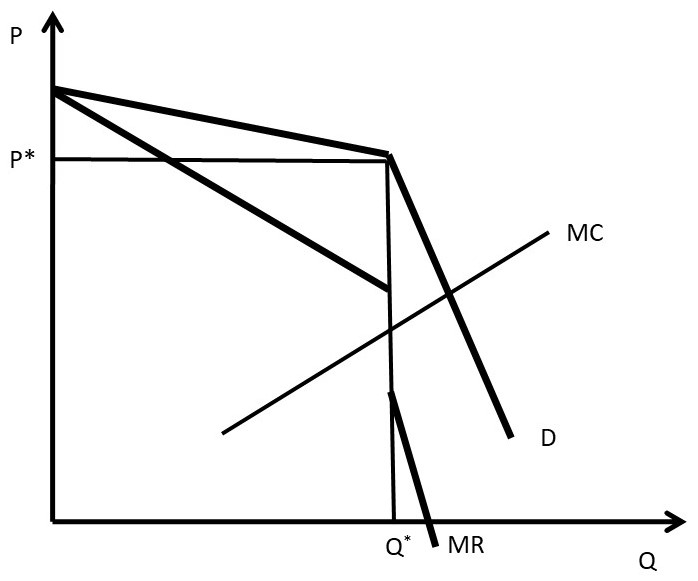
41 if the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will
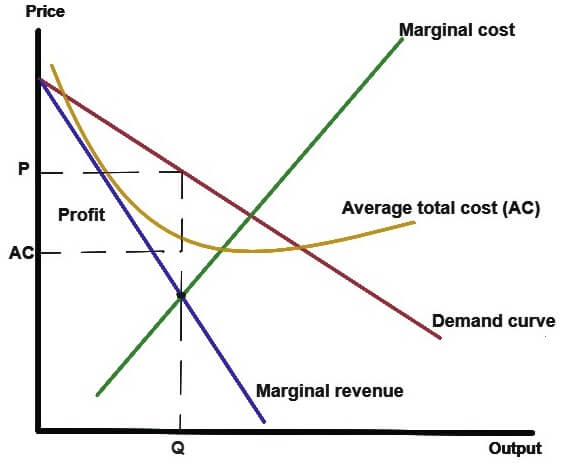
MICRO FINAL PRACTICE CHAPTER 11 Flashcards | Quizlet If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will earn a normal profit. Technological advance improves productivity in a purely competitive industry. This change will result in a shift down of the individual firm's MC curve, causing the market (industry) supply curve to shift to the right. PDF Calculating a Monopolist's Profit or Loss - Cengage Profit for a firm is total revenue minus total cost (TC), and profit per unit is simply price minus average cost. To calculate total revenue for a monopolist, find the quantity it produces, Q* m, go up to the demand curve, and then follow it out to its price, P* m. That rectangle is total revenue. Next find the output level on the average cost
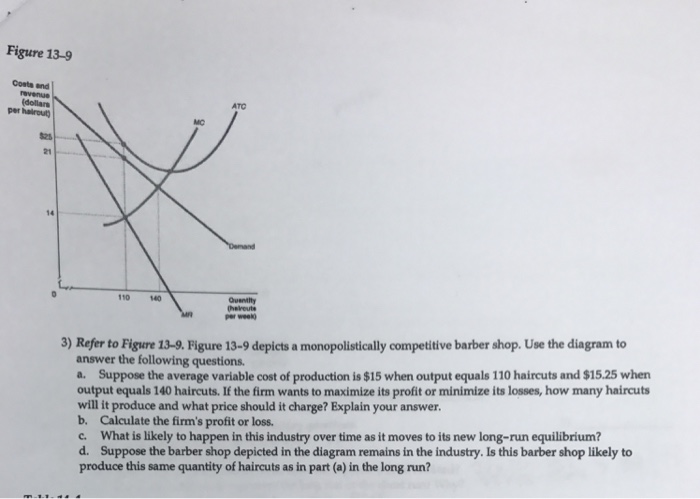
PDF Problem Set 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative ... Figure 13 - 14 illustrates a monopolistically competitive firm. 7) Refer to Figure 13 -14. Which of the following statements describes the firm depicted in the diagram? 7) A) The firm is making no economic profit and will exit the industry. B) The firm is in long - run equilibrium and is breaking even.
If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will
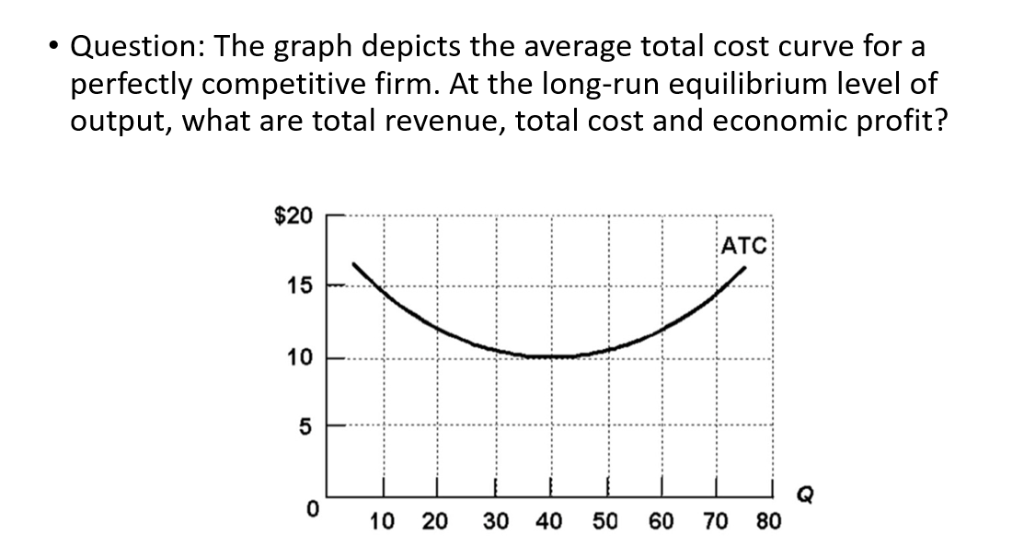
ECON FINAL Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents ... If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will:. Long-Run Equilibrium (With Diagram)| Economics In order to ascertain this, let us suppose that the firm produces an output q = q*. It is seen in Fig. 11.14 that at q = q*, the consumer is willing to pay p*, i.e., the value of the marginal unit of the good to the consumer is p* which is greater than the cost of production of the marginal unit, Eq*. econ 202 -- test 3 Flashcards | Quizlet If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will earn a normal profit. Marginal cost is ________. (TVC+TFC)/Q The diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue is $400
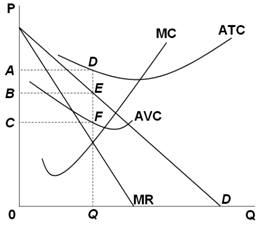
If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will. Solved > 26) Refer to Figure 11-2. A perfectly competitive ... 26) Refer to Figure 11-2. A perfectly competitive firm with zero economic profits is depicted in diagram A) A. B) B. C) C. D) D. E) B or D 27) Refer to Figure 11-2. MICRO MIDTERM Flashcards | Quizlet If all monopolistically competitive firms in the industry have profit circumstances similar to the firm shown above: a. new firms will enter the industry. b. some firms will exit the industry. c. all firms will exit the industry. d. no firms will enter the industry. A Average fixed costs diminish continuously as output increases. True False TRUE PDF Are You suprised - msu.ru Q 1 +Q 2 Q Thus, the firm will produce a total output of Q = Q 1 + Q 2, selling Q 1 at price P 1 to the group of consumers with inelastic demand and Q 2 at price P 2 to the consumers with elastic demand (note that P 1 > P 2). c) The two necessary conditions that enable price discrimination are: 1) The firm must be a monopolist. Refer to the above diagram If this competitive firm ... 54. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: A. suffer an economic loss. B. earn a normal profit. C. earn an economic profit. D. achieve productive efficiency, but not allocative efficiency. 9-13 Chapter 09 - Pure Competition in the Long Run 55. Refer to the above diagram.
