45 force diagram roller coaster loop
Roller Coaster Loops - Penji Analyzing the force diagrams of both positions we arrive at: ... We actually calculated for the height above above the roller coaster loop, not from above the ground (as we were working with the top of the loop when we solved for velocity). To solve for the actual initial height of the roller coaster, we must add the height of the roller ... Roller Coaster - myPhysicsLab Feb 06, 2021 · Custom Roller Coaster. ... The gravity force on the ball is shown in the diagram as m g pointing downwards. The component of this force that is parallel to the track is what causes the ball to accelerate. ... There is a small additional complication in that the track can loop around. This requires us to determine whether the path is increasing ...
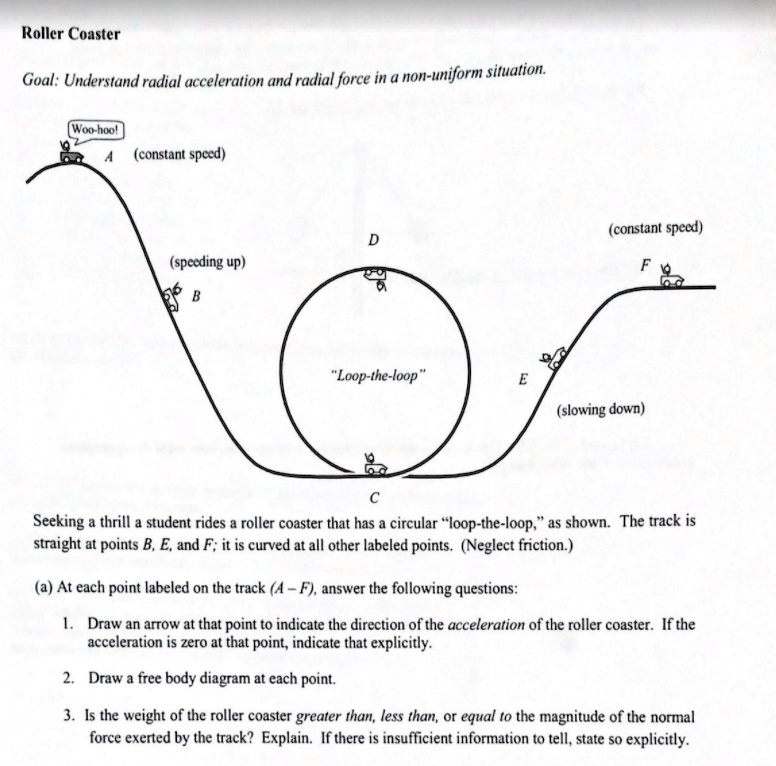
Roller Coaster Loop Problem - Physics Forums Homework Statement The diagram below shows a roller coaster ride which contains a circular loop of radius r. A car of mass m begins at rest from point A and moves down the frictionless track from A to B where it then enters the vertical loop (also frictionless), travelling once around the circle from B to C to D to E and back to B, after which it travels along the flat portion of the track ...
Force diagram roller coaster loop
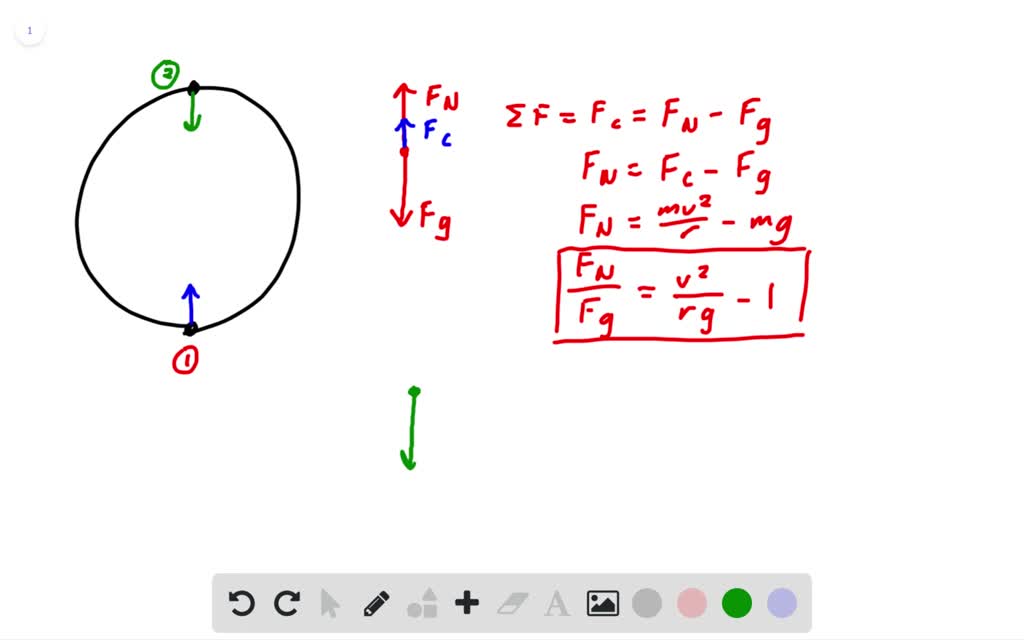
SOLVED:Show that on a roller coaster with a circular ... So for this roller coaster problem, we can draw a force diagram at the bottom of the loop. So where the bottom of the loop? The forced diagram. The two forces acting here We have the normal force and we have mg Victor at the bottom of the loop here, enjoy slightly bigger. So the net force are the boredom is F n border minus mg which is equals to the centripetal force which is M B bottom squared. The Physics Classroom Website The diagram also shows that the vector sum of the two forces (i.e., the net force) points mostly towards