44 compton scattering feynman diagram
When I see people write down the amplitude iM from a Feynman diagram, they never seem to include an incoming wavefunction from the Higgs boson, such as in H --> W+ W- decays. Why is this? Renormalization is a collection of techniques in quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, that are used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities by altering values of these quantities to compensate for effects of their self-interactions.But even if no infinities arose in loop diagrams in quantum field theory, it ...
https://greydonsquare.bandcamp.com/album/compton-scattering
Compton scattering feynman diagram
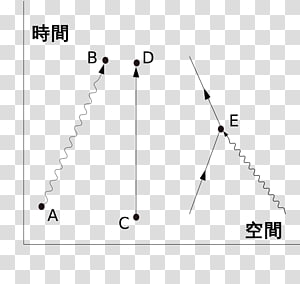
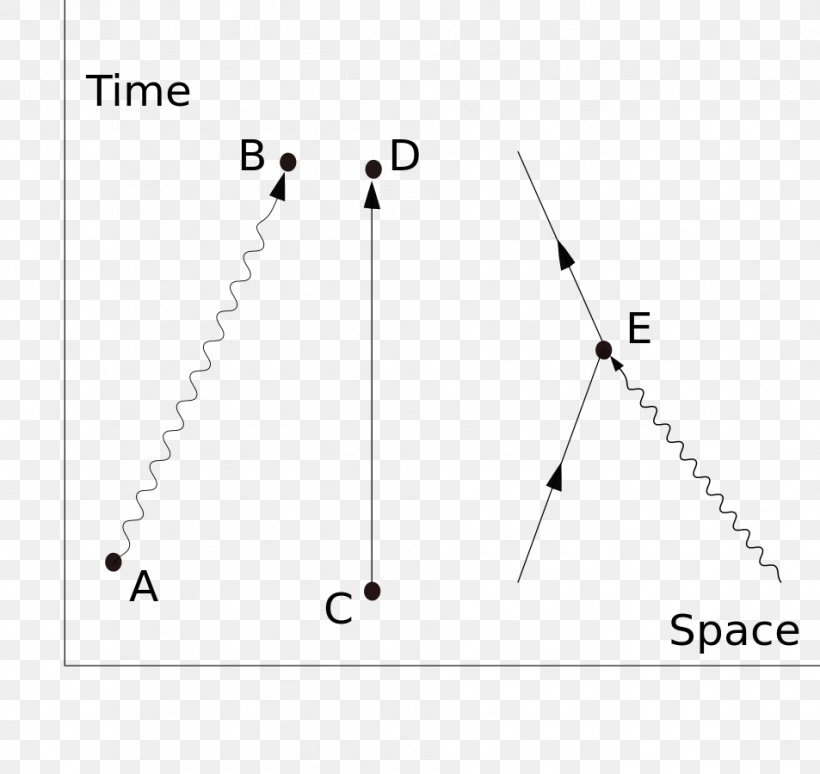
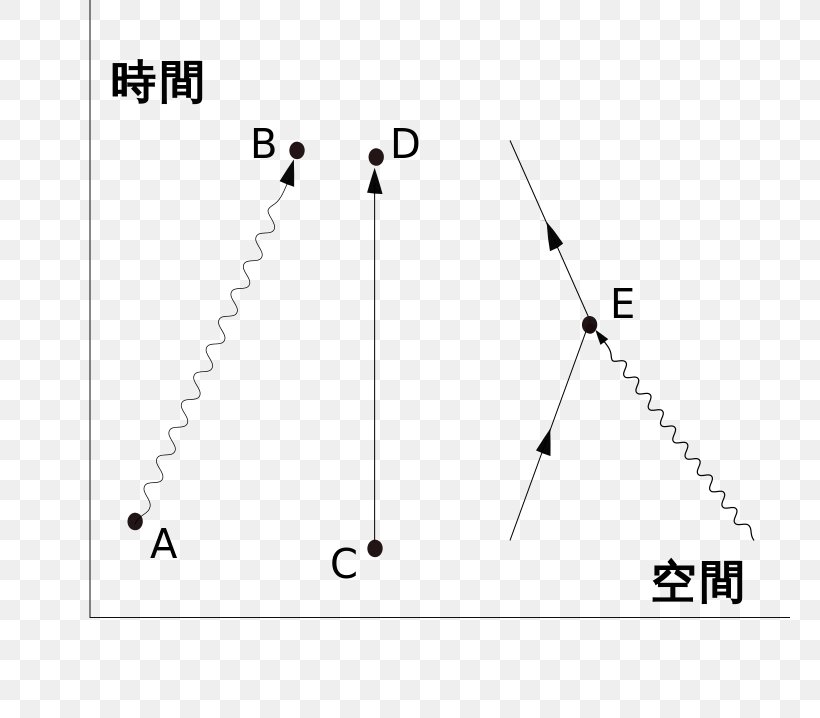
