42 curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
Econ test 2 Flashcards - Quizlet Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total economic profit curve. Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. marginal revenue curve. Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total revenue curve. Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total cost curve. Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - 46151 - Facebook 46. Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A) total cost curve. B) total revenue curve. C) marginal revenue curve. D) total profit curve. Answer: A. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 418 MI: 174 47. Refer to the above diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as:
Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's A) total cost curve. C) marginal revenue curve B) total revenue curve. D) total economic profit curve.
Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
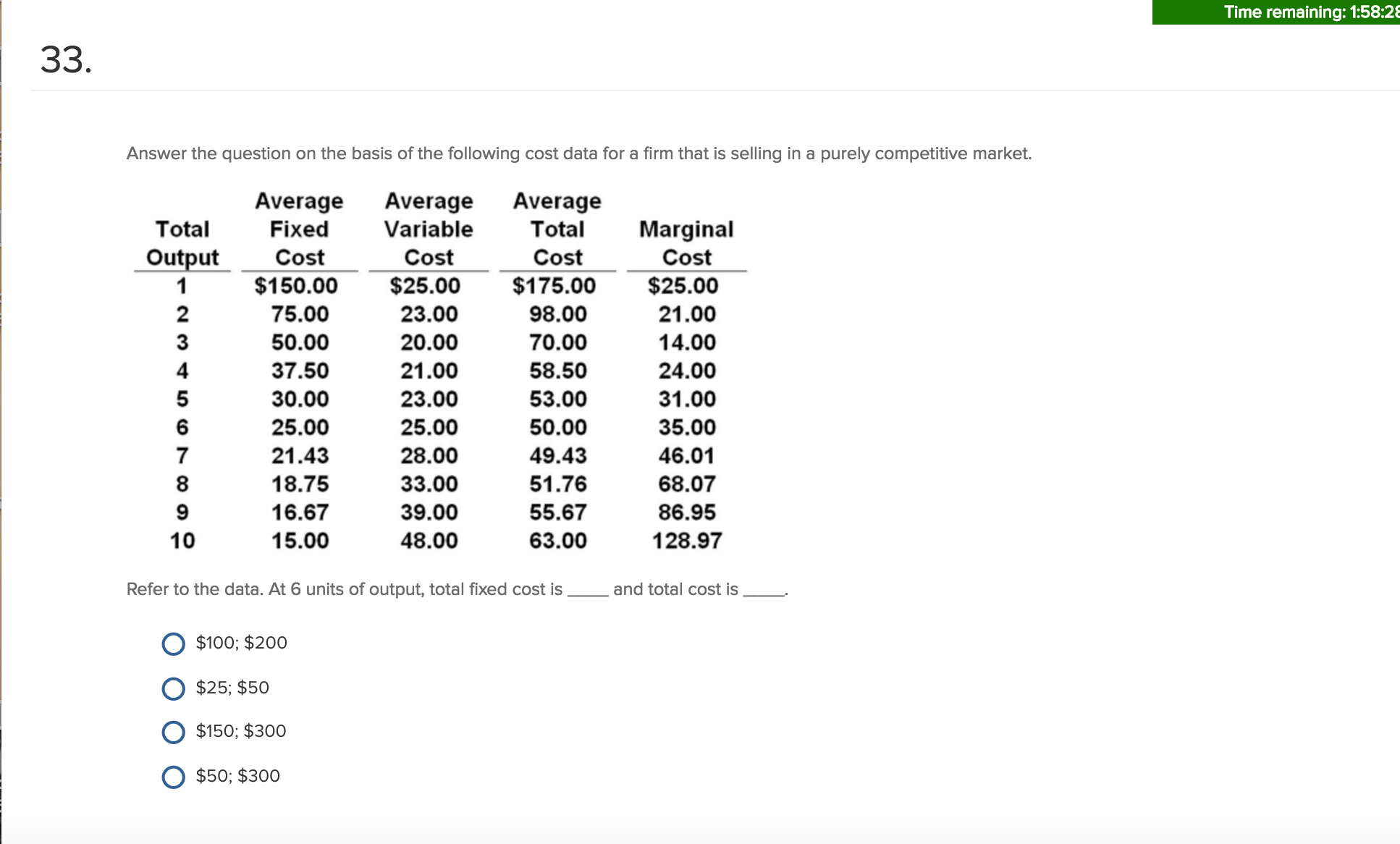
intro to micro chapter 10 quiz Flashcards | Quizlet the accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $28, the competitive firm will a) produce 4 units at a loss of $17.40 b) produce 7 units at a loss of $14.00 c) shut down in the short run d) produce 6 units at a loss of $23.80 micpure If firms enter a purely competitive industry, then in the long run this change will shift the industry: A. demand curve to the left, and the market price will decrease. Ch11quiz - paws.wcu.edu is more elastic than that faced by a single purely competitive firm. 27. Suppose that a pure monopolist can sell 10 units of output at $5 per unit and 11 units at $4.90 per unit.
Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. Type: D... - Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - Facebook 73. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is: A) the abcd segment of the MC curve. C) the cd segment of the MC curve. B) the bcd segment of the MC curve. D) not shown. Answer: B. Type: A Topic: 3 E: 424 MI: 180 74. The short-run supply curve of a purely competitive producer is based on ... Chapter 10 Quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Technological advance improves productivity in a purely competitive industry. This change will result in a shift A. down of the individual firm's MC curve, causing the market supply curve to shift to the left. B. down of the individual firm's MC curve, causing the market supply curve to shift to the right. PDF UNF PMASON - unf.edu is the same as that of a purely competitive indiLstry is its average variable cost curve does not exist because prices are not "given" to a monopolist. Use the following to answer questions 15-16: $19 100 MC ATC MR 160 180 210 Quantity 15, Refer to the above diagram for 8 monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's ... PDF exam: 060205RR - Product Markets - JustAnswer 4. Curve (3) in the diagram above is a purely competitive firm's A. total cost curve. B. marginal revenue curve. C. total economic profit curve. D. total revenue curve. € 5. Which of the following is a characteristic of a pure monopoly economic system? A. Price taker B. Many sellers C. Free entry D. Blocked entry € 6. If production is ...
revmonop The pure monopolist's demand curve is: A. identical with the industry demand curve. B. ... Comparing a pure monopoly and a purely competitive firm with identical costs, we would find in long-run equilibrium that the pure monopolist's: ... Refer to the above long-run cost diagram for a firm. DOC Chapter 9: Four Market Models Which curve and what portion of it constitutes the firm's short run supply curve? The firm's short run supply curve is the MC above the AVC curve. Quick Quiz - Pure Competition - Short Run 1. Refer to the above data. If the market price for the firm's product is $12, the competitive firm will produce: 1. 4 units at a loss of $109. 2. The Supply Curve of a Competitive Firm - GitHub Pages Figure 6.21 "The Supply Curve of an Individual Firm" reveals something remarkable: the individual supply curve How much output a firm in a perfectly competitive market will supply at any given price. It is the same as a firm's marginal cost curve. of the firm is the marginal cost curve. They are the same thing. Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... 38. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. Answer: C Topic: Profit maximization in the short run. Learning Objective: 11-03: Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run.
ECON202 CH10 Heath Flashcards - Quizlet Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's total economic profit curve. Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's marginal revenue curve Refer to the diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as Curve 1 in the diagram is a purely competitive firms A ... 40. Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total profit curve. AACSB: Reflective Thinking Blooms: Apply Difficulty: 2 Medium Learning Objective: 10-04 Convey how purely competitive firms can use the total-revenue-total-cost approach to maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run. Ch10quiz - paws.wcu.edu Refer to the above diagram showing the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. Suppose this firm is maximizing its total profit and the market price is $15. The firm's per unit profit is: PDF AP Unit 6 4. The demand curve of a monopolistically competitive producer is less elastic than that of a purely competitive producer. True False 5. The larger the number of firms and the less the degree of product differentiation, the greater will be the elasticity of a monopolistically competitive seller's demand curve. True False 6.
ECON Pure Competition 1 Short run Flashcards | Quizlet The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for this firm's product is $87, it will produce Multiple Choice 8 units at an economic profit of $130.72. 6 units at a loss of $90. 9 units at an economic profit of zero. 9 units at an economic profit of $281.97.
Solved 3. Quantity Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely ... View the full answer. Transcribed image text: 3. Quantity Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: O total revenue curve. total profit curve. total cost curve O total cost curve. O marginal revenue curve.
ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, but the demand curve for a purely competitive industry is downsloping. Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: a. total cost curve b. total revenue curve c. marginal revenue curve d. total profit curve.
ECO 211 Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit.
Curve 3 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... 39. Curve (3) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. B. total revenue curve . 40. Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve.
Curve 1 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... 43. Curve (1) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A) total cost curve. C) marginal revenue curve B) total revenue curve. D) total economic profit curve. Answer: D. D ) total economic profit curve . McConnell/Brue: Economics, 16/e Page 695. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 416 MI: 172 44.
Pure Competition A supply curve which shows the quantity of a product a firm in a purely competitive industry will offer to sell at various prices in the short run; the portion of the firm's short-run marginal cost curve which lies above its average variable cost curve. V. Profit Maximization: total cost minus total revenue
Ch11quiz - paws.wcu.edu is more elastic than that faced by a single purely competitive firm. 27. Suppose that a pure monopolist can sell 10 units of output at $5 per unit and 11 units at $4.90 per unit.
micpure If firms enter a purely competitive industry, then in the long run this change will shift the industry: A. demand curve to the left, and the market price will decrease.
intro to micro chapter 10 quiz Flashcards | Quizlet the accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $28, the competitive firm will a) produce 4 units at a loss of $17.40 b) produce 7 units at a loss of $14.00 c) shut down in the short run d) produce 6 units at a loss of $23.80
0 Response to "42 curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's"
Post a Comment