the center of the loop for each of the locations. Feelings of weightlessness and heaviness are associated with the normal force; they have little to do with the force of gravity. A person who feels weightless has not lost weight. Roller Coaster Forces - Mr. Cooper's Science Website An object can accelerate from gravity, force, and apparent weight. So if you throw a ball in the air (force) then the wieght of it will allow it to go up in the air but the gravity wil pull it back down. Also if you push a cart (force) then depending on how much it wieghs thats how far it will go.
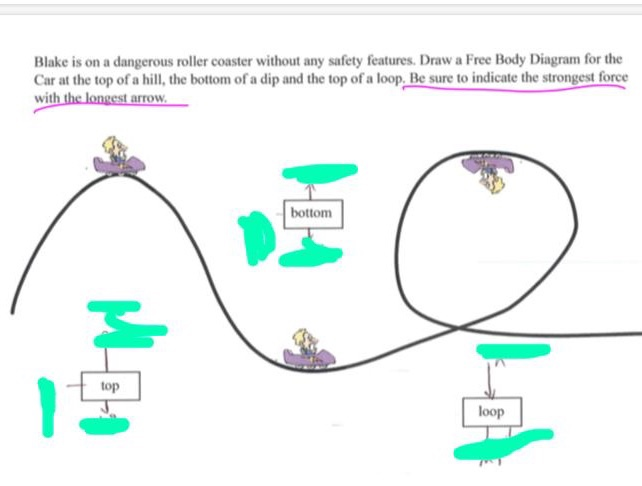
Force diagram roller coaster loop. The Physics Of Roller Coasters - Science ABC The magnitude of the force acting on the roller coaster car (or passenger) can be calculated using the formula FGRAV=m.g, where the acceleration due to gravity is represented by g (where g=9.8 m/s 2 ). The magnitude of the normal force depends on three factors—the speed of the car, the radius of the loop, and the mass of the rider. Centripetal Force Sample Problem Roller Coaster Loop AHEAD and click on this site...it wont hurt.Free simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website Roller Coaster Forces - HowStuffWorks Roller Coaster Forces Enthusiasts ride Kingda Ka, one of the world's tallest and fastest roller coasters, at Six Flags Great Adventure in Jackson, N.J. Debbie Egan-Chin/Getty Images In the last few sections, we looked at the forces and machinery that send roller coasters rocketing around their tracks. a. Draw the free-body diagram for the roller coaster at ... a. Draw the free-body diagram for the roller coaster at the top of the loop. (1 point) b. Write the expression for the net force in the y-direction at the top of the loop, in terms of w, FN, m, v, and r. (1 point) c. Write the equation that will tell you the velocity at which the coaster will fall when it reaches the top of the loop. (1 point) d.
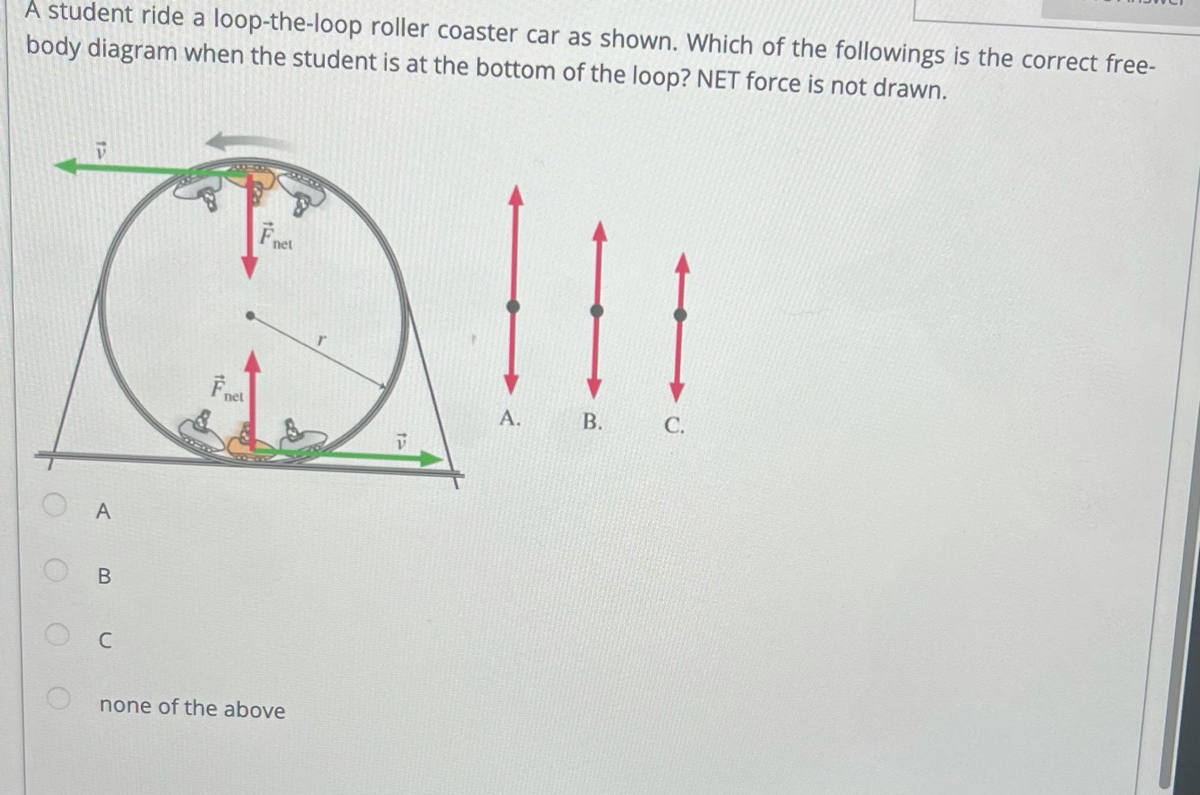
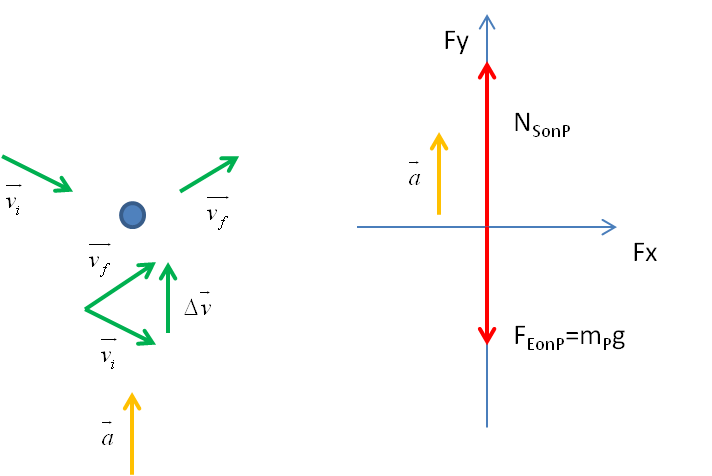
Solved You ride a roller coaster with a loop-the-loop ... You ride a roller coaster with a loop-the-loop. Construct a force diagram for it being at the bottom of the loop. Question: You ride a roller coaster with a loop-the-loop. Construct a force diagram for it being at the bottom of the loop. How rollercoasters work | Science of ... - Explain that Stuff Aug 02, 2021 · ↑ Highest g-force on a roller coaster quotes values of 5–6.3g. Values of 3.5–5g are quoted in Feel the G's: The Science of Gravity and G-Forces by Suzanne Slade, Capstone, 2009, p.6 ↑ Sources of information for the chart: Shuttle launch [PDF] , Indy 500 cornering (p.36), Dragster , Jet pilot , Apollo lunar module impact with ocean after ... Roller Coaster Physics & G Forces - Coasterforce Several forces are felt when riding a coaster, and keeping these within safe values is a vital skill for coaster designers. These forces are known as G-Forces or "G's". G stands for Gravity and the number in front of it represents how many times the force of gravity is felt at a particular point. Free-Body Diagrams for Objects in Uniform Circular Motion ... The free body diagram above depicts the roller coaster at the bottom of the loop, where Normal Force is pointed upwards and Force of Gravity is pointed downwards. This gives us a net force equation of Fnet = Fn - Fg.
