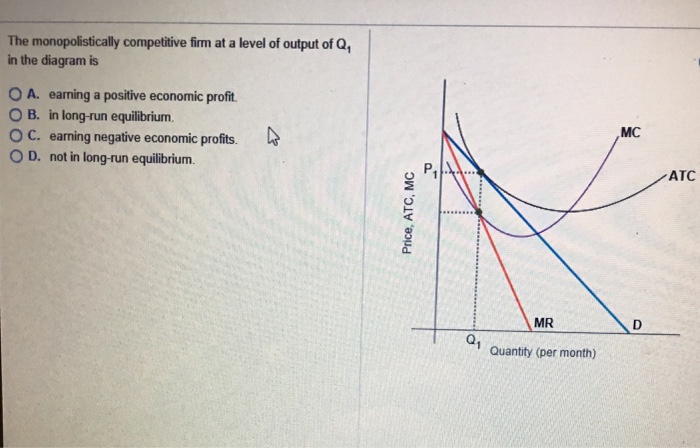
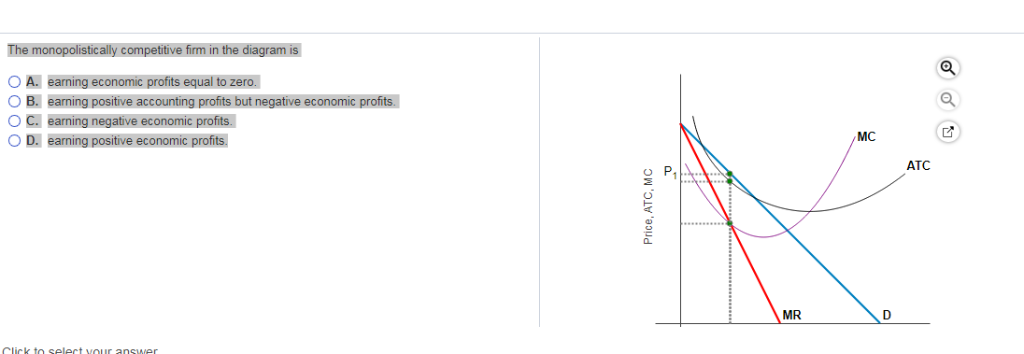
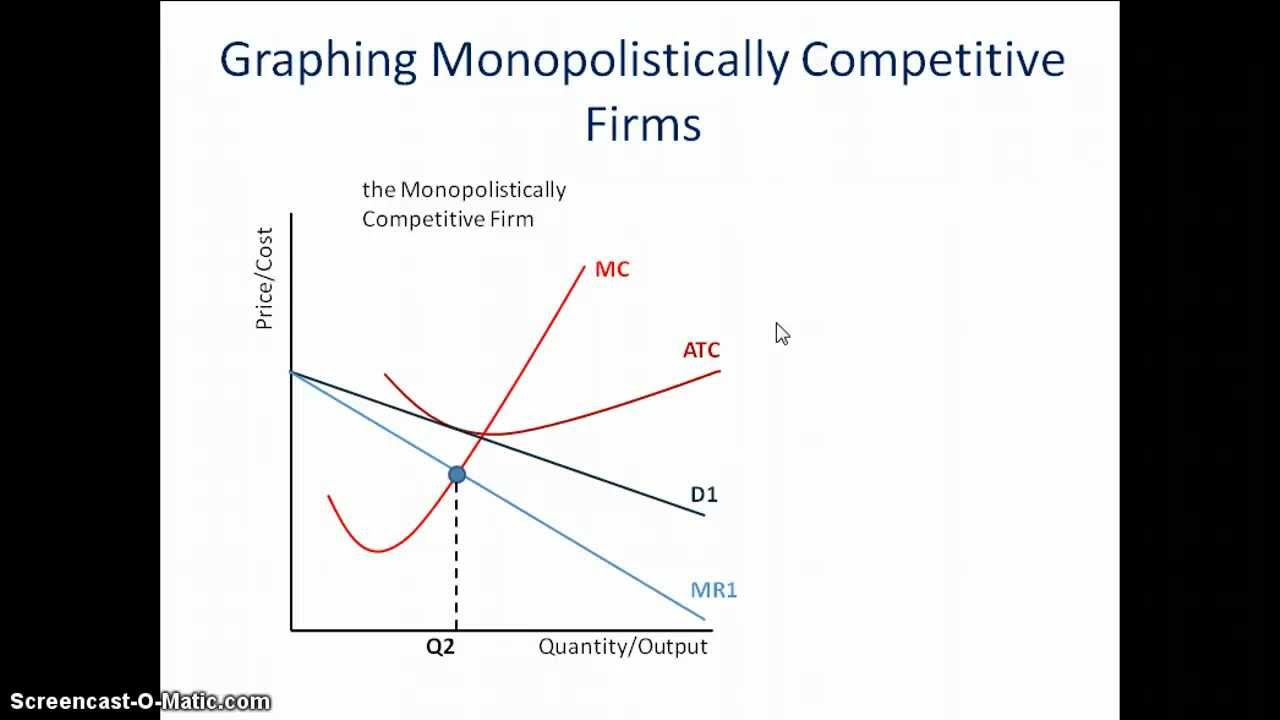
41 the monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is
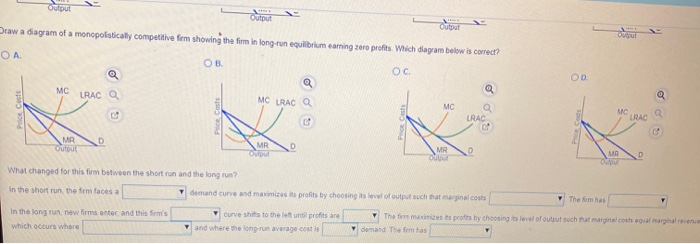
Suppose that a typical firm in a monopolistically competitive... 51. A monopolistically competitive firm is producing an output level where marginal revenue. 17 # 5) Sparkle is one firm of many in the market for toothpaste, which is in long-run equilibrium. a. Draw a diagram showing Sparkle's demand curve, marginal revenue curve, average cost curve, and marginal... AmosWEB is Economics: Encyclonomic WEB*pedia A monopolistically competitive firm is a price maker, with some degree of control over price. Once again, unlike perfect competition, a monopolistically The second of the folds is the pursuit of profit maximization by each firm in the industry. This ensures that firms produce the quantity of output that...
How Do Monopolistically Competitive Market Firms... - Chron.com The "Monopolistic Competitive" Model. This model of market competition has several crucial features. The products produced must almost be identical. This model holds that profits are made in the short term. They are based on convincing the market that their products are different in type, if not in price.
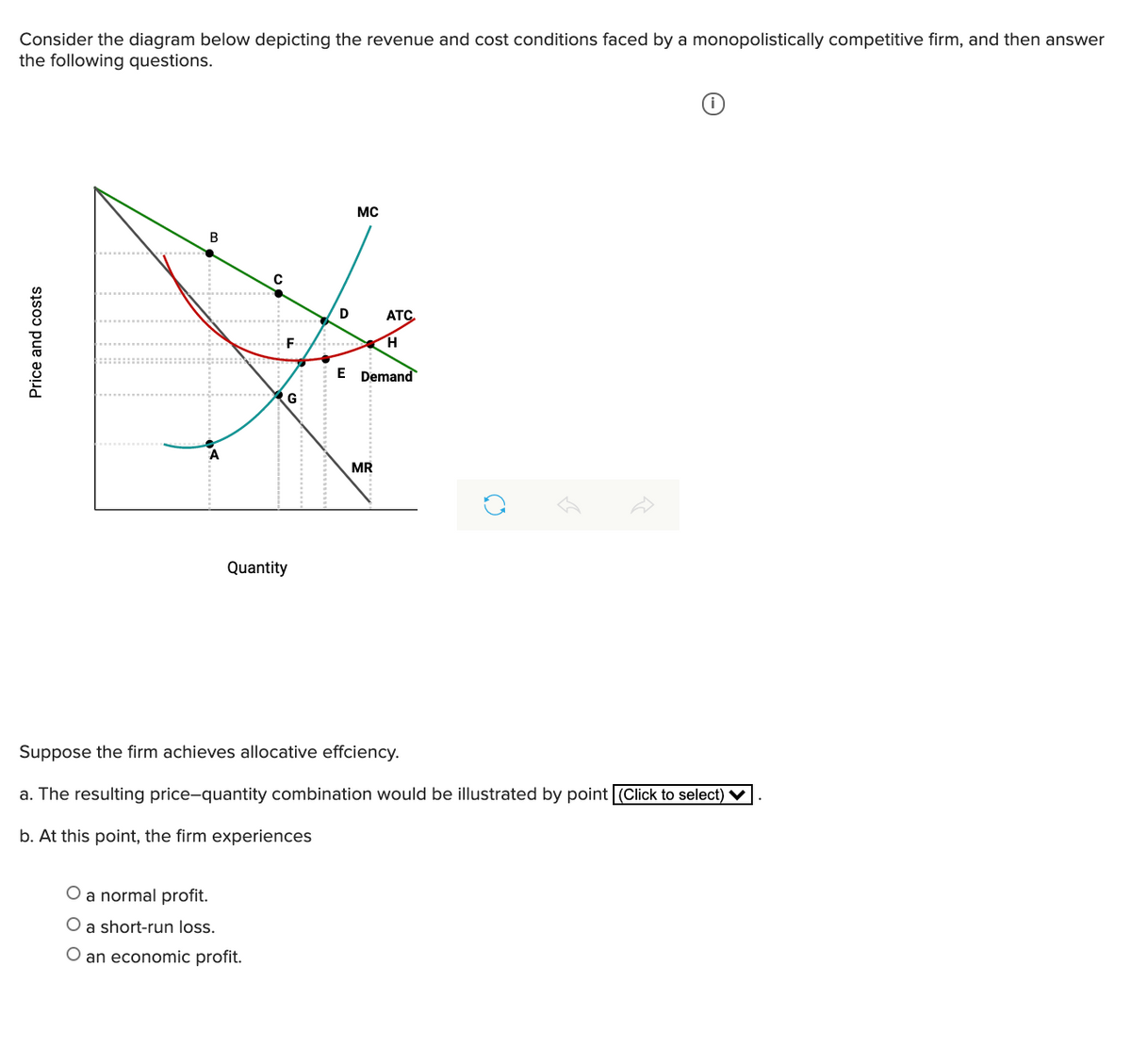
The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is
Equilibrium of a Firm under Monopolistic Competition Note that a monopolistically competitive firm always operates somewhere to the left of the minimum point of its AC curve. Hence a perfectly competitive market is 'efficient' in the sense that resources are allocated efficiently. Society gets larger output and consumers get output at a low price. Key Differences Between Monopoly and Monopolistic Competition Monopolistic competition is prevalent in the manufacturing industry, such as tea, shoes, refrigerators, toothpaste, TV sets, etc. No competition exist in a monopoly market while stiff competition due to non-price competition exists between firms the monopolistically competitive market. Monopolistic Competition - definition, diagram and... - Economics Help Firms are allocatively and productively inefficient. Diagram monopolistic competition short run. Some firms will be better at brand differentiation and therefore, in the real world, they will be able to make Many industries, we may describe as monopolistically competitive are very profitable, so...