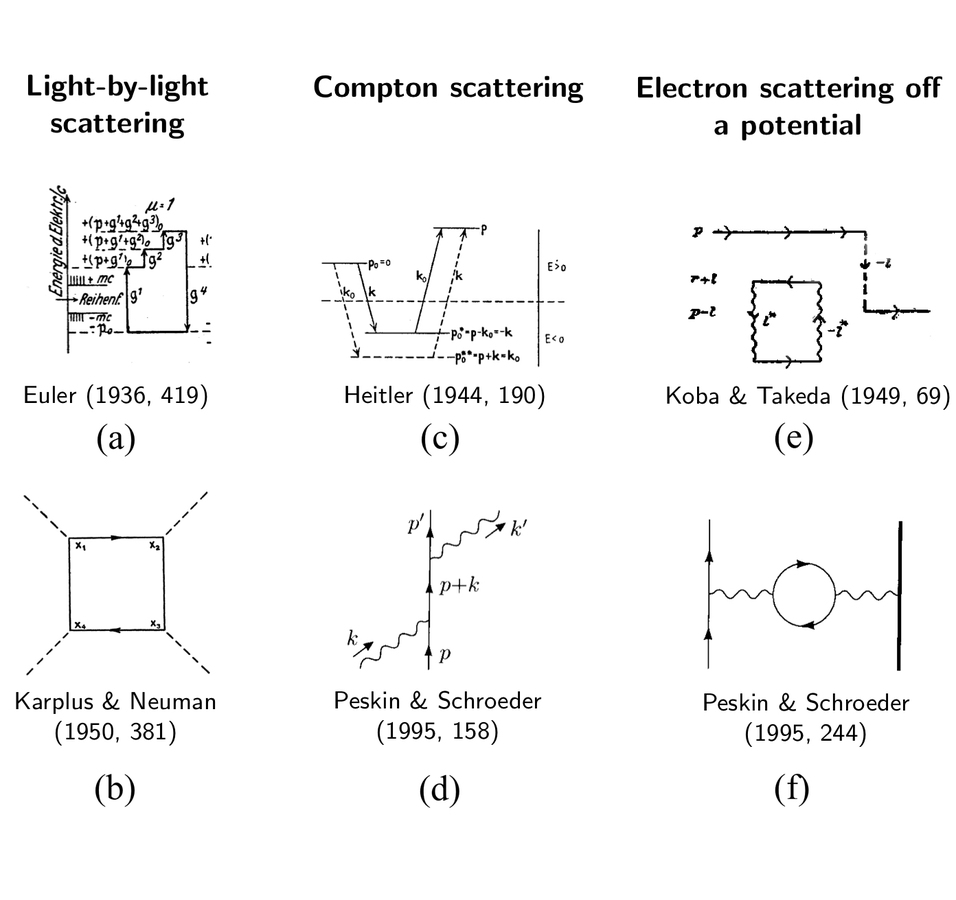
Figure 18.2: Feynman diagram for e−e+ → µ−µ+ in QED. ... Figure 18.7: Feynman diagrams contributing to Compton scattering at leading order in. cant answer “what type of correlation” in non strong ones because of this, also dont get how to determine an estimate taken from line of best bit to be “resonably accurate” or “inaccurate” [Link to image](http://puu.sh/msXF5/a9cc0335f9.jpg) As far as I am aware these diagrams aren't very detailed so I am missing something. The first one makes sense if you ignore momentum issues, but the second one makes little sense to me. So an excited electron shoots out a photon and then a brief amount of time later another photon appears and just happens to hit the electron? I'm guessing something more is going on?
Compton scattering feynman diagram. Is the theory that they actually travel backwards in time or is this just written this way for convenience? On a slightly related note, space-time cones are bent at a black hole’s event horizon such that the future exists only inside the black hole and everything else is the past. Is it possible that Hawking radiation isn’t just a matter antimatter pair randomly popping into existence, but is instead an antiparticle traveling backwards in time that collides with the black hole? Download scientific diagram | Feynman diagrams for Compton scattering. from publication: QED Phenomena in an Ultrastrong Magnetic Field. I am aware there is an s-channel present in this process (e^- + photon -> e^- + photon), but I thought there would only be a t-channel and not a u-channel (given that final particles are distinguishable). However, there is only a u-channel and not a t-channel... why? I have tried to see the difference between the corresponding diagrams (Here's a [picture](https://i.imgur.com/21x3NGc.jpg) of what I have drawn) but I cannot see the reason. Am I missing something or have I drawn something inco... I have a panel dataset for 200 countries from 1980 to 2020. Two of the variables are GDP growth and level of financial development. I have to find the means for every country for both these variables (which I could) and plot these means together on a scatter diagram. How do I do this on Stata?
The Feynman diagram shown in Fig. 14.15(B) describes Compton scattering in which a photon scatters off a free electron producing a photon and an electron with ... I'm a third year physics student, just starting to do particle physics and as such am using Feynman diagrams a lot. Unfortunately, my lecturer seems to have assumed we're all fluent in using them, which we aren't (the course is an introduction course). I was wondering if anyone had any resources that explain step by step how to construct a Feynman diagram for a given process. Like if I was given an equation involving some weird vertex, how would I systematically approach drawing the diagram. Te... Edited for Physics 4C at College of Alameda (http://alameda.peralta.edu/physics/physics-4). Recorded from Physics 4C at College of Alameda, ... Hi, I have difficulty comprehending Feynman diagrams. Although I'm a high schooler, could you please explain to me like I'm five as to what exactly a FD *shows* and what it's used for? Thanks.
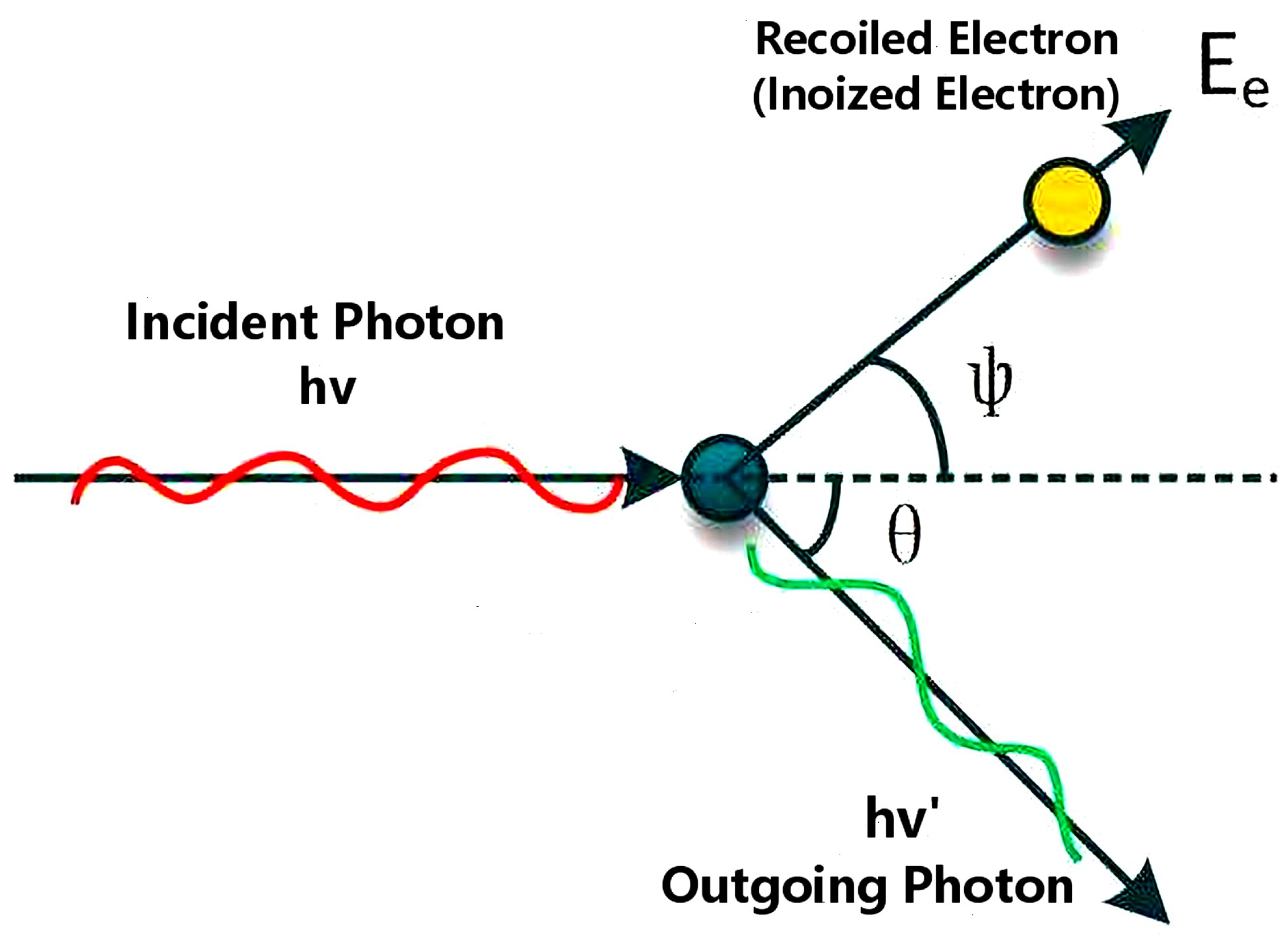
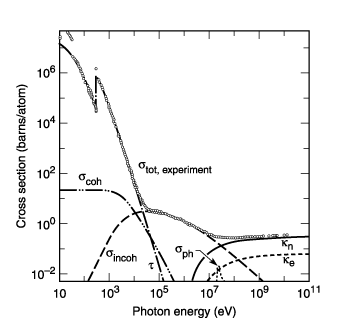
Compton scattering is the predominant interaction between X-rays and soft tissue in medical imaging. Compton scattering is an inelastic scattering of the X-ray photon by an outer shell electron. Part of the energy of the photon is transferred to the scattering electron, thereby ionizing the atom and increasing the wavelength of the X-ray. The scattered photon can go in … The electron is initially at rest, in a Schwarzchild background and the photon is directed radially outwards from the body toward the electron. Using momentum four vectors, with the primed vectors being the momentum after scattering, where Q describes the photon and P describes the electron. Q =(h/y){1, n} Q' =(h/y){1, n'} y: the wavelength of photon n: unit vector in direction of three momentum P ={m, 0} P' ={m, mv} Conservation of four momentum gives Q + P = Q' + P' or Q + P - Q'... C. V. Raman. In this Indian name, the name Chandrasekhara is a patronymic, and the person should be referred to by the given name, Raman. Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman FRS ( / ˈrɑːmən /; 7 November 1888 - 21 November 1970) was an Indian physicist known for his work in the field of light scattering. In Compton scattering, when the photon is scattered at 90deg... The maximum energy of the scattered photon is equal to the rest mass energy of electron, even as the energy of the incident photon tends to infinity... The idea that the energy of the scattered photon is capped makes sense to me intuitively, but I can't wrap my head around explaining it in physics terms, or why the max energy is equal to the rest mass energy of an electron... Anyone can help explain this to me?
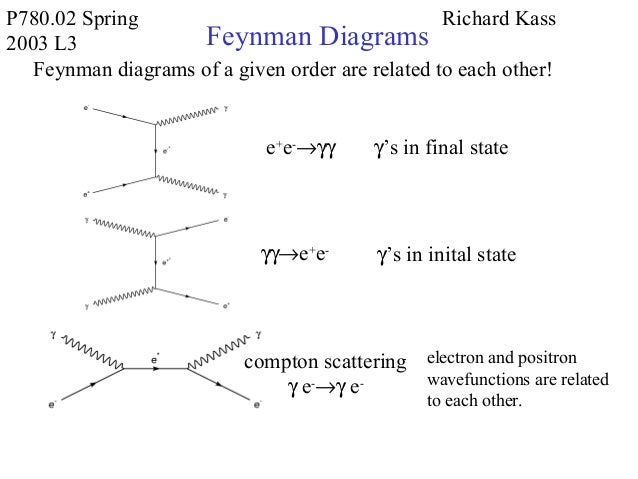
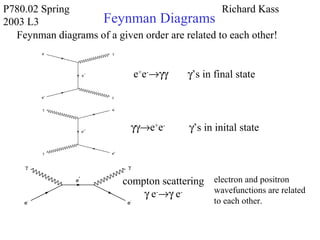
L3: Feynman Diagram 6 Feynman diagrams of a given order are related to each other: Relationship between Feynman Diagrams e+e- → γγ γγ → e+e-Compton scattering γe- → γe-Electron and positron wave functions are related to each other. γ’s in final state γ’s in initial state
07.12.2018 ... It shows the two geometric ways energy and momentum can be exchanged between the two incoming particles to produce the two outgoing, to first ...
so i just watched [this](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oBNZOOuqO6c&list=RDCMUCxqAWLTk1CmBvZFPzeZMd9A&index=13) video about reading Feynman diagrams, and the presenter mentioned around 6:20 that you can rotate a diagram to describe a different interaction. specifically rotating a diagram of A) an electron releasing a photon can be rotated to become a diagram of B) an annihilating electron positron pair. now,i understand that the details of the interactions are completely different.i'm...
Download scientific diagram | Feynman diagrams for the Compton scattering in lowest order. In diagram a) a photon is first absorbed and subsequently emitted ...
17.01.2014 ... We present a derivation of the differential cross section for the Compton scattering of an electron and a photon.
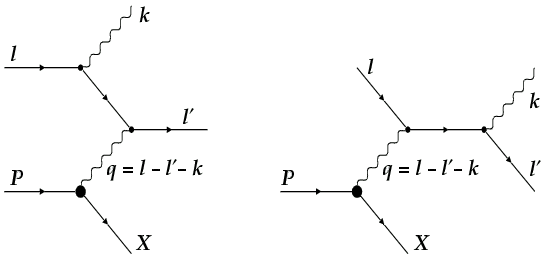
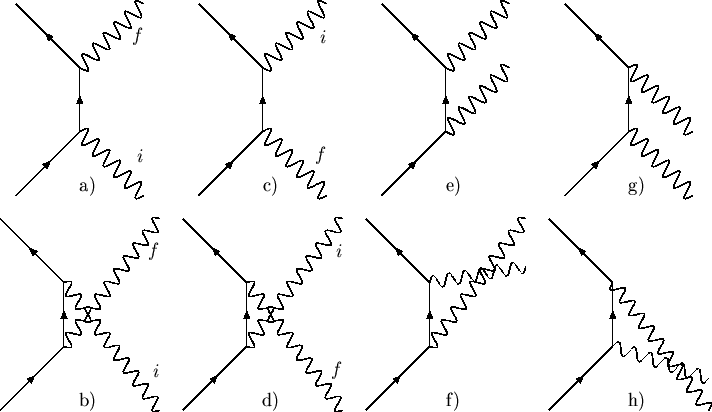
and p2, The corresponding Feynman diagrams are shown in the figure. Page 9. Chapter 1. CALCULATION OF THE SQUARE MATRIX ELEMENT. 5. Figure ...
She doesn't miss a beat in either the characterization or action, scattering clues with a delicate, precise hand. This is, in the end, the story of the anatomy of the human heart." - Booklist (starred review) Dana Schwartz’s Anatomy: A Love Story is a gothic tale full of mystery and romance. Hazel Sinnett is a lady who wants to be a surgeon more than she wants to marry. Jack Currer …
Hello, So I’m imagining a process happening in my head for the decay of muons, by which I mean I can draw a Feynman diagram to describe the event im thinking of (including loops and such). How can I see if this process is actually possible? Is there a way to directly go from a hypothetical Feynman diagram to an amplitude? How do I know what the coupling constants are? Are the propagators simply that of familiar fermions/bosons? Thanks for any advice?
Bit of a trivial question, but am I correct in thinking O(e) Feynman diagrams are essentially 1 vertex feynman diagrams thus the amplitude contains only 1 power of the coupling constant "e"?
Name or phenomenon, Description, Diagram. Beta decay · beta particle is emitted from an atomic nucleus, Beta Negative Decay.svg. Compton scattering ...
