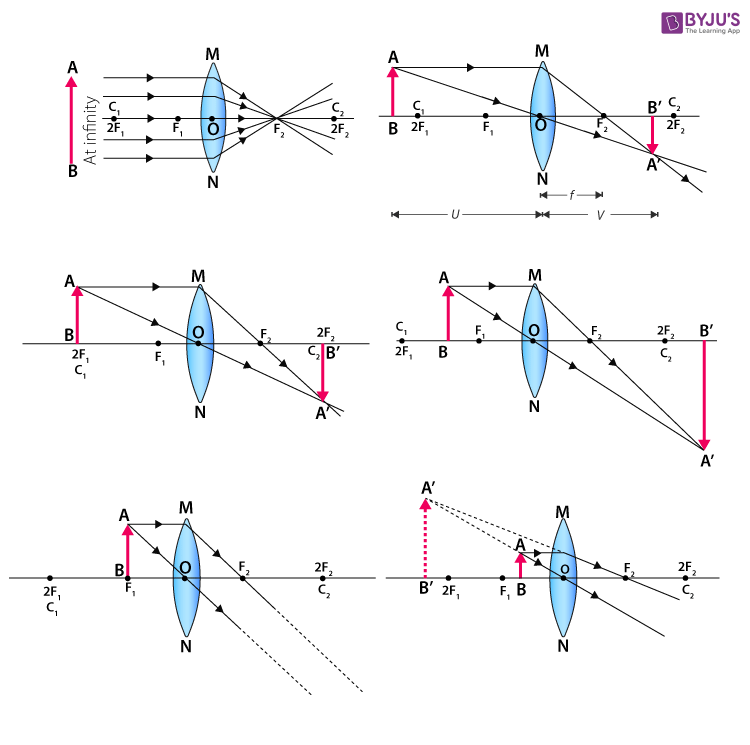
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are:
Section 1: Introduction (Refraction and Lenses) 4 Convex (converging) and concave (diverging) lenses are drawn as, V W To understand image formation we use ray diagrams. Here is an …
For a thin lens in air, the distance from this point to the lens is the focal length, though it is negative with respect to the focal length of a converging lens. Convex-concave (meniscus) lenses can be either positive or negative, depending on the relative curvatures of the two surfaces.
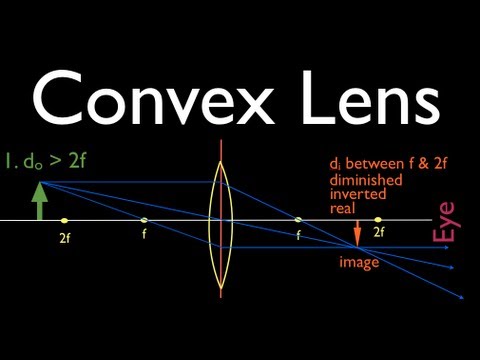
Figure 11.6. 11: Ray tracing predicts the image location and size for an object held closer to a converging lens than its focal length. Ray 1 enters parallel to the axis and exits through the focal point on the opposite side, while ray 2 passes through the center of the lens without changing path.
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed. Given that The height of object = 5cm
A converging lens can produce both real and. 3 the magnifying power. Trick to drawing ray diagrams for converging lens. The other ray of light always passes through the focal point of the lens. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of twoa converging lens and a screen are so arranged that an image of the sun falls on the screen.
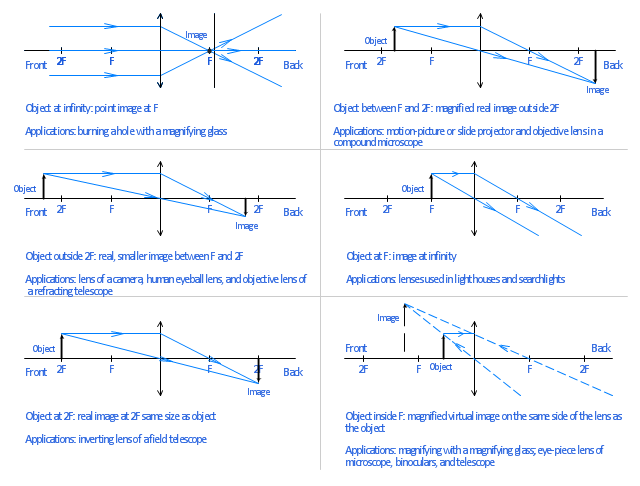
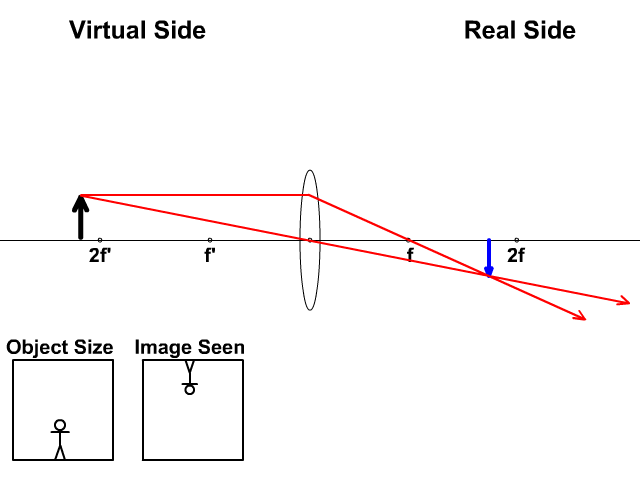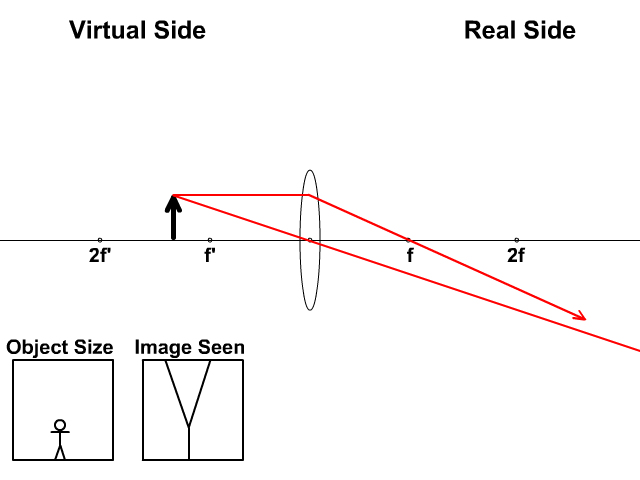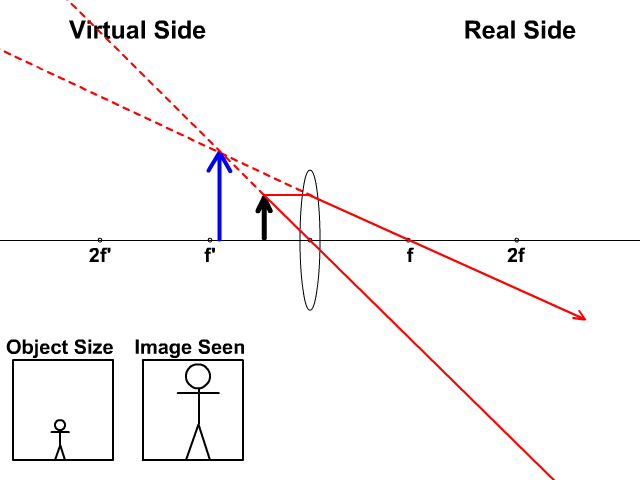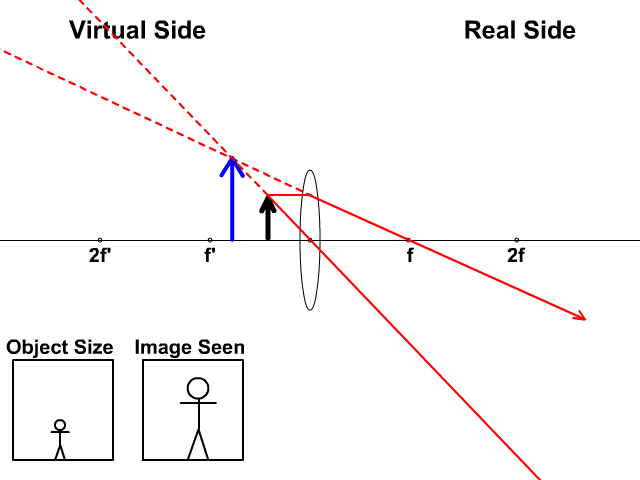
Ray Diagram for Object Located in Front of the Focal Point. In the three cases described above - the case of the object being located beyond 2F, the case of the object being located at 2F, and the case of the object being located between 2F and F - light rays are converging to a point after refracting through the lens.
Convex Lens - Ray diagram. Last updated at Nov. 18, 2021 by Teachoo. For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positions Hence, we take different cases Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity In this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)
Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray.
In each diagram use an arrow 10 cm tall pointing upwards as the object. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. Concave And Convex Mirrors Ray Diagram For Convex And Concave Mirror. Converging mirror ray diagram. The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located […]
Apr 26, 2020 · For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa
Converging Lens es A convex lens is a converging lens which bends light ray s into focus. The focal length, f, is the distance to the focal point where parallel ray s converge as shown. A Ray Diagram is a simple picture using only 2 or 3 light ray s reflected off an object to visualize how images are formed.
Jul 07, 2020 · A converging lens is an optical lens that converges all rays of light passing through it. The primary purpose of a converging lens is to focus the incoming rays from an object and converge them to form an image.






















---teachoo.png)




0 Response to "43 converging lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment