41 energy diagram catalyzed vs uncatalyzed reaction
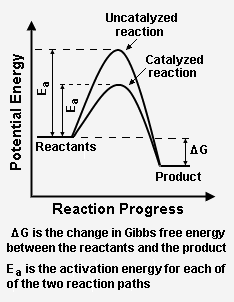
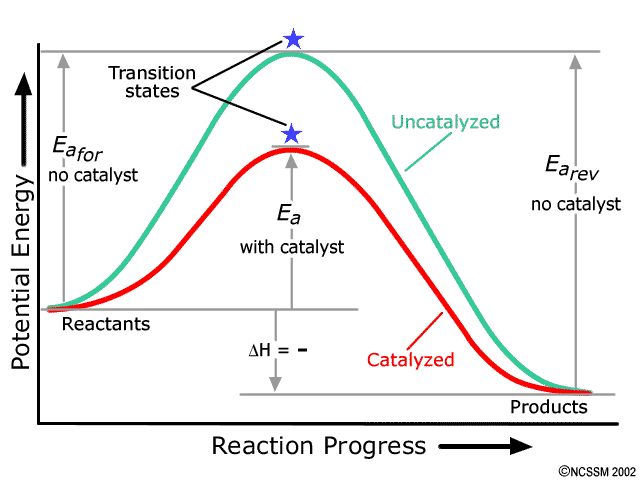
Media Portfolio - wps.ablongman.com Reaction coordinate diagrams for catalyzed vs. uncatalyzed reaction involving change of mechanism. Notes This figure shows the case where catalysis occurs because the catalyst lowers the energy of the activated complex by changing the reaction mechanism. Section 13.3: The Rate of a Reaction The black line represents energy changes in an uncatalyzed reaction. The colored line shows the energy changes for the same reaction in the presence of a catalyst. A catalyst can provide such an alternative pathway. A catalyst is a substance that, when added to a reaction mixture, increases the rate of the overall reaction yet is recovered ...
Energy Reaction Diagram and Similar Products and Services ... Reaction Coordinate Diagrams great butane.chem.uiuc.edu. The reaction coordinate diagram for the ozone photolysis reaction is a little different from those above because this is an endothermic reaction.Together, the products O 2 and atomic O, have a higher energy than the reactant O 3 and energy must be added to the system for this reaction.

