43 spinal nerve root diagram
Nerve root: Part of the nerve that branches off the spinal cord or cauda equina. At each level, a pair of nerve roots emerge from the right and left sides of the spinal cord. Each pair consists of a dorsal root at the back and a ventral root in the front. Spinal nerve: A single nerve formed when the dorsal and ventral nerve roots merge ... The dorsal root ganglion for each nerve is an enlargement of the spinal nerve. There are 31 spinal nerves, named for the level of the spinal cord at which each one emerges. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves designated C1 to C8, twelve thoracic nerves designated T1 to T12, five pairs of lumbar nerves designated L1 to L5, five pairs of ...
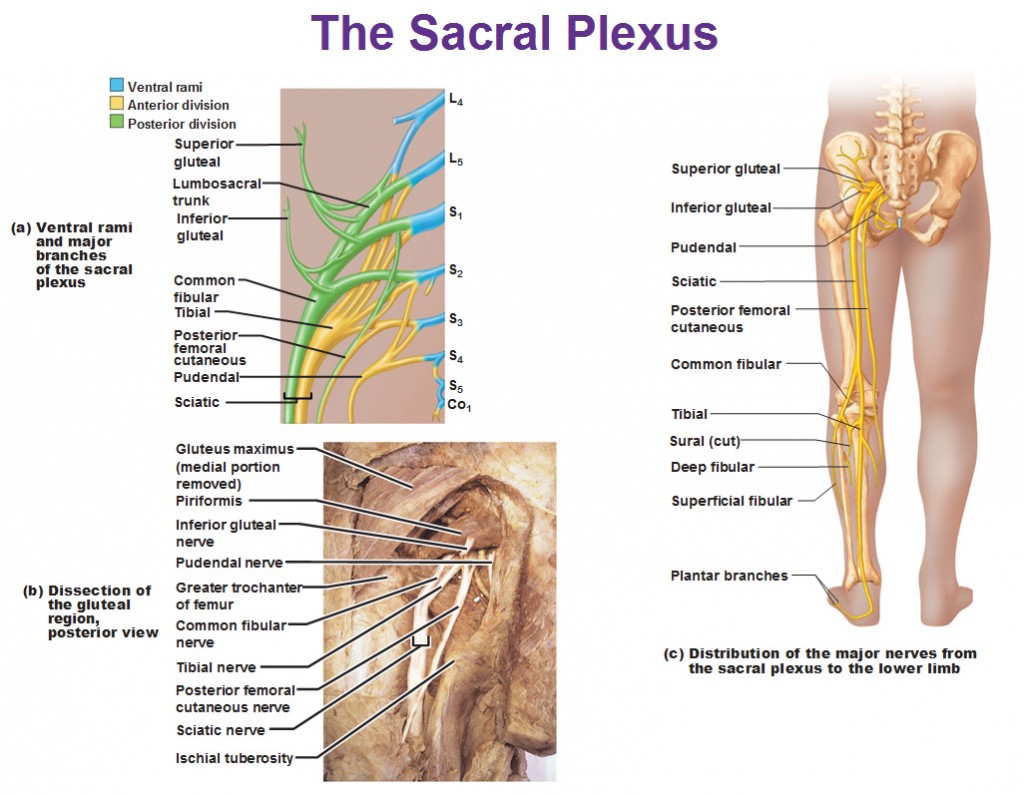
The first nerve root exits between S1 and S2. One pair of coccygeal (Co1) nerves meets in the area of the tailbone. By way of the peripheral nervous system (PNS), nerve impulses travel to and from the brain through the spinal cord to a specific location in the body. The PNS is a complex system of nerves that branch off from the spinal nerve ...

Spinal nerve root diagram
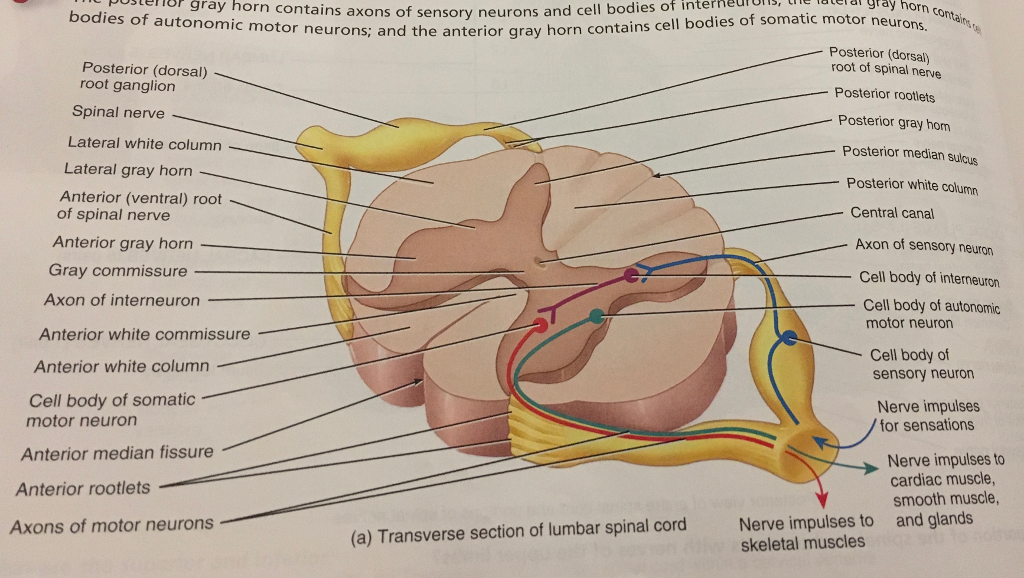
The rootlets unite to form an anterior (ventral) or posterior (dorsal) root of a spinal nerve. The anterior/ventral root contains efferent nerve fibres, which carry stimuli away from the CNS towards their target structures.The cell bodies of the anterior root neurons are located in the central grey matter of the spinal cord. Structure . The spinal nerves are relatively large nerves that are formed by the merging of a sensory nerve root and a motor nerve root. These nerve roots emerge directly from the spinal cord—sensory nerve roots from the back of the spinal cord and the motor nerve roots from the front of the spinal cord. As they join, they form the spinal nerves on the sides of the spinal cord. -->Posterior root swells into the dorsal root ganglion Distal to the ganglion: >anterior and posterior roots merge, leave the dural sheath, and form the spinal nerve proper >> nerve then exits the vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramen
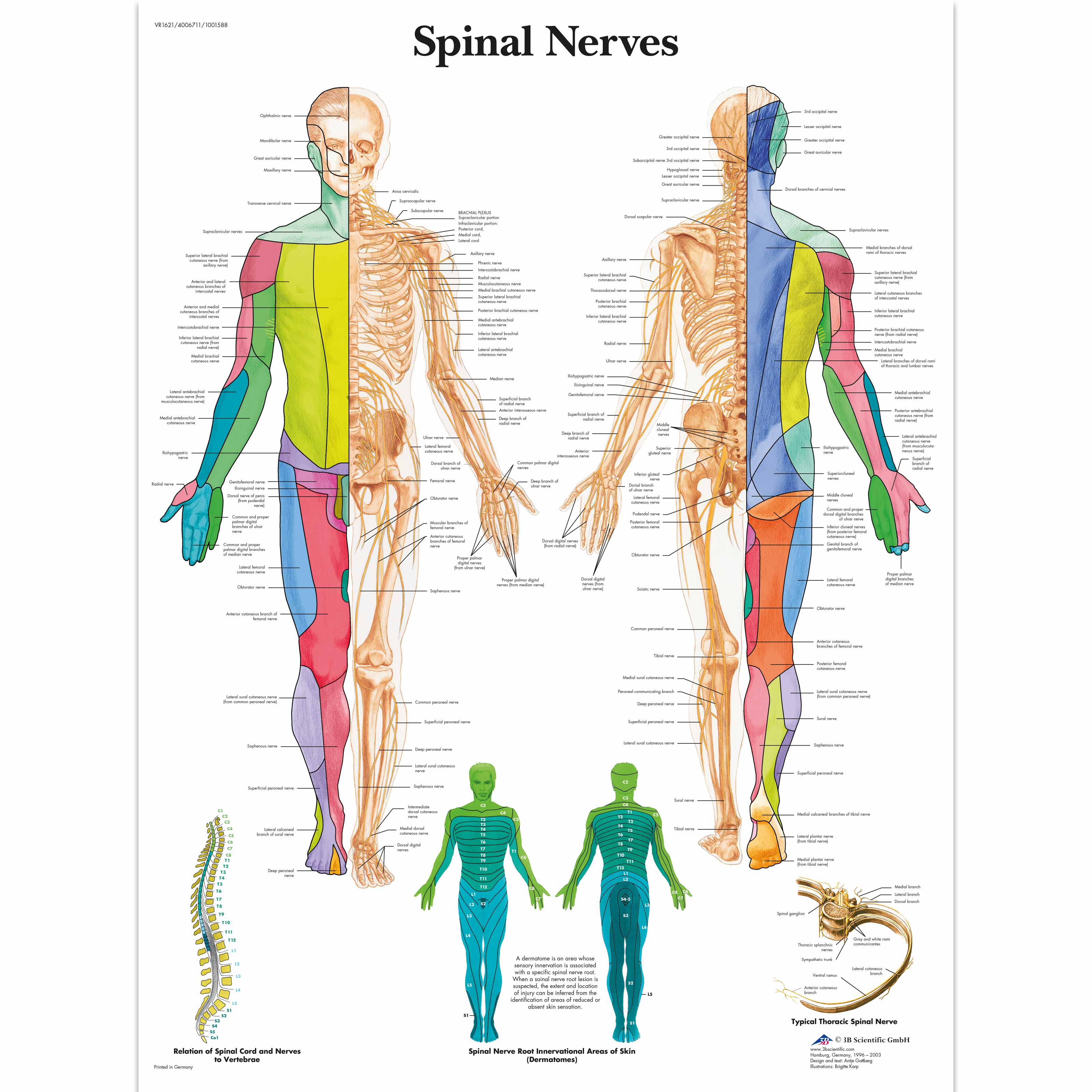
Spinal nerve root diagram. The cervical nerves arise from the spinal cord in the form of rootlets, or fila radicularia, smaller neuron bundles that coalesce to form roots. For each spinal nerve, an anterior and posterior root join to form the completed nerve. Shortly after branching out of the spinal cord, the cervical nerves form the cervical and brachial plexuses. Spinal Nerve Roots. Create healthcare diagrams like this example called Spinal Nerve Roots in minutes with SmartDraw. SmartDraw includes 1000s of professional healthcare and anatomy chart templates