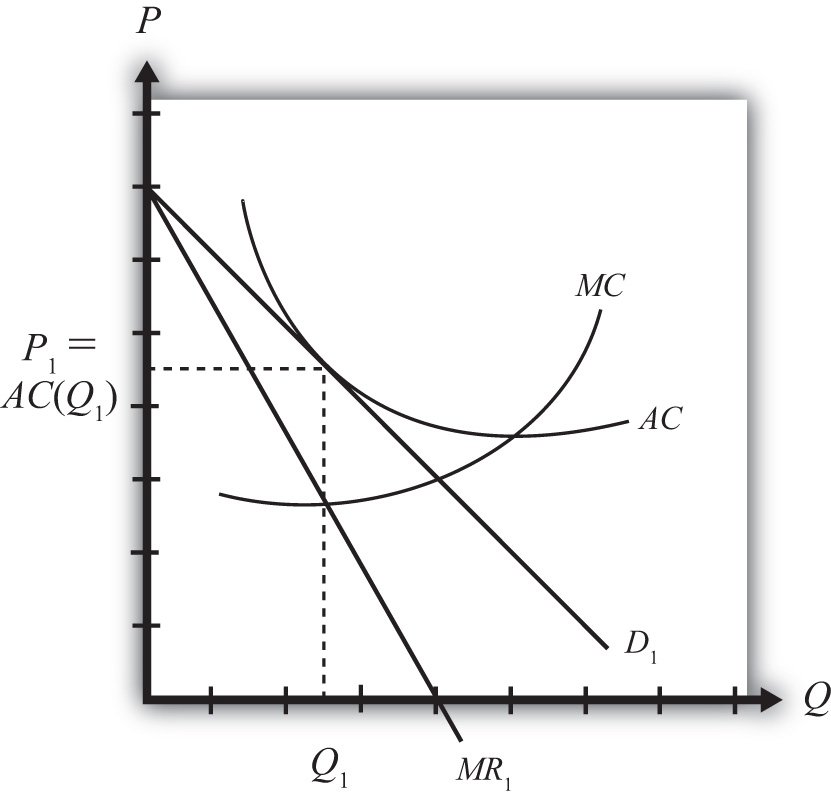
The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is. Chapter 13 Study Set - Subjecto.com firms will engage in nonprice competition. A monopolistically competitive firm's marginal revenue curve: PDF Topic 2 : Price System and the Firms in a monopolistically competitive market compete using non-price competition. Since firms do not fully exploit their factors, there is excess capacity in the market. This makes firms productively inefficient (also note: the firm does not operate at the bottom of the AC curve). What are examples of monopolistically competitive firms? - Quora We define a market as monopolistically competitive if the following things are true: 1. There are many firms 2. Each firm produces a different product, and the firm has a monopoly for the sale of that ... Pretty much any market in which brands are important is going to be in monopolistic competition. 