Energy diagram catalyzed vs uncatalyzed reaction
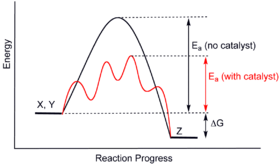
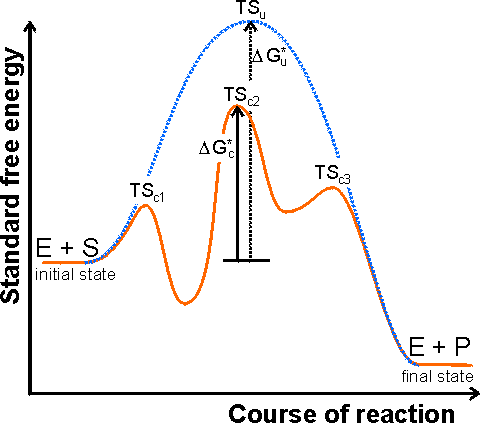
Catalysis | Chemistry for Majors - Lumen Learning The uncatalyzed reaction proceeds via a one-step mechanism (one transition state observed), whereas the catalyzed reaction follows a two-step mechanism (two transition states observed) with a notably lesser activation energy. This difference illustrates the means by which a catalyst functions to accelerate reactions, namely, by providing an ... Energy Diagram Catalyzed Vs Uncatalyzed Reaction Below is an energy diagram illustrating the difference in a catalyzed reaction versus an uncatalyzed reaction. Label the energy diagram and answer the question that follows% (1). Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher ... 16.3c Drawing the reaction energy diagram of a catalyzed ... About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
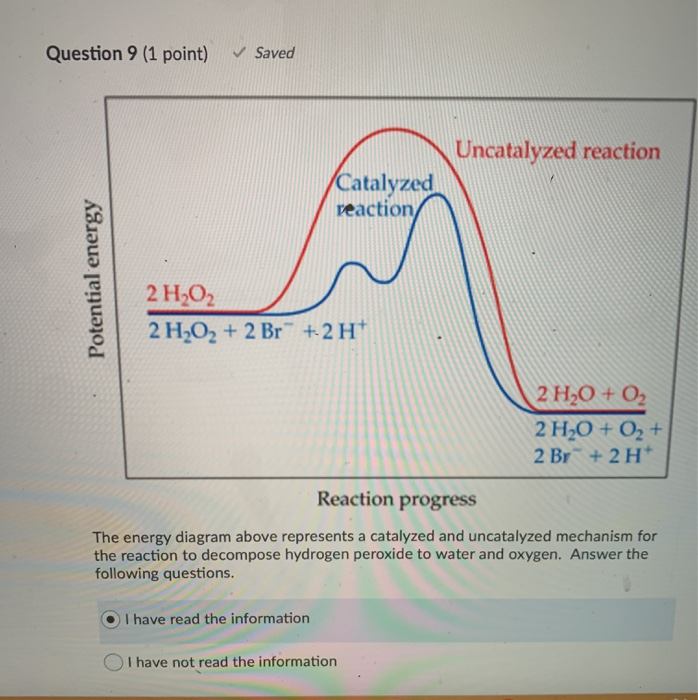
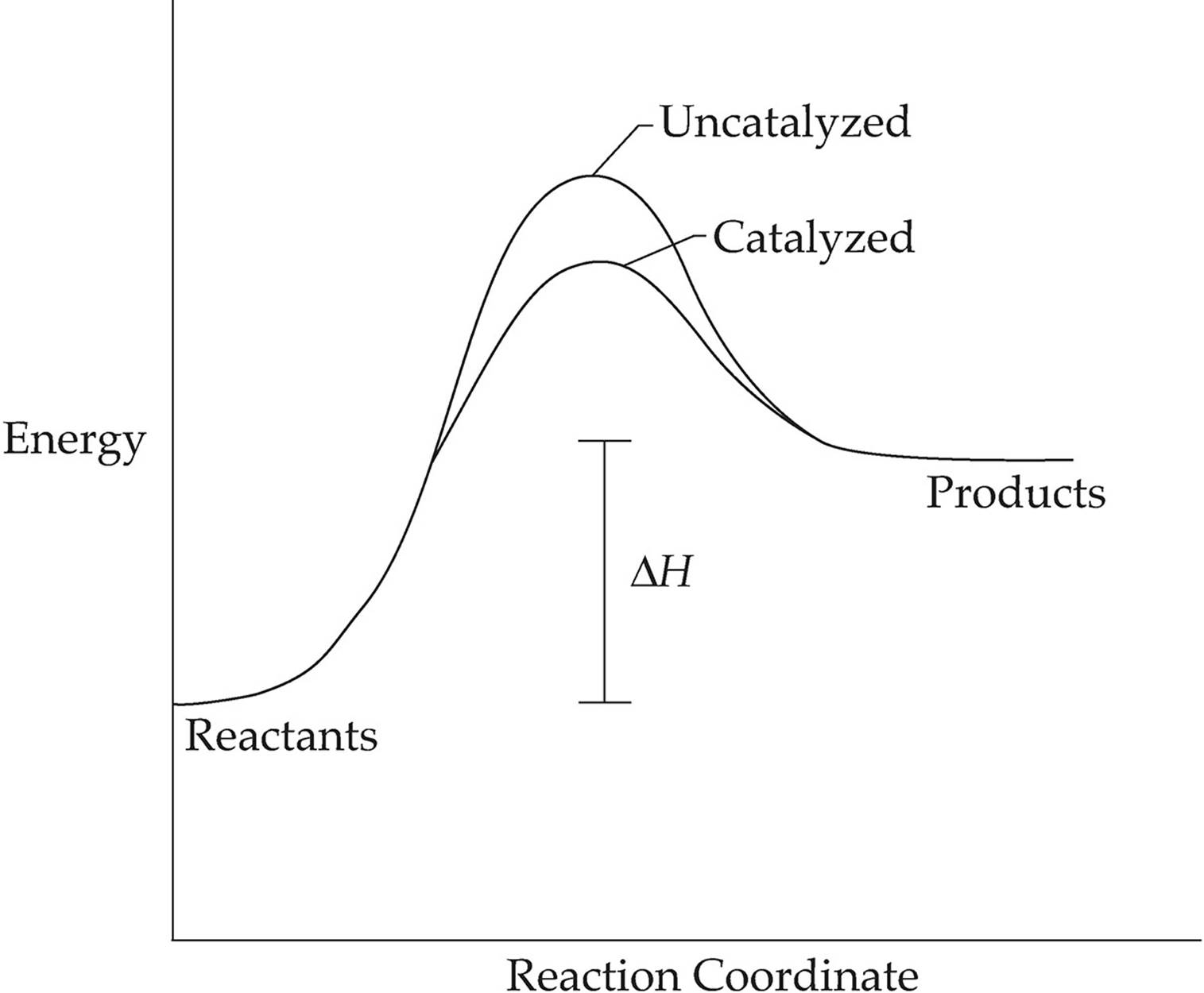
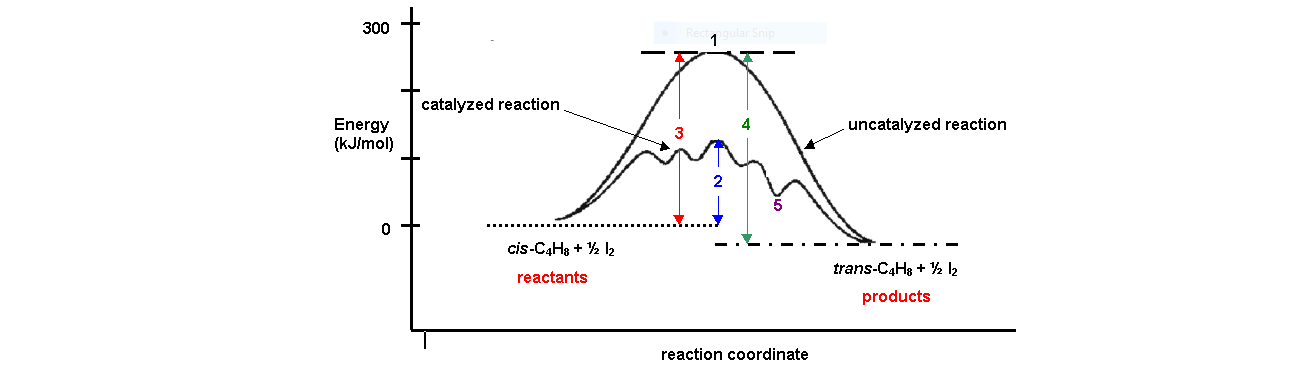
Energy diagram catalyzed vs uncatalyzed reaction. 15.7 Catalysis - Introductory Chemistry - 1st Canadian ... Catalyzed and Uncatalyzed Reaction Pathways Potential energy diagrams of catalyzed and uncatalyzed reaction pathways. In the catalyzed pathway, an iodine atom is generated that reacts with cis-but-2-ene to produce a reaction intermediate that has broken its carbon-carbon double bond and formed a new C-I bond and a radical (Figure 15.16 "But-2 ... Energy and enzymes | Biological Principles Energy diagram of enzyme-catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions, from Wikipedia The peak of this energy diagram represents the transition state: an intermediate stage in the reaction from which the reaction can go in either direction. Solved 1) Draw the reaction energy diagram (enthalpy vs ... Question: 1) Draw the reaction energy diagram (enthalpy vs reaction time) for the uncatalyzed exothermic reaction A + B => C + D that shows reactants, products, Ea, and delta H. On the same diagram, draw the catalyzed exothermic reaction a) is the catalyzed Ea larger or smaller than the uncatalyzed Ea? why? Difference between catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions ... Catalyzed reaction has a lower activation energy because there is an enzyme present in the reaction. Uncatalyzed reaction has a higher activation energy because there is no enzyme present in the ...