that you can modify and make your own. Spinal Nerves . There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Again, they are named according to where they each exit in the spine (see figure below). Each spinal nerve is attached to the spinal cord by two roots: a dorsal (or posterior) root which relays sensory information and a ventral (or anterior) root which relays motor information.Therefore, once the two roots come together to form the spinal ... This is because the C1 spinal nerve typically doesn't have a sensory root. As a result, dermatomes begin with spinal nerve C2. Dermatomes have a segmented distribution throughout your body.
On the chart below you will see 4 Columns (Vertebral Level, Nerve Root, Innervation, and Possible Symptoms). Under 'Vertebral Level': C1-C7 is the NECK, ; T1-T12 is the UPPER BACK/rib cage area, and ; L1-L5 is the LOWER BACK.; Simply line up the "Vertebral Level" with the "Possible Symptoms" and you will see some surprising connections of symptoms that relate to your spine. Spinal nerves are mixed nerves that transmit motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the central nervous system and the periphery Each spinal nerve carries afferent (sensory) fibers and efferent (motor) fibers to and from the spinal cord, the former of which comprise the posterior/dorsal rootsEach posterior root presents a ganglion as it emerges from the intervertebral foramen. The spine is divided into 4 segments. Cervical: 7 vertebral segments, 8 nerve roots. Thoracic:12 vertebral segments,12 nerve roots. Lumbar: 5 vertebral segments,5 nerve roots. Sacral: 5 fused segments,5 nerve roots . The spinal cord is connected to the brain stem and carries a number of motor and sensory tracts. spine on sitting. Chart of Spinal Nerve Supply and The Effect of Spinal Misalignment Every area of the body is controlled by nerves. The normal function of these can be disturbed by misalignments of the vertebrae effecting the disease conditions shown below. 4 3 2 1 12 11 9 10 8 7 6 5 4 2 1 7 6 3 5 4 1 2
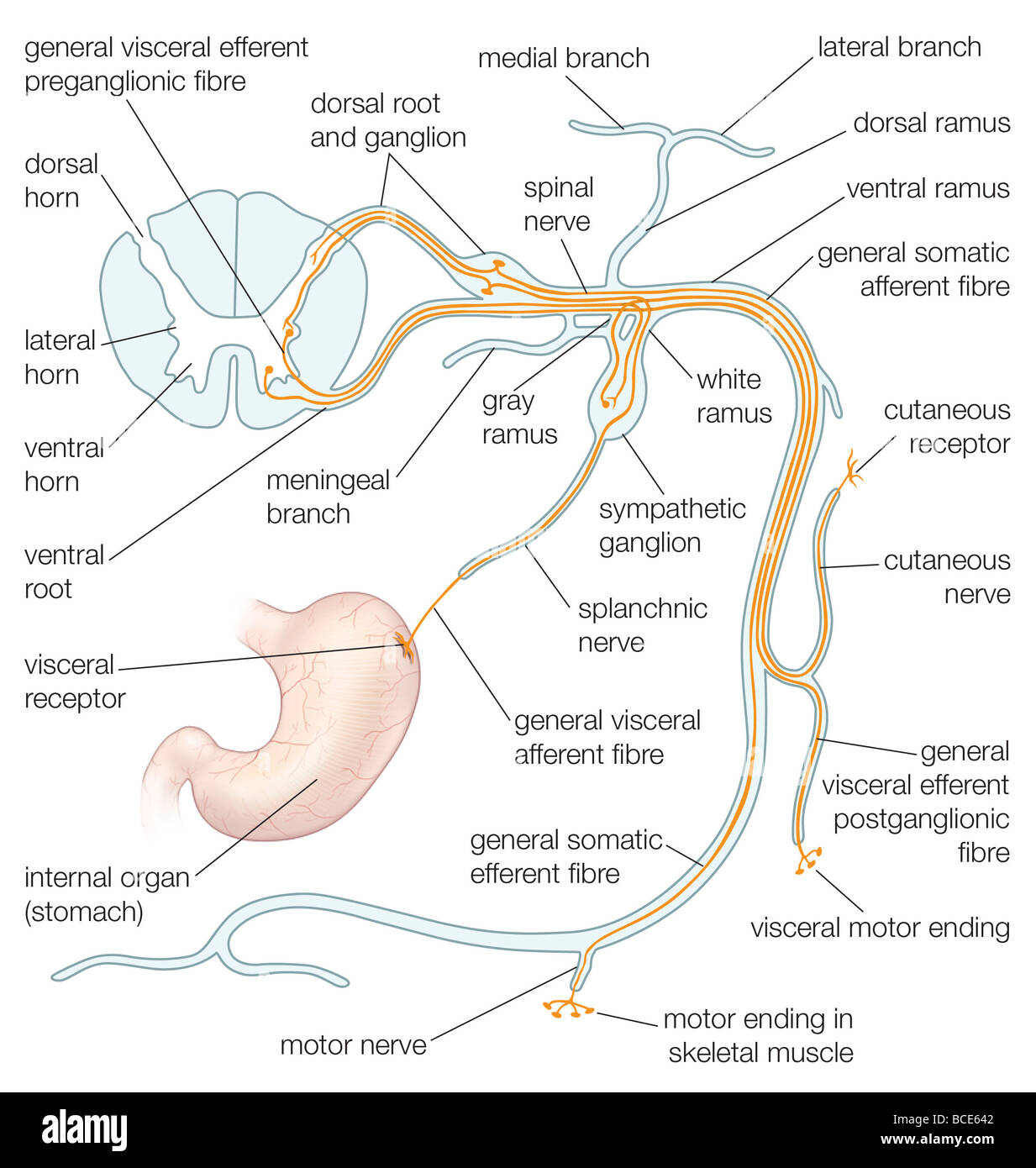
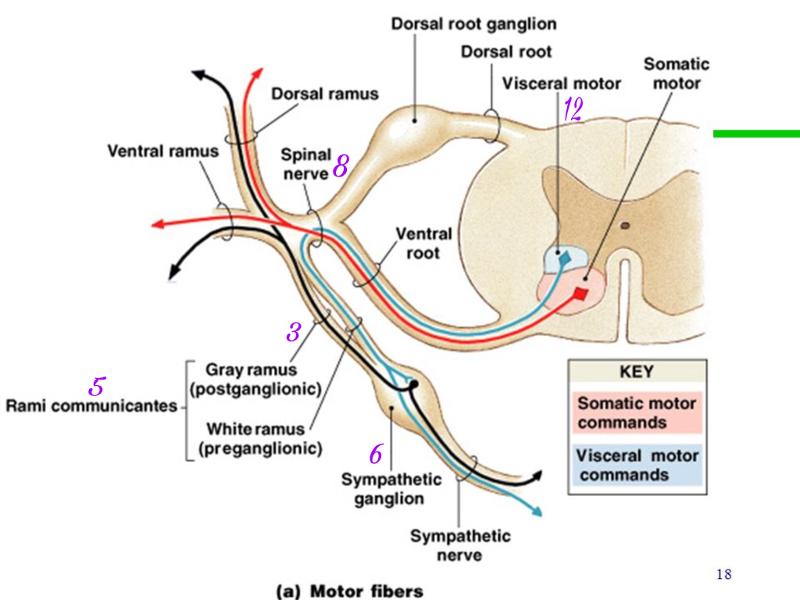
The pudendal nerve originates from the sacral spinal nerves and innervates the descending colon, rectum, urinary bladder, and genitals. Coccygeal Spinal Nerves. There is 1 coccygeal spinal nerve pair. Sympathetic nerve Sympathetic ganglion Spinal nerve Ventral ramus Dorsal ramus Dorsal root ganglion Dorsal root Visceral motor Somatic Ventral root The distribution of motor neurons in the spinal cord and motor fibers within the spinal nerve and its branches. Although the gray ramus is typically proximal to the white ramus, A dermatome map is a diagram that identifies dermatomes, or areas of skin that are innervated by a single nerve, and their corresponding nerve roots along the length of the spinal . Dermatomes are areas of skin that receive sensations from sensory nerves exiting the spinal cord. Sensory nerves provide the feeling of hot, cold, pain, etc. Nerve root pain originates from nerves that have been damaged or are compressed in the spine. Nerves carry information that control body movements and sensations to the brain. When a nerve in the spine is damaged it can cause pain, increased sensitivity, numbness and muscle weakness.