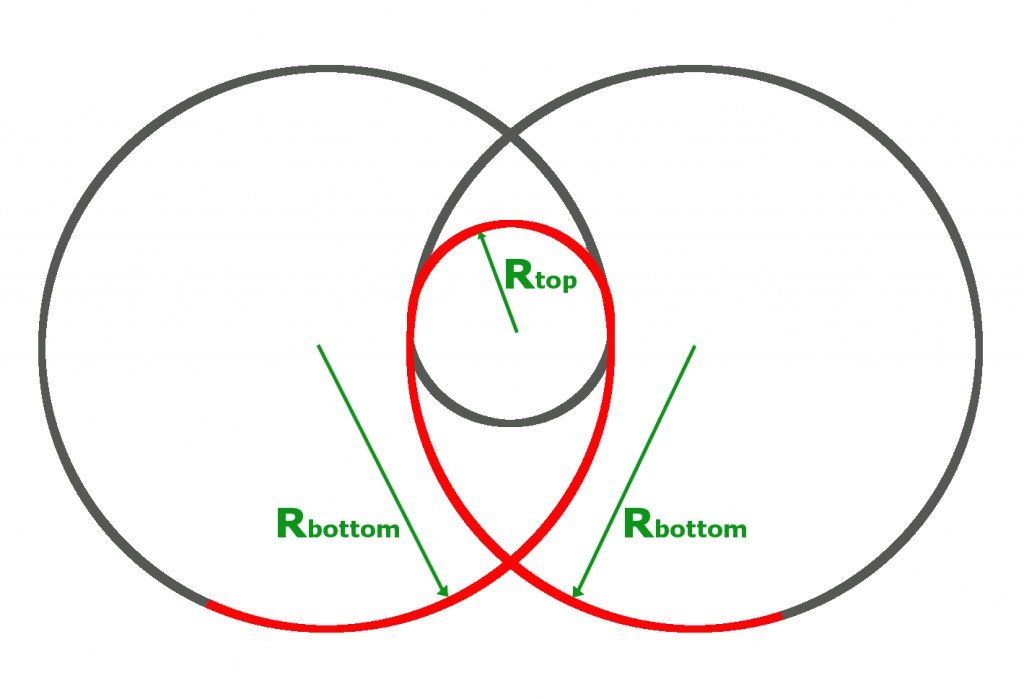
Roller Coasters and Amusement Park Physics The diagram at the right shows a clothoid loop with two circles of different radius inscribed into the top and the bottom of the loop. Note that the radius at the bottom of the loop is significantly larger than the radius at the top of the loop. ... The tension force in this demonstration is analogous to the normal force for a roller coaster ... What is a Clothoid loop? - R4 DN How do you make a loop out of cardboard roller coasters? Use a ruler and pencil to draw lines that divide it into three one-inch-wide segments. Fold the outer two segments up 90 degrees along these lines. To build a loop or a hill track piece: Start with the same steps you used to make a straight piece. Why Roller Coaster Loops Are Never Circular - Gizmodo The answer is that there is a force (provided by the rails), that is pushing the trucks of the coaster towards the center of the loop. This force is called the Centripetal Force. Newton's first ... Roller coaster - Physics Forums Feb 28, 2009 #1 ceday 11 0 Homework Statement The normal force equals the magnitude of the gravitational force as a roller coaster car crosses the top of a 60m diameter loop-the-loop. Homework Equations What is the car's speed at the top? The Attempt at a Solution hello, this problem doesn't give much information
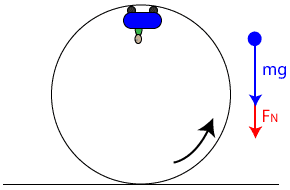
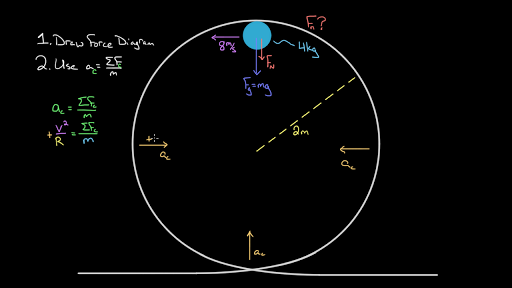
Free Body Diagrams on a Loop‐the‐Loop Roller Coaster ... force in the loop must be centripetal force F net ‐F N mg) F N mg at the minimum speed to get around the loop, F N 0 down (-) up (+) At the top of the loop, the only forces acng on the rollercoaster are the normal force exerted by the track and the weight of the rollercoaster. If the rollercoaster is

Normal Force on a Hill, Centripetal Force, Roller Coaster Problem, Vertical Circular Motion, Physics