9.2 Market considerations for monopolistically competitive firms A monopolistically competitive firm perceives a demand for its goods that is an intermediate case between monopoly and competition. The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price in much the same way as a monopolist.
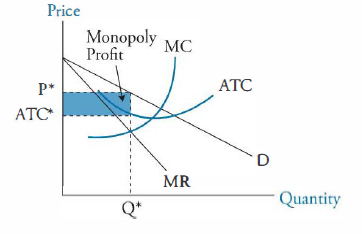
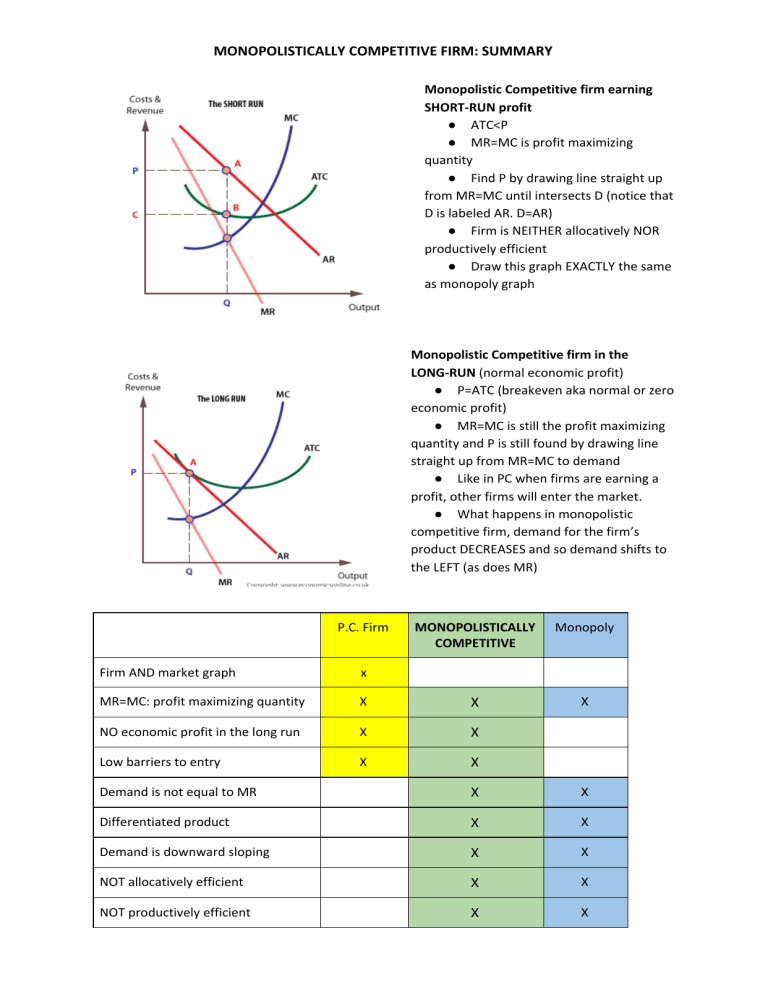
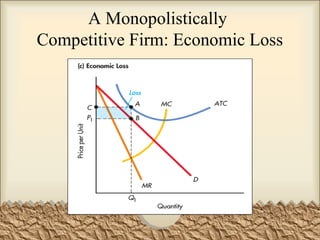
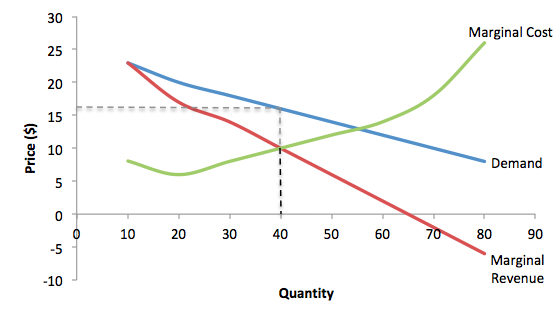
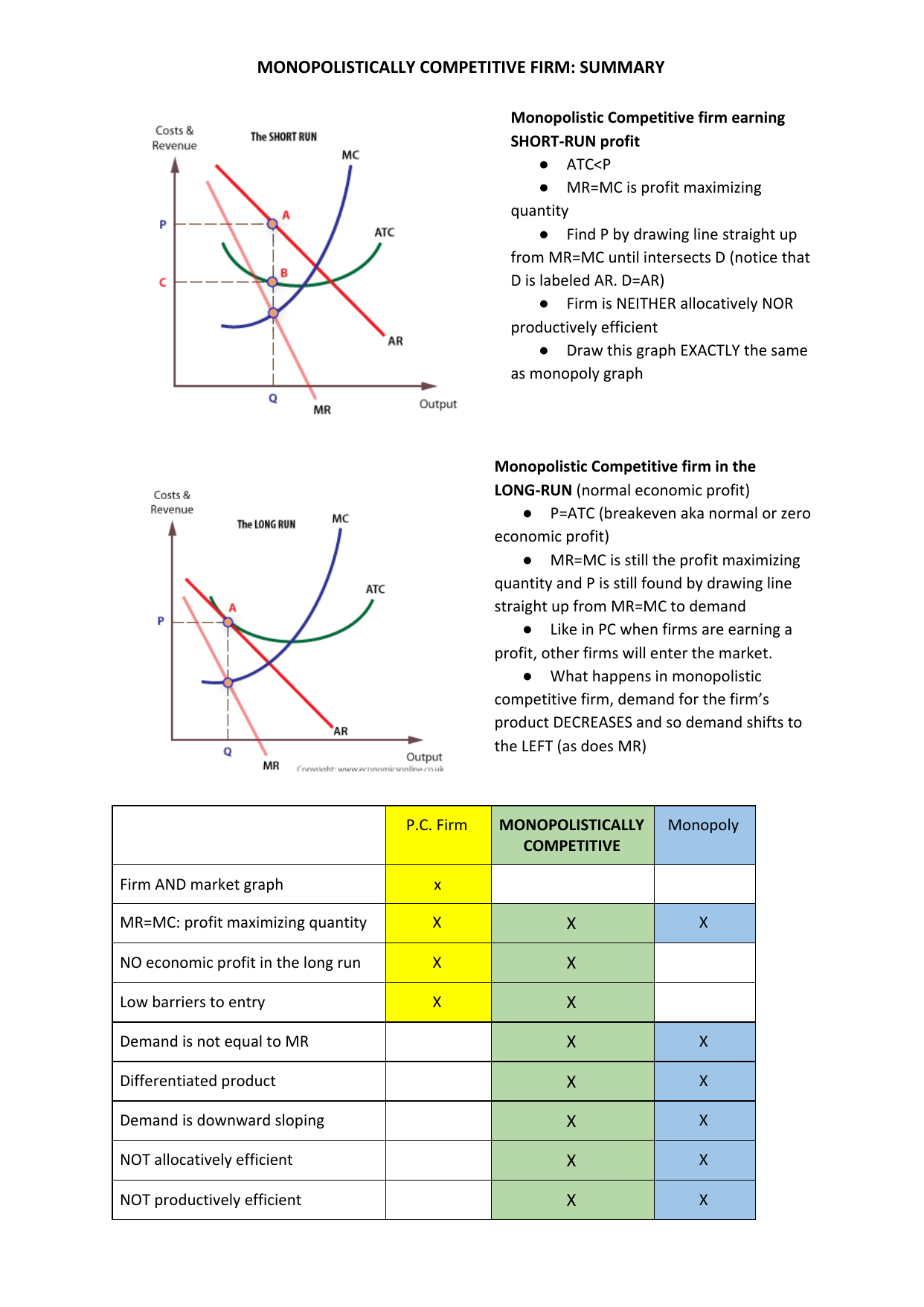
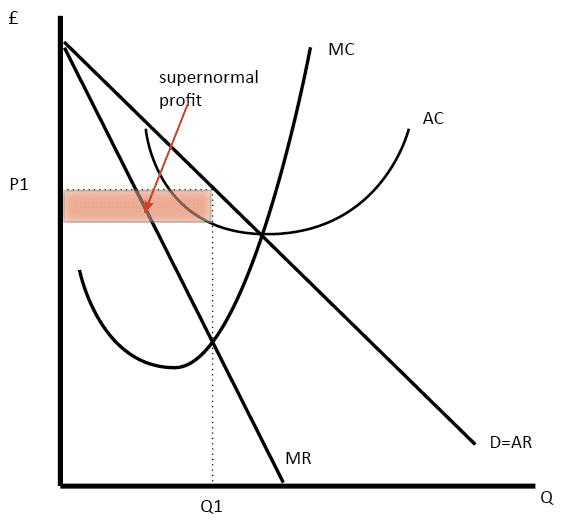
Monopolistic Competition: Short-Run Profits and Losses, and... In the short run, a monopolistically competitive firm maximizes profit or minimizes losses by producing that quantity where marginal revenue = marginal cost. Note in the above diagram that firms would lose money if they produced more to achieve either allocative or productive efficiency. Monopolistic Competition | Boundless Economics Unlike in perfect competition, firms that are monopolistically competitive maintain spare capacity. Models of monopolistic competition are often used to model One of the key similarities that perfectly competitive and monopolistically competitive markets share is elasticity of demand in the long-run. 10.1 