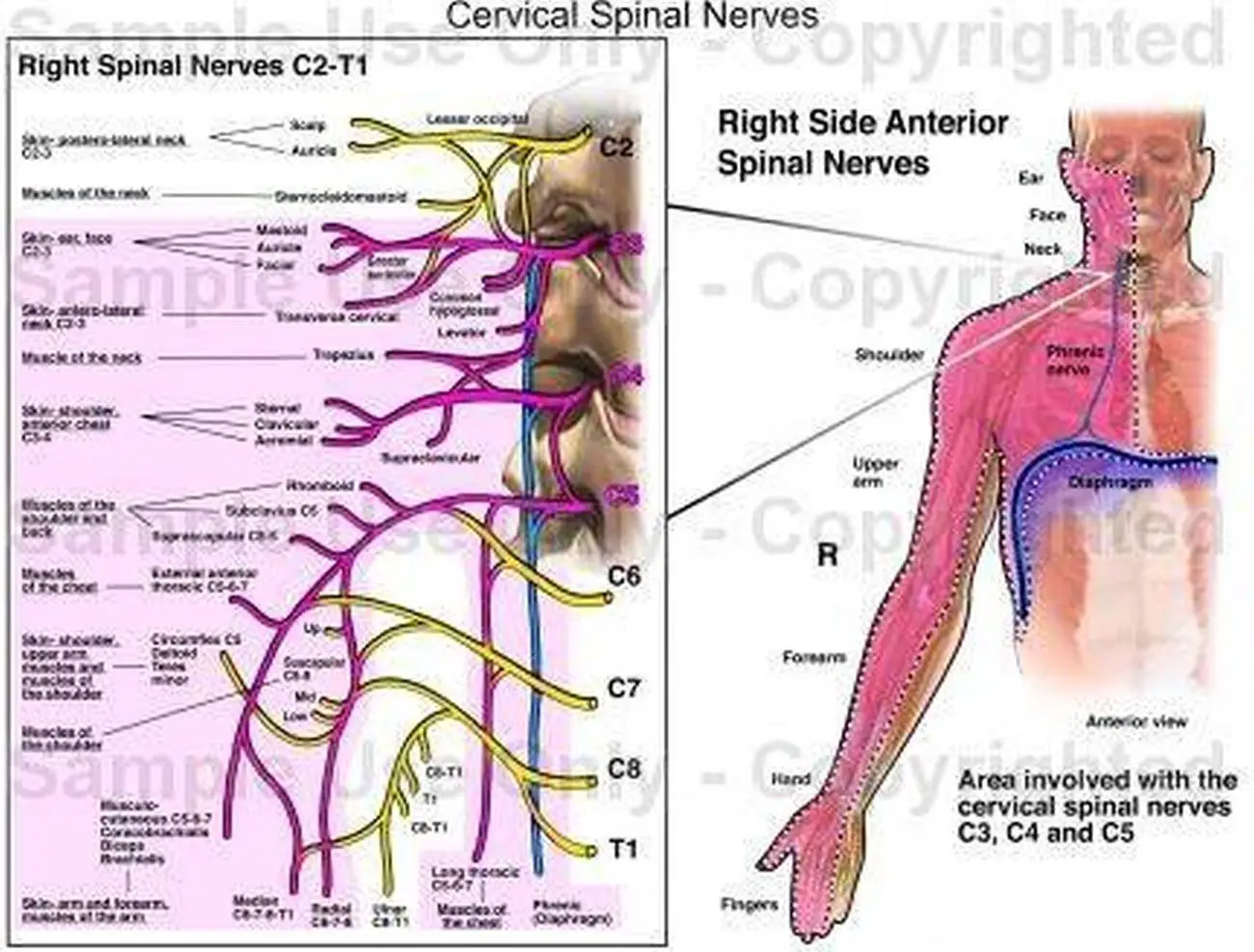
C5 is the nerve "root" that exits the spinal cord above the fifth vertebra in the neck. It travels into the brachial plexus and eventually becomes the nerves that feed muscles around the shoulder and chest. It also provides sensation to parts of the upper arm. C6 is the nerve "root" that exits the spinal cord above the sixth vertebra in the neck.