Centripetal Force | Physics - Lumen Learning Any force or combination of forces can cause a centripetal or radial acceleration. Just a few examples are the tension in the rope on a tether ball, the force of Earth’s gravity on the Moon, friction between roller skates and a rink floor, a banked roadway’s force on a car, and forces on the tube of a spinning centrifuge.
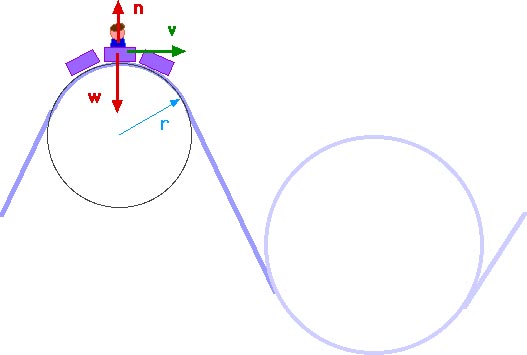
Circular Motion (and other things) We might ask how fast the coaster can go until the rider just (barely) looses contact with the seat. That means the normal force between seat and rider is zero. That occurs for. n = mg - m v 2 / r = 0. m v 2 / r = mg. v 2 / r = g. v 2 = g r. We have described this with a diagram showing a guest on the top of a hill of a roller coaster.
How can the Normal Force on an upside down roller-coaster ... The roller coaster's trajectory bends downwards because there are downward-acting forces, pointing towards the center of the loop. If it's not going fast enough, the car will fall off the track, and move on a slightly different downward-bending trajectory because of gravity.
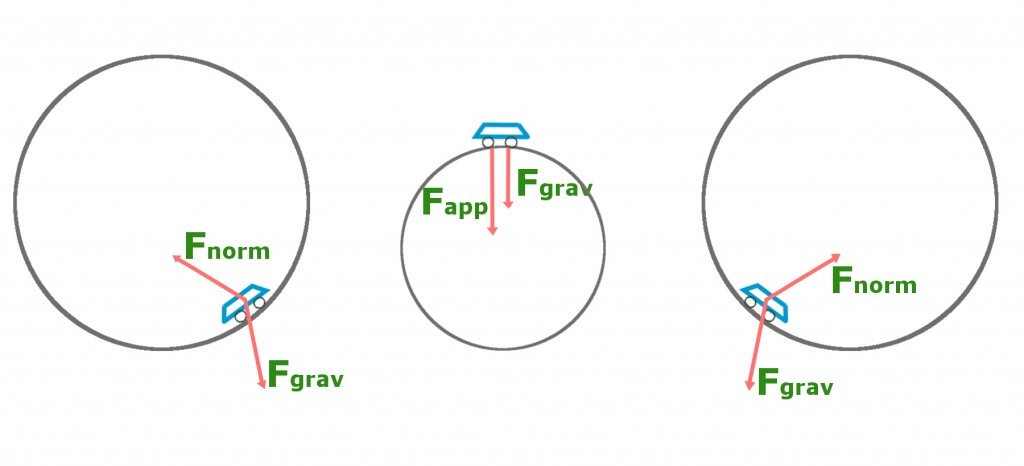
Solved You ride a roller coaster with a loop-the-loop ... Question: You ride a roller coaster with a loop-the-loop. Construct force diagram for this position. Draw the vectors starting at the black dot. The location, orientation and relative length of the vectors will be graded. This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer
Circular Motion Physics Classroom Answers A roller coaster car is at the top of a circular loop (on the inside of the track). A roller coaster car is at the bottom of a circular loop (on the inside of the track). Clothes move in a circle during the spin cycle in a washing machine. C) The Physics Classroom, 2009
Loop-the-Loops - Roller Coaster Loops - HowStuffWorks At the very bottom of the loop, the acceleration force is pushing you down in the same direction as gravity. Since both forces push you in the same direction, you feel especially heavy at this point. As you move straight up the loop, gravity is pulling you into your seat while the acceleration force is pushing you into the floor.