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Economics A monopolistically competitive firm perceives a demand for its goods that is an intermediate case between monopoly and competition. The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price in much the same way as a monopolist. Monopolistic competition - Wikipedia Long-run equilibrium of the firm under monopolistic competition. The firm still produces where marginal cost and marginal revenue are equal; however Monopolistically competitive markets have the following characteristics: There are many producers and many consumers in the market, and no...
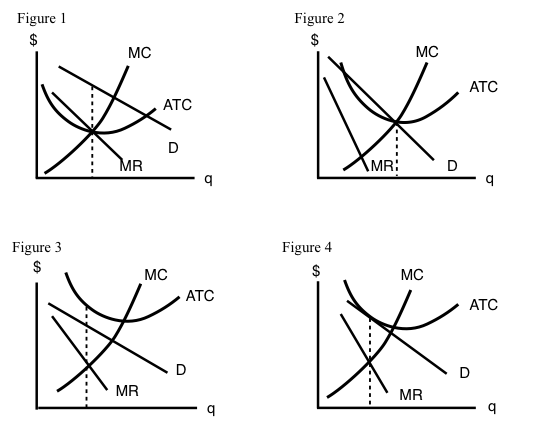
Monopolisitc competition Each firm in a monopolistically competitive market is like a monopoly. Thus, the monopolistically competitive firm follows a monopolit's rule for profit maximation: it chooses the quantity at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost and then uses its demand curve to find the... Many firms - There are many firms in monopolistically competitive... In essence, monopolistically competitive markets are named as such because, while firms are competing with one another for the same group of customers to some degree In addition, firms in monopolistically competitive markets suffer from "excess capacity," which means that they are not... Monopolistic Competition Definition Monopolistic competition characterizes an industry in which many firms offer products or services that are similar, but not perfect, substitutes. The term was first used in the 1930s by economists Edward Chamberlain and Joan Robinson, to describe the competition between firms with similar, but not... 8.4 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Microeconomics The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price similar to the way that a monopolist does. 4. Which of the four diagrams illustrates a monopolistically competitive firm able to make positive economic profits in the short run?
The demand curve faced by a monopolistically competitive firm is The demand curve of monopolistic competition is elastic because although the firms are selling differentiated products, many are still Answer added by Muhammad Sohail, Senior Design Engineer , Saudi Electricity Company 6 years ago. · Monopolistically competitive firm in demand curve faced...