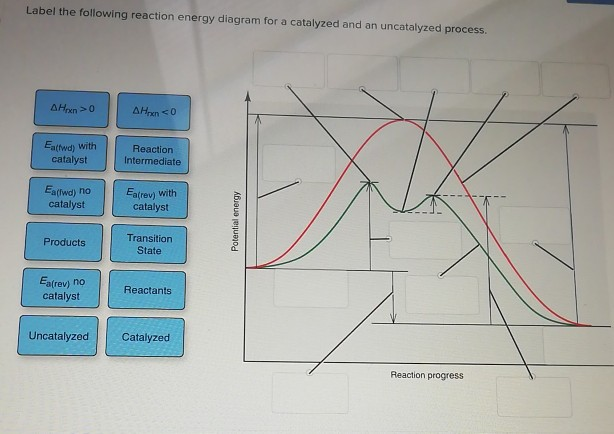
Potential Energy Diagram of Catalyzed and Uncatalyzed ... Analyzing the potential energy diagram of a regular/uncatalyzed and a catalyzed (adding a catalyst) reaction. Remember that the 🔼H of reaction remains the s... PDF Chem 109 C Bioorganic Compounds - UC Santa Barbara Draw energy diagrams to compare and classify catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions: note: the reaction rate is the rate of the slowest step. CATALYSIS ... catalyzed vs uncatalyzed reaction (review Section 5.13) 12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry - opentextbc.ca A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. This graph compares the reaction coordinates for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation. 33 Label The Following Reaction Energy Diagram For A ... The solid line in the energy diagram represents changes in energy as the reactant is converted to product under standard conditions. Which equation below indicates how the presence of an enzyme affects the activation energy of the reaction catalyzed versus uncatalyzed. The mechanism may be different for a catalyzed reaction reaction vs the ...
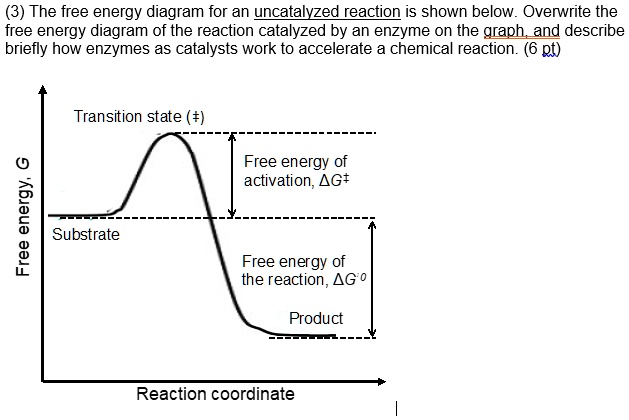
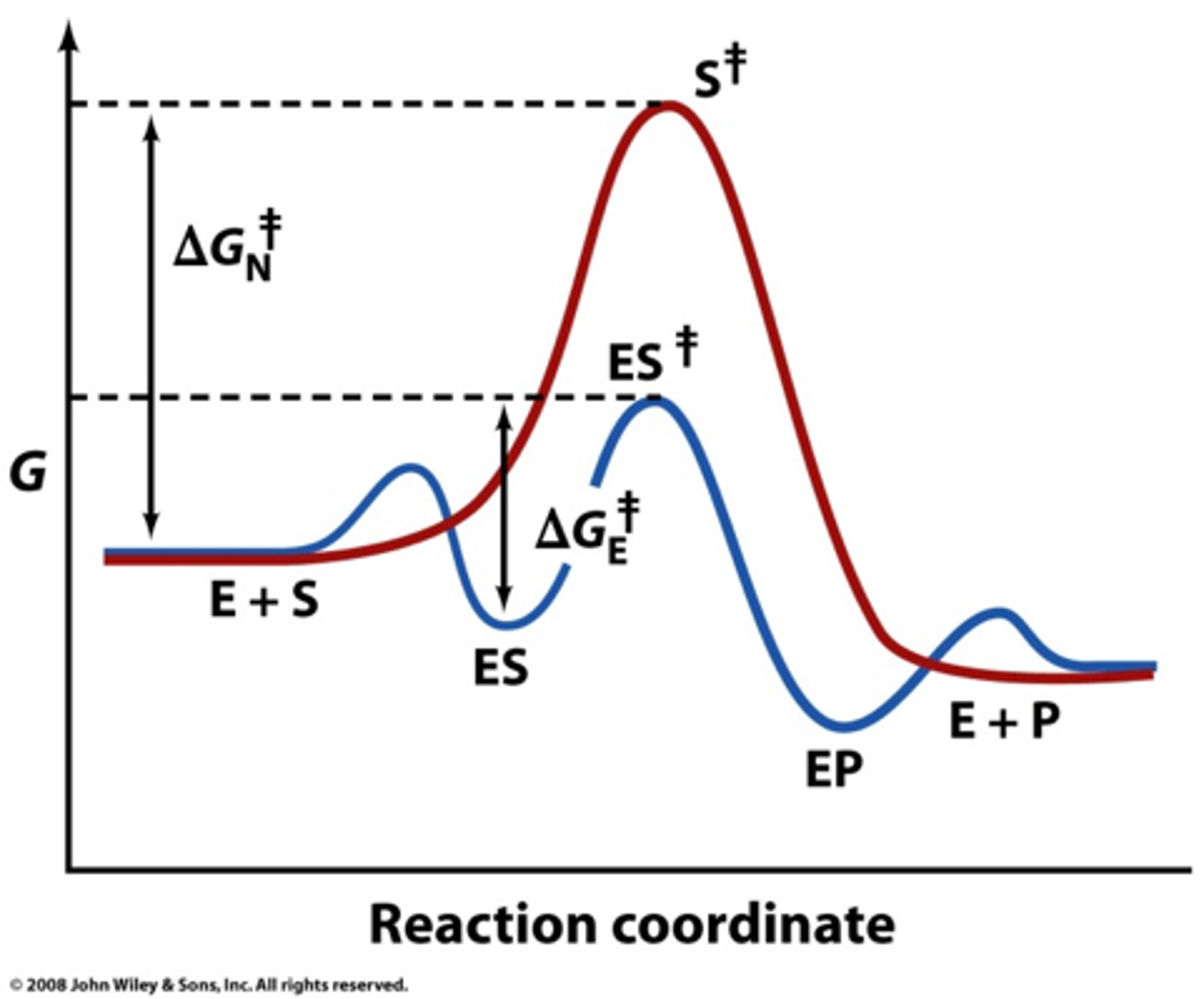
Why does a catalyst cause a reaction to speed up? | Socratic Catalyst lowers the activation energy The following Transition State Diagram shows a catalyzed reaction vs an uncatalyzed reaction. In other words, the catalyzed reaction has a lower activation energy 'hill' to climb than the uncatalyzed reaction. CHEM 440 - Enzyme kinetics - Gonzaga University Left: Reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction representing the mechanistic model we are considering. The free energy of activation, Δ G ‡, which for our present purposes can be considered as equivalent to activation energy, is much lower for the catalyzed reaction compared with the uncatalyzed reaction: Potential Energy Diagrams - Kentchemistry.com A potential energy diagram plots the change in potential energy that occurs during a chemical reaction. This first video takes you through all the basic parts of the PE diagram. Sometimes a teacher finds it necessary to ask questions about PE diagrams that involve actual Potential Energy values. 41 label the following reaction energy diagram for a ... B the s where v0 vmax. The mechanism may be different for a catalyzed reaction reaction vs Below is an energy diagram illustrating the difference in a catalyzed reaction versus an uncatalyzed reaction. Draw and label a reaction coordinate diagram for an uncatalyzed reaction s p and the same reaction catalyzed by an enzyme e.