› jambuna › rollercoasterrollercoaster - Physics & Astronomy This will involve a two-step process: first the net force (magnitude and direction) must be determined; then the net force must be used with the free body diagram to determine the normal force. This two-step process is shown below for the top and the bottom of the loop. Bottom of Loop Fnet= m * a Fnet= (1000 kg) * (20 m/s2, up) Fnet= 20 000 N, up
Forces on a vertical loop.mp4 - YouTube What forces supply the centripetal force in a vertical roller coaster loop? What's the minimum velocity to make it around the loop?
Physics of Roller Coasters - Lesson - TeachEngineering Mar 08, 2022 · Roller coaster designers discovered that if a loop is circular, the rider experiences the greatest force at the bottom of the loop when the cars are moving fastest. After many riders sustained neck injuries, the looping roller coaster was abandoned in 1901 and revived only in 1976 when Revolution at Six Flags Magic Mountain became the first ...
Loop-the-Loops - Roller coaster - Google Search The loop-the-loop in a roller coaster acts exactly the same way as a merry-go-round. As you approach the loop, your inertial velocity is straight ahead of you. But the track keeps the coaster car, and therefore your body, from traveling along this straight path. The force of your acceleration pushes you from the coaster-car floor, and your ...
Students making sense of motion in a vertical roller ... The roller coaster loop problem in this paper is more realistic than many textbook problems, but is still an idealization of real roller coasters, which are never completely friction-less. The center of mass in the train moves with a smaller radius than the radius of the track and the position in the train influences the forces on the rider.
Beyond velocity and acceleration: jerk, snap and higher ... Oct 13, 2016 · The total force, X on the body from the roller coasters also needs to compensate for the force of gravity, ... acceleration versus time diagram for a ride close to the back in the roller coaster helix ... Pendrill A-M 2005 Roller coaster loop shapes Phys. Educ. 40 517. Go to reference in article Crossref Google Scholar.
schematron.org › force-diagram-roller-coaster-loopForce Diagram Roller Coaster Loop - schematron.org In this paper, we look into the mathematical description of various possible loop shapes, as well as their riding properties. Solving for Centripetal Force using a Free Body Diagram A 70 kg student is riding a roller coaster and is at the top of the vertical loop. The loop has a radius of 16 m, and the car's velocity at the top is 12 m/s.
loop the loop you ride a roller coaster with a loop the loop compare as best you can the normal forc
Roller coaster element - Wikipedia Roller coaster elements are the individual parts of roller coaster design and operation, such as a track, hill, loop, or turn. Variations in normal track movement that add thrill or excitement to the ride are often called "thrill elements".
Loop Shapes in Roller Coasters - Göteborgs universitet The roller coaster data base [1] includes many pictures of roller coasters loops for comparison. 2 The circular vertical loop The frictionless circular roller coaster loop with negligible train length is a popular textbook problem. The speed is then obtained directly from the conservation of energy, i.e. mv 2 /2=mg h.