[Here it is.](https://ibb.co/X27wdtf) I've been pulling my hair out over this for the past 45 minutes. Also, what is the significance of the electron neutrino here? Does it turn into an electron because if the electron were to just appear, conservation of momentum would be violated? As you can see, I'm quite new to this. Any help would be greatly appreciated.
Figure 7.7: Feynman diagrams for Compton scattering. \begin{figure}\begin{center} \begin{picture}(. In the first diagram (figure ...
When there is a scattering angle of 0, many graphs and data show that no wavelength shift has occurred. Is this because at an angle of 0, no collision has occurred therefore no wavelength shift? i am not sure
differential cross section of the Compton scattering. dσ. dΩ. = α. 2. 2 m2 (k′ k ).
I see people draw Feynman diagrams directly for a Lagrangian showing which terms lead to them, but I don't know why those terms mean that Feynman diagram is possible. They also say you can write down the Feynman rules from the Lagrangian. For example the QCD Lagrangian: L = Tr\[G\_uv \* G^(uv)\] + Σ^(k) \[*q\_k* \* (i𝛾^(u)D\_u - m\_k) \* q\_k \] Apparently the field strength term (1st term) allows for 4 gluon and 3 gluon interactions and the last term allows for 2 quark - 1 gluon interactions?...
how can i insert feynman diagrams into an equation?
Electric field particles are represented with arrows of time that allow us to deduce if the particle in question is normal matter (electrons) or anti-matter (positrons), for example. What is the reason exactly as to why photons are not represented with any arrows?
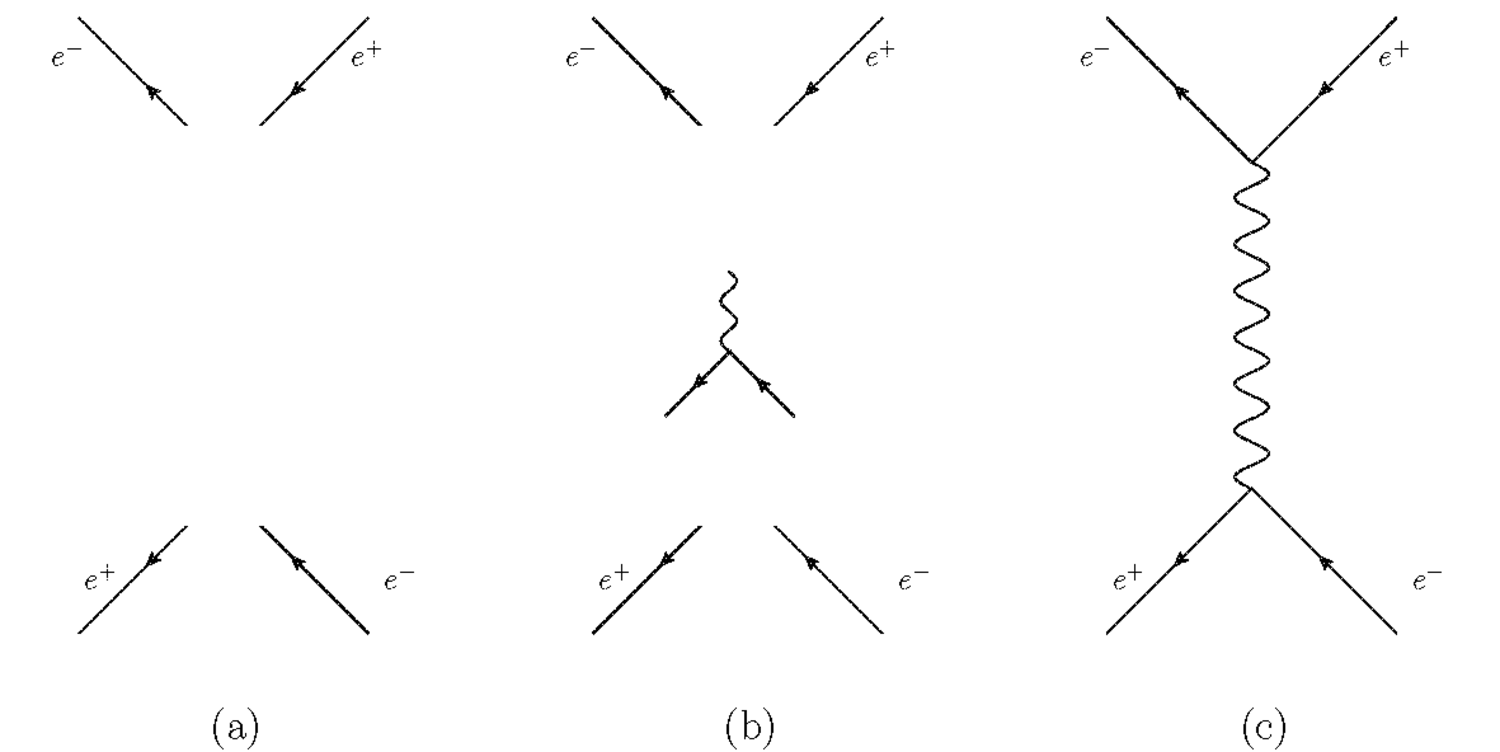
https://imgur.com/a/yYwCXTM Photon absorption in (c). The way I look at this diagram is that an e+ e- and photon get together, but what happens at the vertex? Where do the 3 particles go to?