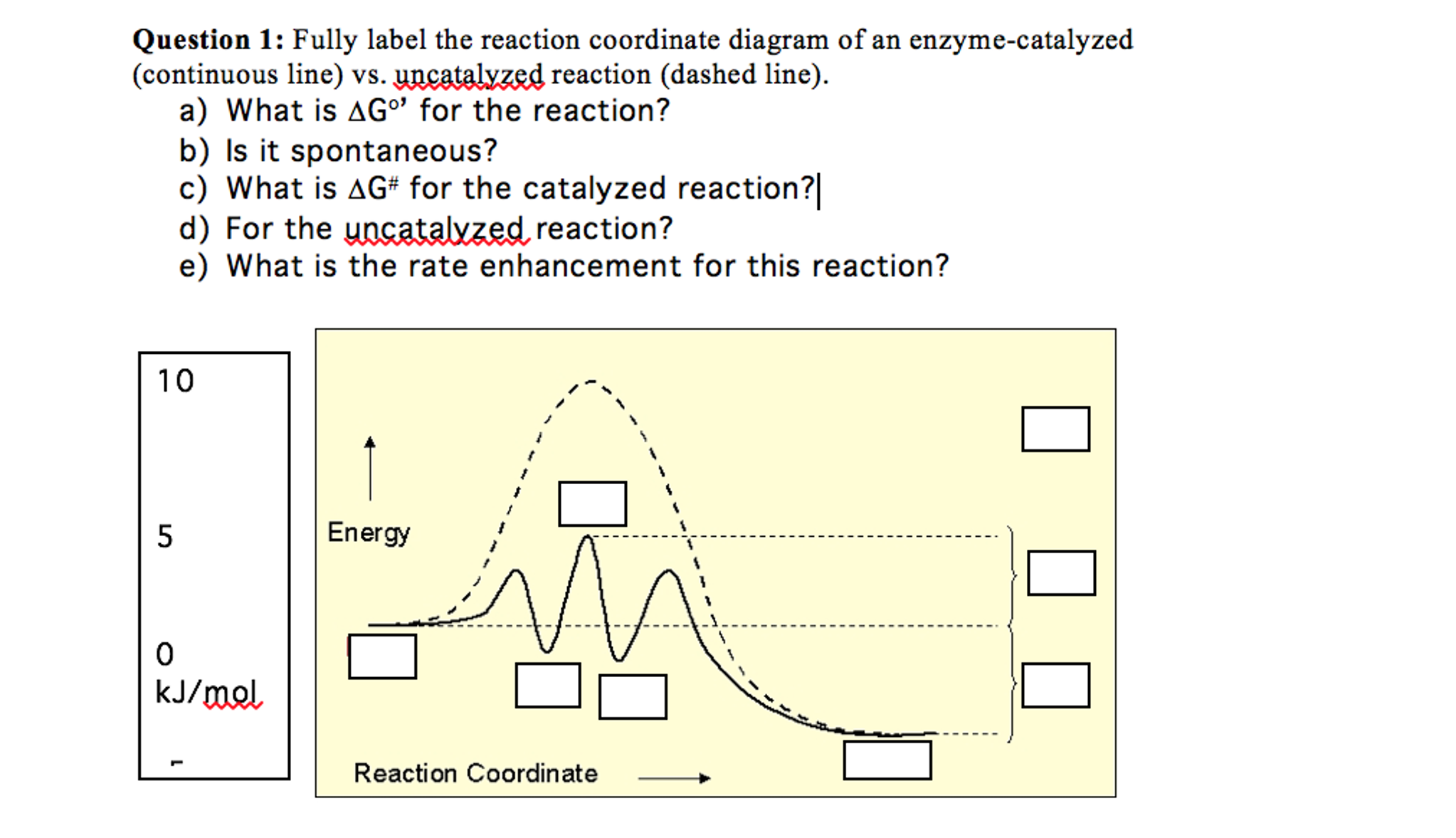
Answered: Draw a graph of free energy G (y-axis)… | bartleby Draw a graph of free energy G (y-axis) vs reaction progress (x-axis) that illustrates what the kinase is doing in terms of the free energy by showing (i) the substrate (also label what the substrate is [it's name]), (ii) the products (also give the name of the products), (iii) draw and label the uncatalyzed and catalyzed reactions, and be sure that the parts of the graph are properly labeled..
Activation energy and catalysis anwer key 1i. Draw an energy vs reaction coordinate diagram to illustrate a reaction in which the energy of the products is greater than the energy of the reactants. Label all quantities as per Fig. 1. See diagram (3) in sample exercise 14.10 on pg 595 of Brown and LeMay, 11th ed.
D37.2 Catalysts and Reaction Mechanisms - Chemistry 109 ... D37.2 Catalysts and Reaction Mechanisms A catalyst increases the rate of a reaction by altering the mechanism, allowing the reaction to proceed via a pathway with lower activation energy than for the uncatalyzed reaction.A catalyzed mechanism must involve at least two steps, one where the catalyst interacts with a reactant to form an intermediate substance, and one where the intermediate then ...