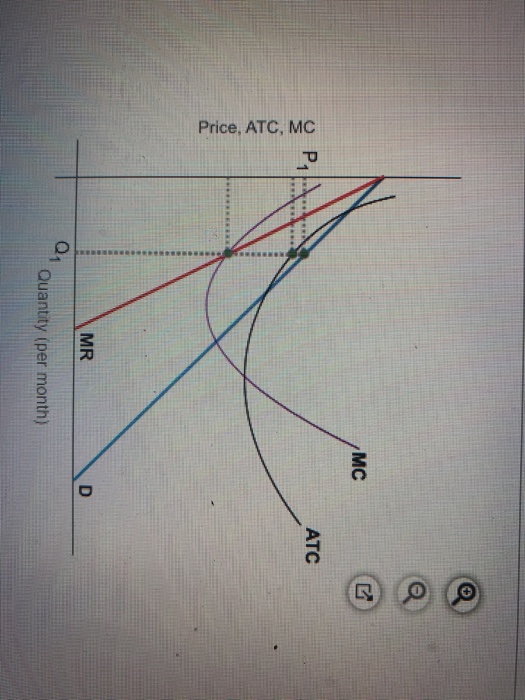
Chapter 8 Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and... 41 Profit-Maximizing Monopolistically Competitive Firm In Action Monopolistic Competition Profit-Maximizing Monopolistically Competitive 46 Long-Run and Monopolistic Competition In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms produce a level of output such that: > =...
chapter: Solution Monopolistic Competition and Product Differentiation If they are not monopolistically competitive firms, are they monopolists, oligopolists, or perfectly competitive firms? a. A local band His demand,, and average total cost curves are shown in the accompanying diagram. P P P Profit D P Q P MR P Since this hairdresser (and all other hairdressers)...
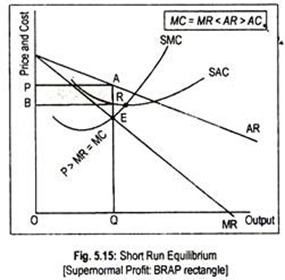
Econ 212-Micro Chapter 13 Quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Percentage of total industry sales accounted for by the largest firms in the industry. Purely competitive firms, monopolistically competitive firms, and pure monopolies all earn positive economic profits in the...
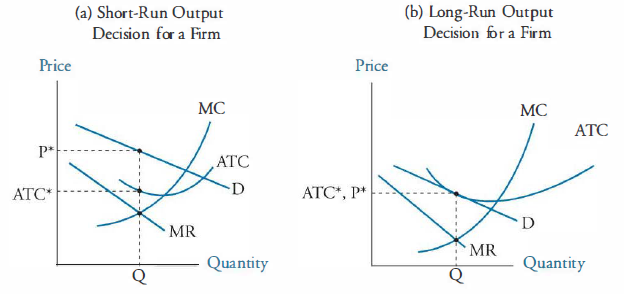
Monopolistic Competition in the Long-run The monopolistically competitive firm's long‐run equilibrium situation is illustrated in Figure . The entry of new firms leads to an increase in the Excess capacity. Unlike a perfectly competitive firm, a monopolistically competitive firm ends up choosing a level of output that is below its minimum...