1 coccygeal nerve; For most spinal segments, the nerve roots run through the bony canal, and at each level a pair of nerve roots exits from the spine. Cervical spine nerve roots. In the neck, the nerve root is named for the lower segment that it runs between (e.g. C6 nerve root at C5-C6 segment). Lumbar spine nerve roots.
Spine and Nerves. The vertebral column's most important physiologic function is protecting the spinal cord, which is the main avenue for communication between the brain and the rest of the body ...
Download scientific diagram | Diagram of spinal root and spinal nerve microscopic anatomy. As of subarachnoid angle (SA), the epineurium (Ep) is in continuity with the dura mater (DM). The ...
Derived from two Greek root words in "derma" (skin) and "tomos" (a slice), dermatomes refers to a section of skin supplied by a spinal nerve, starting with the cervical spine (in the neck) down to the sacrum (the base of our pelvis). These areas are not perfectly exact, and multiple nerves may innervate a single general area.
The spinal nerves consist of a group of 31 nerves. These nerves are attached to the spinal cord by two roots- dorsal sensory root and ventral motor root. The sensory root fibres carry sensory impulses to the spinal cord. The motor roots, on the contrary, carry impulses from the spinal cord.
Drag the labels onto the diagram to identify the spinal nerve roots and meninges. 1. ventral rootlets of spinal nerve 2. ventral root 3. dorsal root 4. dorsal rootlets of spinal nerve 5. dorsal root ganglion 6. spinal nerve 7. pia mater 8. arachnoid mater 9. dura mater.
The parenthesis next to the spinal nerve root means this level contributes to the innervation but is not the primary nerve root. For example: the serratus anterior muscle is innervated by the long thoracic nerve with contributions from spinal nerve root C5, 6, 7 (8).
(tissue, organs, etc.), which may cause irritation and/or compression of nerve roots and affect these components.1 The nervous system controls and coordinates all organs and structures of the human body. Many nerves come from the spinal cord, pass through foramina
The roots combine to form the spinal nerve and then they split apart again and are now called rami (ramus for singular). The dorsal root is posterior to the ventral (front) root. The dorsal rami innervate the deep muscles of the back for motor control, such as the erector spinae and also a horizontal strip of skin for sensory input.
spinal nerve root (see the following image). Dermatomes of the head, face, and neck. There are 31 segments of the spinal cord, each with a pair (right and left) of ventral (anterior) and dorsal (posterior) nerve roots that innervate motor and sensory function, respectively. The anterior and posterior nerve roots combine on each side to form the
-->Posterior root swells into the dorsal root ganglion Distal to the ganglion: >anterior and posterior roots merge, leave the dural sheath, and form the spinal nerve proper >> nerve then exits the vertebral canal through the intervertebral foramen
Structure . The spinal nerves are relatively large nerves that are formed by the merging of a sensory nerve root and a motor nerve root. These nerve roots emerge directly from the spinal cord—sensory nerve roots from the back of the spinal cord and the motor nerve roots from the front of the spinal cord. As they join, they form the spinal nerves on the sides of the spinal cord.
The rootlets unite to form an anterior (ventral) or posterior (dorsal) root of a spinal nerve. The anterior/ventral root contains efferent nerve fibres, which carry stimuli away from the CNS towards their target structures.The cell bodies of the anterior root neurons are located in the central grey matter of the spinal cord.





















0 Response to "43 spinal nerve root diagram"
Post a Comment