Answered: (a) Draw an activation energy diagram… | bartleby Science Biology Q&A Library (a) Draw an activation energy diagram for this reaction under catalyzed and uncatalyzed conditions and explain what it means for the activation energy to be lowered from 18 to 13 kcal/mol by ferric ions but from 18 to 7 kcal/mol by catalase. Please draw in the space provided below. (b) Suggest two properties of catalase that make it a more suitable intracellular ...
Solved Fully label the reaction coordinate diagram of an ... free energy change for catalyzed reaction is: g (final)- g (initial)… View the full answer Transcribed image text : Fully label the reaction coordinate diagram of an enzyme-catalyzed (continuous line) vs. uncatalyzed reaction (dashed line).
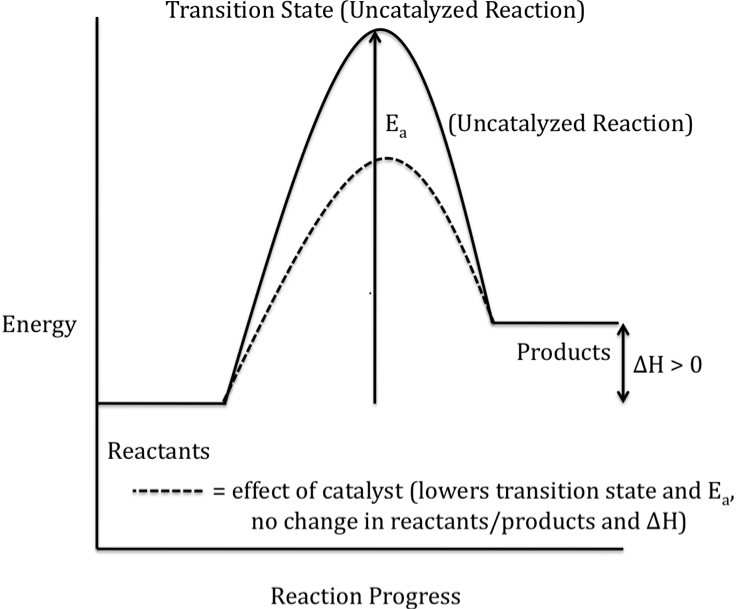
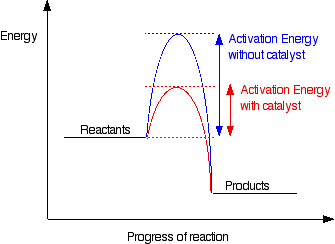
What is the potential energy diagram for catalyzed and ... Answer: The overall diagram will depend on whether the reaction is endothermic (final H is higher then initial H) or exothermic (final H is lower than initial H) BUT: Catalysed reactions lower the activation energy - the hump that needs to be overcome for the reaction to proceed. (Catalysts ofte...