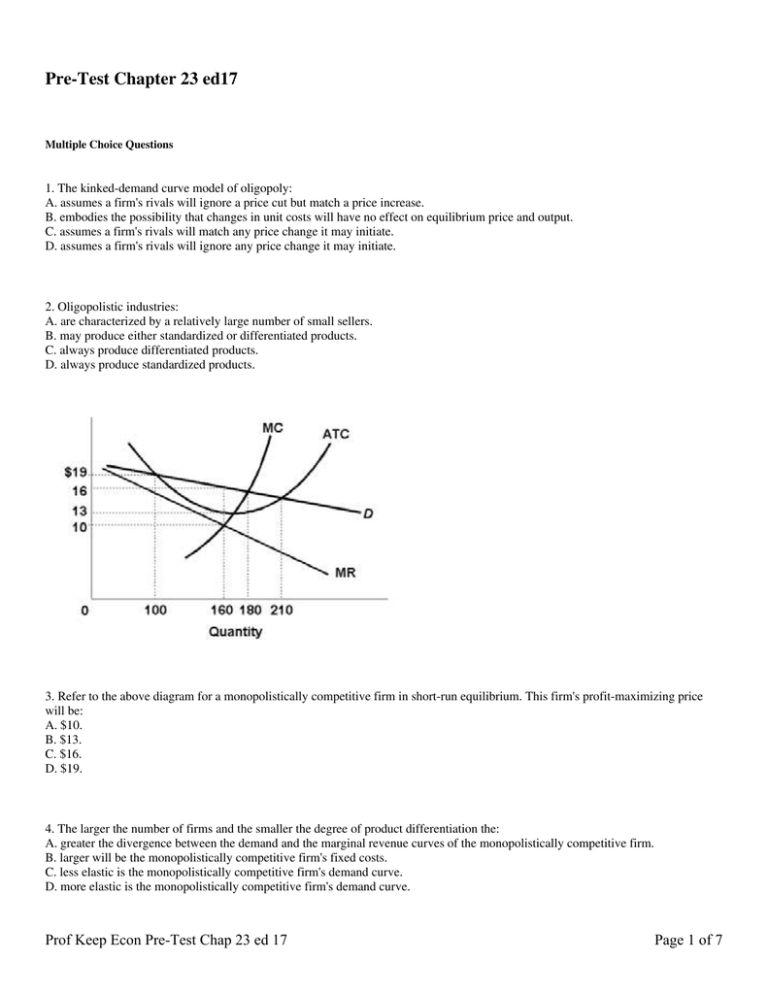
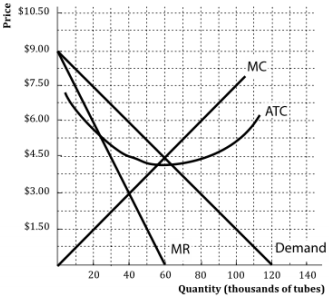
Solved 1.Refer to the diagram above. The monopolistically The monopolistically competitive firm shown: a. will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output. 2.Refer to the above cost data for a purely competitive seller: If product price is $45, the firm will
Monopolistic competition | The survival of small firms Monopolistically competitive firms are most common in industries where differentiation is possible, such as The existence of monopolistic competition partly explains the survival of small firms in modern economies. As the diagram illustrates, assuming profit maximisation, there is allocative...
Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm... The monopolistically competitive firm shown in the above figure:cannot operate profitably, at least in the. If all monopolistically competitive firms in the industry have profit circumstances similar to the firm shownabove:some firms will exit the industry.
The Effects of Trade in a Monopolistically Competitive Industry Use a monopoly diagram for a representative monopolistically competitive firm to depict a long-run equilibrium. Understand how the market equilibrium Suppose initially that the two countries are in autarky. For convenience, we will assume that the firms in the industry are symmetric relative to the...
Chapter 17 MC — Monopolistic Competition Chapter 17 Monopolistic Competition Multiple Choice 1. In a monopolistically competitive industry, firms set price a. equal to marginal cost since each 2. A profit-maximizing firm in a monopolistically competitive market differs from a firm in a perfectly competitive market because the firm in the...
monopolistically competitive. Pure Competition » Monopolistic Competition Slide 16 Pure Competition and Monopolistic Competition • Pure competition is a standard against When there are many firms, but the product is differentiated, the market is monopolistically competitive. » This brand competition may involve...
PDF Chapter 15. Monopolistically competitive firms can earn an economic profit in the long run. 16. Free entry is the basic reason that monopolistically competitive Without drawing a diagram, describe what happens in the long run. 4. Compare the advantages and disadvantages of per-fect competition and...
Monopolistic Competition - definition, diagram and... - Economics Help Firms are allocatively and productively inefficient. Diagram monopolistic competition short run. Some firms will be better at brand differentiation and therefore, in the real world, they will be able to make Many industries, we may describe as monopolistically competitive are very profitable, so...
Key Differences Between Monopoly and Monopolistic Competition Monopolistic competition is prevalent in the manufacturing industry, such as tea, shoes, refrigerators, toothpaste, TV sets, etc. No competition exist in a monopoly market while stiff competition due to non-price competition exists between firms the monopolistically competitive market.
Equilibrium of a Firm under Monopolistic Competition Note that a monopolistically competitive firm always operates somewhere to the left of the minimum point of its AC curve. Hence a perfectly competitive market is 'efficient' in the sense that resources are allocated efficiently. Society gets larger output and consumers get output at a low price.












0 Response to "41 the monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is"
Post a Comment