45 complete the enthalpy diagram for an ionic compound dissolving in water
Dec 11, 2019 · complete the enthalpy diagram for an ionic compound dissolving in water. Answer. + 20. Watch. 1. Enthalpy change of solution and Enthalpy change of Hydration When ionic compounds dissolve in water, there is usually a temperature change. Sometimes this is exothermic (e.g. dissolving calcium chloride) and sometimes endothermic (e.g. dissolving ammonium nitrate). The experiments are easy to carry out in a laboratory, and the usual equations ...
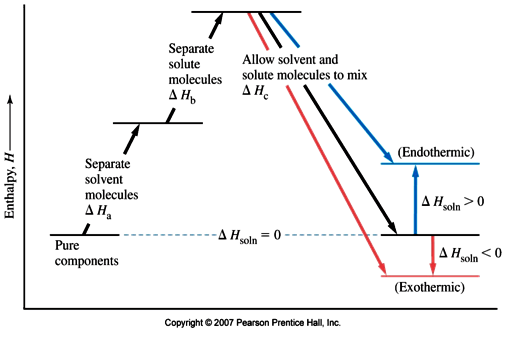
Dissolving ionic compounds in water When an ionic compound dissolves in water two processes occur 1. Energy has to be taken in to break up the lattice and separate the positive and negative ions. This is the lattice enthalpy 2. The ions become surrounded by solvent and bonds form - energy is released when these ions form bonds with water molecules.
Complete the enthalpy diagram for an ionic compound dissolving in water
Lithium Carbonate is the carbonate salt of lithium, a soft alkali metal, with antimanic and hematopoietic activities. Lithium interferes with transmembrane sodium exchange in nerve cells by affecting sodium, potassium-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase (Na+, K+-ATPase); alters the release of neurotransmitters; affects cyclic adenosine monophosphate concentrations; and blocks inositol ... 12.0 g of an impure sample of arsenious oxide (acting as acidic oxide) was dissolved in water containing 7.5g of sodium bicarbonate and resulting solution was diluted to 250 ml. 25 ml of this ... Water puffs up (increases volume) when it freezes; Ice floats. The heat of vaporization of water (540 cal/g) is over twice that of methanol (263 cal/g) and nearly ten times that of chloroform (59 cal/g). Water is a powerful solvent for ions and polar substances and is a poor solvent for non-polar substances.
Complete the enthalpy diagram for an ionic compound dissolving in water. Chemistry questions and answers. Complete the enthalpy diagram for an ionic compound dissolving in water B (g) Y (g) AHsolution B' (aq) Y- (aq) Ahydration Ht final exothermic H solute AHvaporization BY (S) Hinitial endothermic Hormation This reaction is. A complete enthalpy diagram will include starting energy, ending energy, and E a and delta H. This enthalpy diagram has starting products, ending products, delta H, and activation energy labeled... Complete the enthalpy diagram for an ionic compound dissolving in water: exothermic B7g) Y-(g) B(aq) Y-laq) endothermic AHvaporzation LHspute ] AHnydration ... 1 (a) The dissolving of an ionic compound in water is accompanied by an energy change, the enthalpy change of solution, ∆H sol. MgCl 2+2(s) + aq → Mg (aq) + 2Cl –(aq) Describe, in terms of bond breaking and bond making, what happens to the solid ionic lattice when an ionic compound dissolves in water.
It dissolved easily in water to give a solution of pH 12. When placed in a test-tube and heated in a roaring Bunsen flame, the compound melted after several minutes heating. What can be deduced from this record? A At least one of the recorded observations is incorrect. B The compound was magnesium chloride, MgCl 2. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Complete the enthalpy diagram for an ionic compound dissolving in water. A (g) X- (g) AHnydration AHusion exothermic AX (s) initial ??,aporization endothermic A (aq) x- (aq) A Hsolution Hrinal ??,ormation AHsolute This reaction is. Question: NAMI Served Complete the enthalpy diagram for an Ionic compound dissolving in water. 14 OH solucion A'lg) X-(g) A formation endothermic AHsolute ... Chemistry questions and answers. Complete the enthalpy diagram for an Ionic compound dissolving in water 14 (80045.22 A'lg) X- (g) endothermic Enthalpy, H AX (S) A' (aq) X (aq) Strusion Heral exothermic This reactions.
Lithium may also be absorbed via the lungs. A systemic resorption of lithium was shown in a study on 27 intensive care unit patients, who were mechanically ventilated with lithium-chloride-coated heat and moisture exchangers for at least 5 days. Serum lithium was non-detectable at the first measurement, whereas 0.01-0.05 mM appeared in the blood from the 1st to the 4th day. (ii) Give the name of the compound with the formula NH 4 NO 3 (b) Sodium oxide, Na 2 O, is an ionic compound. The sodium and oxide ions are held together by ionic bonds. (i) State the meaning of the term ionic bond. (ii) The diagram shows the arrangement of the electrons in a sodium atom and in an oxygen atom. Calculate the amount of heat required (in kilojoules) to heat 5.00 grams of water from -16.0 C to 11.0 c.-enthalpy of vaporization for water is 40.56 kJ/mol-enthalpy for fusion of water is 6.007 kJ/mol -specific heat for ice is 2.090 J/(gram x *C)-specific heat for water is 4.184 J/(gram x *C)-specific heat for steam is 2.030 J/(gram x *C) The enthalpy change for an ionic compound MX consisting of ions with single charges is represented as M+ (g) + X− (g) → MX (s) Na+ (g) + Cl- (g) Enthalpy Enthalpy of lattice dissociation Enthalpy...