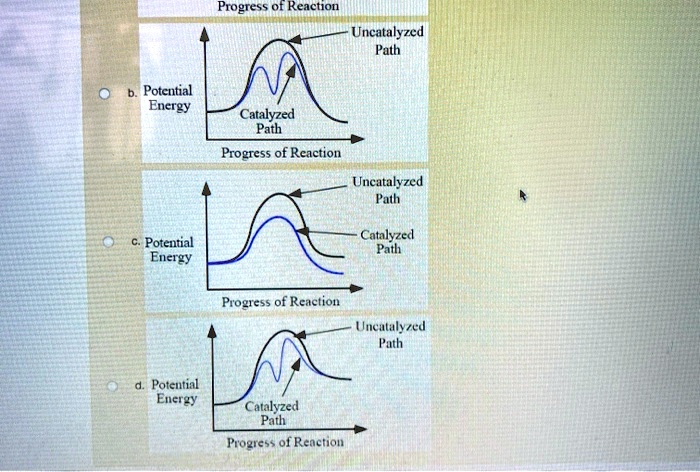
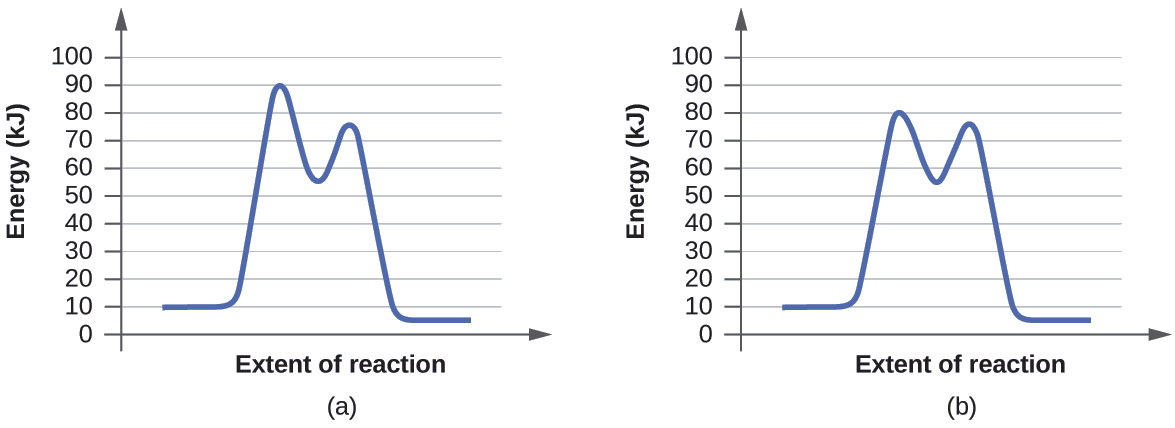
12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry 2e - OpenStax The catalyzed reaction is the one with lesser activation energy, in this case represented by diagram b. Check Your Learning Reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. Both reactions involve a two-step mechanism with a rate-determining first step. Compute activation energies for the first step of each ...
Kubota Wiring Diagram - goldingfarmsfoods.com Wiring Diagrams Energy Diagram Catalyzed Vs Uncatalyzed Reaction Sep 22, 2016 · *This diagram shows the simple wiring diagram for negative ground Delco SI series alternators.* The ignition switch is most commonly powered from the starter battery stud, but source may vary depending on application.
Energy diagrams for enzyme‐catalyzed reactions: Concepts ... The energy diagram for a reaction model consisting of one enzyme, one substrate, and one product is depicted in many books where it is compared with that for the uncatalyzed reaction. The survey of several Biochemistry textbooks reveals a high diversity of profiles for the same process.
Energy Diagram Catalyzed Vs Uncatalyzed Reaction Label the energy diagram and answer the question that follows% (1). The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide is exothermic. The reaction is catalyzed by iodide ion. The equation for the uncatalyzed reaction is. 2 H 2 O 2 (l) 2 H 2 O (l) + O 2 (g) Sketch a possible graph for this reaction, first without a catalyst and then with a catalyst.
Catalysts Definition and How They Work - ThoughtCo A catalyst is a chemical substance that affects the rate of a chemical reaction by altering the activation energy required for the reaction to proceed. This process is called catalysis. A catalyst is not consumed by the reaction and it may participate in multiple reactions at a time. The only difference between a catalyzed reaction and an uncatalyzed reaction is that the activation energy is ...
16.3c Drawing the reaction energy diagram of a catalyzed ... About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ...
Energy Diagram Catalyzed Vs Uncatalyzed Reaction Below is an energy diagram illustrating the difference in a catalyzed reaction versus an uncatalyzed reaction. Label the energy diagram and answer the question that follows% (1). Catalyzed reactions have a lower activation energy (rate-limiting free energy of activation) than the corresponding uncatalyzed reaction, resulting in a higher ...
Catalysis | Chemistry for Majors - Lumen Learning The uncatalyzed reaction proceeds via a one-step mechanism (one transition state observed), whereas the catalyzed reaction follows a two-step mechanism (two transition states observed) with a notably lesser activation energy. This difference illustrates the means by which a catalyst functions to accelerate reactions, namely, by providing an ...






















0 Response to "41 energy diagram catalyzed vs uncatalyzed reaction"
Post a Comment