5-8 Vertical Circular Motion - WebAssign Figure 5.21: A car on a roller-coaster track. (left), as well as (right) the free-body diagram when the car is at the bottom of the loop.2 pages
SOLVED:Loop-the-loop You ride a roller coaster with a loop ... The the force diagram will be composed of two forces the downward force of gravity and the upward force from the normal course from the seat of the roller coaster. Now at position one. Since we're being pulled towards the center of the circle, this centripetal force will be upwards and I will no take that as FC and this is equal to the net force.
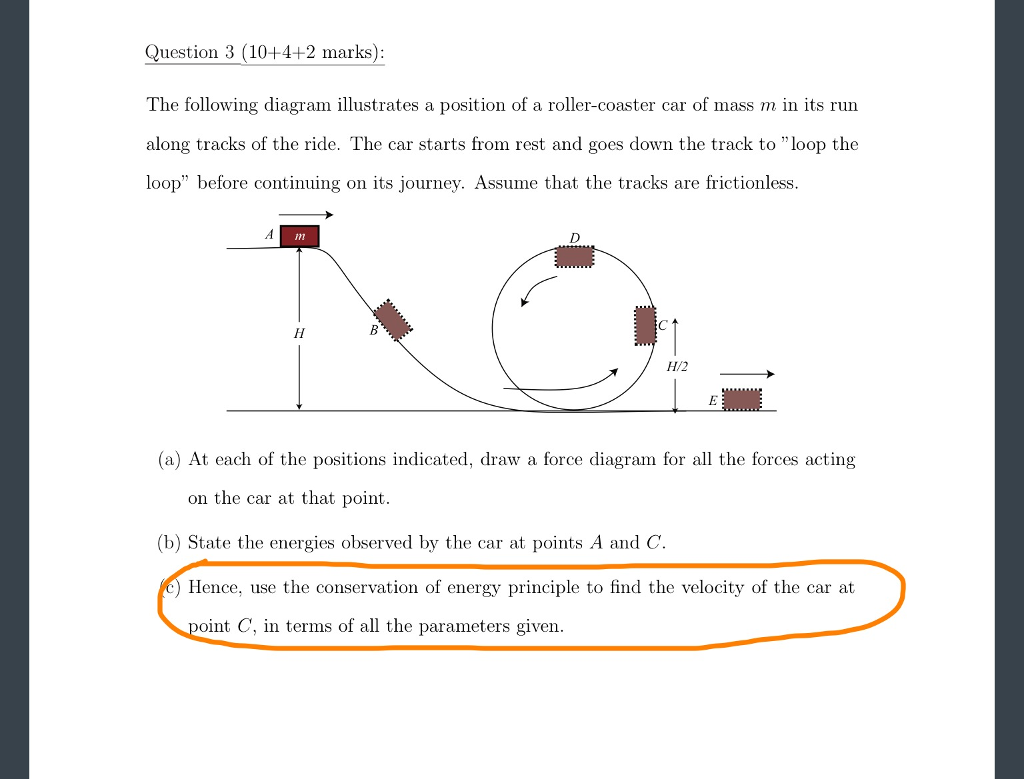
Conservation of Energy - Problems - The Physics Hypertextbook Assume minimal energy losses due to air resistance, rolling resistance, or other forms of friction and answer the following questions. Determine the speed of the coaster at the top of the loop if the normal force of the rails on the wheels is half the weight of the coaster (that is, if the frame of reference acceleration is ½g).
Roller Coaster Forces - Mr. Cooper's Science Website An object can accelerate from gravity, force, and apparent weight. So if you throw a ball in the air (force) then the wieght of it will allow it to go up in the air but the gravity wil pull it back down. Also if you push a cart (force) then depending on how much it wieghs thats how far it will go.
The Physics Classroom Website The diagram also shows that the vector sum of the two forces (i.e., the net force) points mostly towards the center of the loop for each of the locations. Feelings of weightlessness and heaviness are associated with the normal force; they have little to do with the force of gravity. A person who feels weightless has not lost weight.
SOLVED:Show that on a roller coaster with a circular ... So for this roller coaster problem, we can draw a force diagram at the bottom of the loop. So where the bottom of the loop? The forced diagram. The two forces acting here We have the normal force and we have mg Victor at the bottom of the loop here, enjoy slightly bigger. So the net force are the boredom is F n border minus mg which is equals to the centripetal force which is M B bottom squared.


















0 Response to "45 force diagram roller coaster loop"
Post a Comment