[Link to image](http://puu.sh/msXF5/a9cc0335f9.jpg) As far as I am aware these diagrams aren't very detailed so I am missing something. The first one makes sense if you ignore momentum issues, but the second one makes little sense to me. So an excited electron shoots out a photon and then a brief amount of time later another photon appears and just happens to hit the electron? I'm guessing something more is going on?
cant answer “what type of correlation” in non strong ones because of this, also dont get how to determine an estimate taken from line of best bit to be “resonably accurate” or “inaccurate”
Figure 18.2: Feynman diagram for e−e+ → µ−µ+ in QED. ... Figure 18.7: Feynman diagrams contributing to Compton scattering at leading order in.










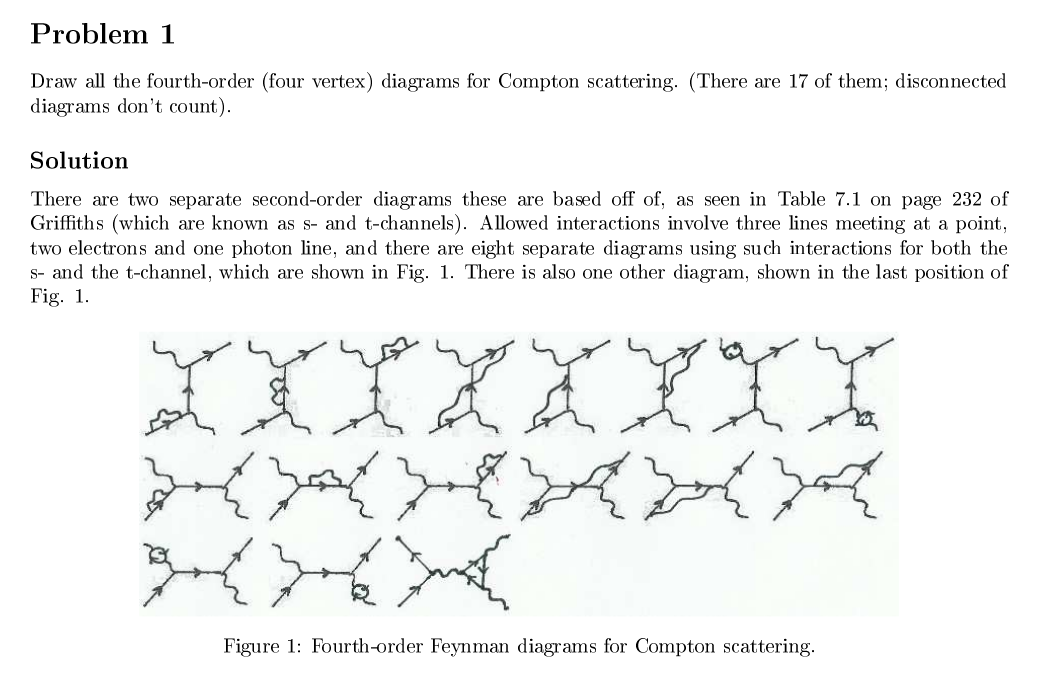















0 Response to "44 compton scattering feynman diagram"
Post a Comment