Many ionic compounds are soluble in water, however, not all ionic compounds are soluble. Ionic compounds that are soluble in water exist in their ionic state within the solution. You will notice in Figure 7.2 that the sodium chloride breaks apart into the sodium ion and the chloride ion as it dissolves and interacts with the water molecules.
Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Complete the enthalpy diagram for an ionic compound dissolving in water. exothermic B* (9) Y- (g) AHvaporization AHsolute B* (aq) Y- (aq) endothermic Enthalpy, H Hfinal Anydration Arusion BY (s) A Hormation Hinitial AH solution This reaction is.
(b) Identify a compound from the table that can be dissolved in water to produce a basic solution. Write the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs to cause the solution to be basic. Either LiF or NaF is acceptable. F- + HF+ OH- 1 point is earned for choosing one of the correct compounds.
Below is an example of a reaction for the dissolution of an ionic compound in water. NaCl ( s) → Na + ( aq) + Cl - ( aq ) When a soluble ionic compound is placed in water, the solid is converted to the product of the dissolution reaction—the solid vanishes, converting to dissolved ions in solution. 3
4 *P44255A0420* 2 The solubility of a solid in water is the maximum mass of the solid that can dissolve in 100 g of water at a given temperature. An aqueous solution containing this maximum mass can be described as a saturated solution. The graph shows the solubilities of three solids at different temperatures.
Complete the enthalpy diagram for an ionic compound dissolving in water B (g) Y-(g) vaporization Δ Hsolution B(aq) Y (aq) fusion final endothermic exothermic AHformation BY(S) Hinitial AHnydration AHsolute This reaction is
PLAY. Match. Gravity. select all the options that represent the intermolecular forces broken or formed when NaCl is dissolved in water. Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. - some hydrogen bonding and dipole-dipole interactions in water are broken. - ionic bonds are broken in the solute.
When some substances are dissolved in water, they undergo either a physical or a chemical change that yields ions in solution. These substances constitute an important class of compounds called electrolytes.Substances that do not yield ions when dissolved are called nonelectrolytes.If the physical or chemical process that generates the ions is essentially 100% efficient (all of the dissolved ...
Many ionic compounds are soluble in water, however, not all ionic compounds are soluble. Ionic compounds that are soluble in water exist in their ionic state within the solution. You will notice in Figure 7.2 that the sodium chloride breaks apart into the sodium ion and the chloride ion as it dissolves and interacts with the water molecules.
Chemistry questions and answers. Complete the enthalpy diagram for an ionic compound dissolving in water. AHfusion A* (g) X- (g) AHformation AHsolute Hinitial AX (S) Enthalpy, H AHsolution A Hvaporization exothermic A* (aq) X- (aq) Hrinal endothermic AHhydration This reaction is.
(ii) The temperature change in this experiment shows that dissolving lithium iodide in water to form lithium iodide solution is an exothermic process. Complete the energy level diagram to show the position of the lithium iodide solution. Label the diagram to show ûH, the molar enthalpy change. (2) (Total for Question 5 = 11 marks)
Ionic compounds are often soluble in water, because the attractions formed between ions and water are frequently strong enough to make their solution either exothermic or only slightly endothermic. For example, the solution of sodium hydroxide is exothermic, and the solution of sodium chloride is somewhat endothermic.
The diagram represents the solution process (lattice energy, heat of hydration, and heat of solution) for an ionic compound dissolving in water. ht Arrow Brepresents enthalpy of mixing and is exothermic.
Water puffs up (increases volume) when it freezes; Ice floats. The heat of vaporization of water (540 cal/g) is over twice that of methanol (263 cal/g) and nearly ten times that of chloroform (59 cal/g). Water is a powerful solvent for ions and polar substances and is a poor solvent for non-polar substances.
12.0 g of an impure sample of arsenious oxide (acting as acidic oxide) was dissolved in water containing 7.5g of sodium bicarbonate and resulting solution was diluted to 250 ml. 25 ml of this ...
Lithium Carbonate is the carbonate salt of lithium, a soft alkali metal, with antimanic and hematopoietic activities. Lithium interferes with transmembrane sodium exchange in nerve cells by affecting sodium, potassium-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase (Na+, K+-ATPase); alters the release of neurotransmitters; affects cyclic adenosine monophosphate concentrations; and blocks inositol ...

0 Response to "45 complete the enthalpy diagram for an ionic compound dissolving in water"
Post a Comment