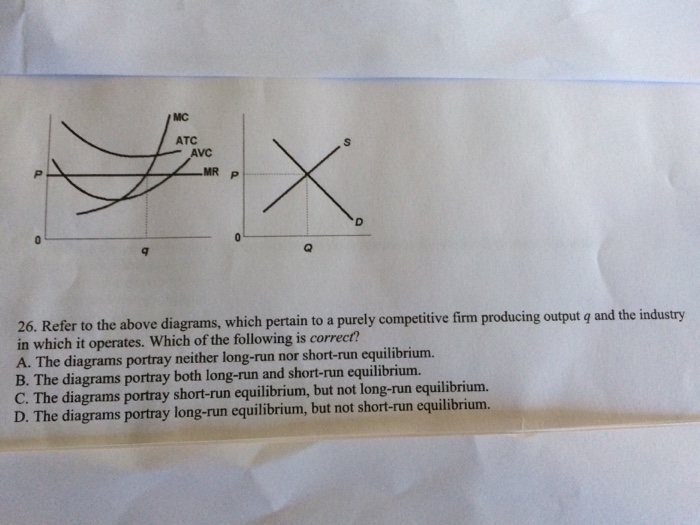
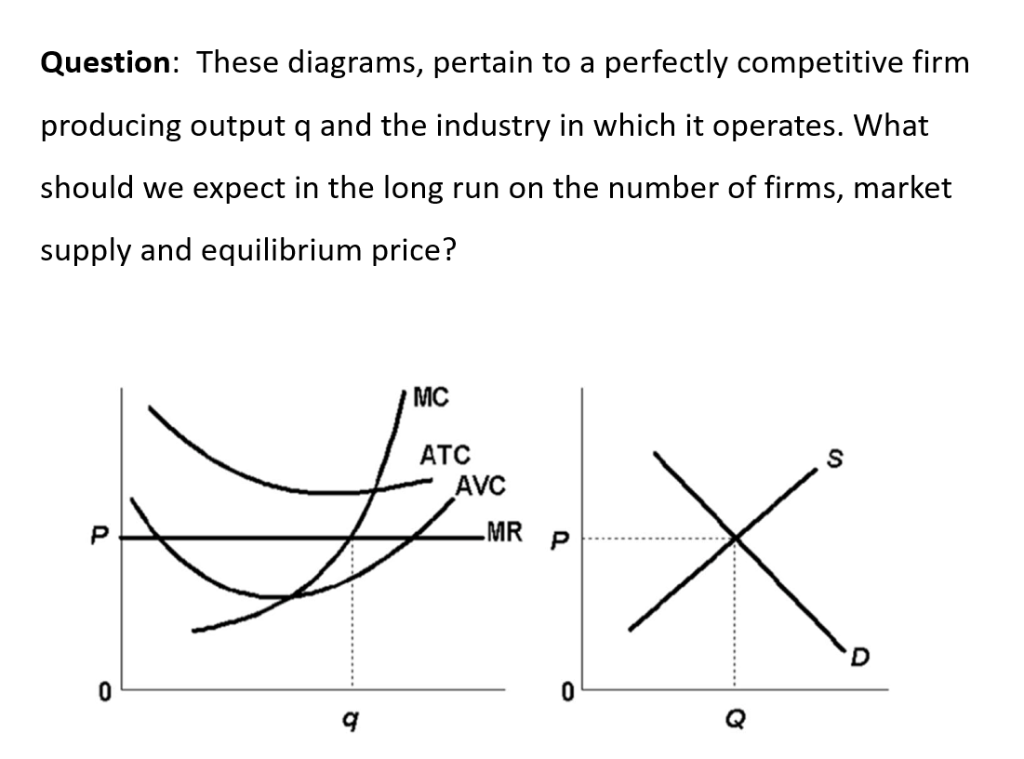
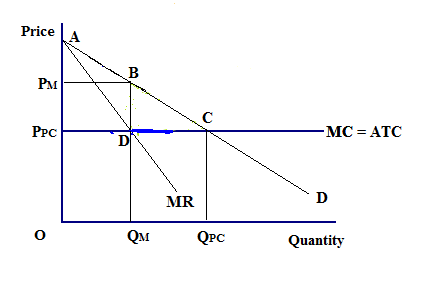
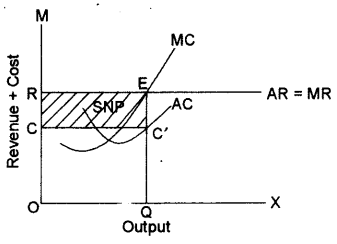
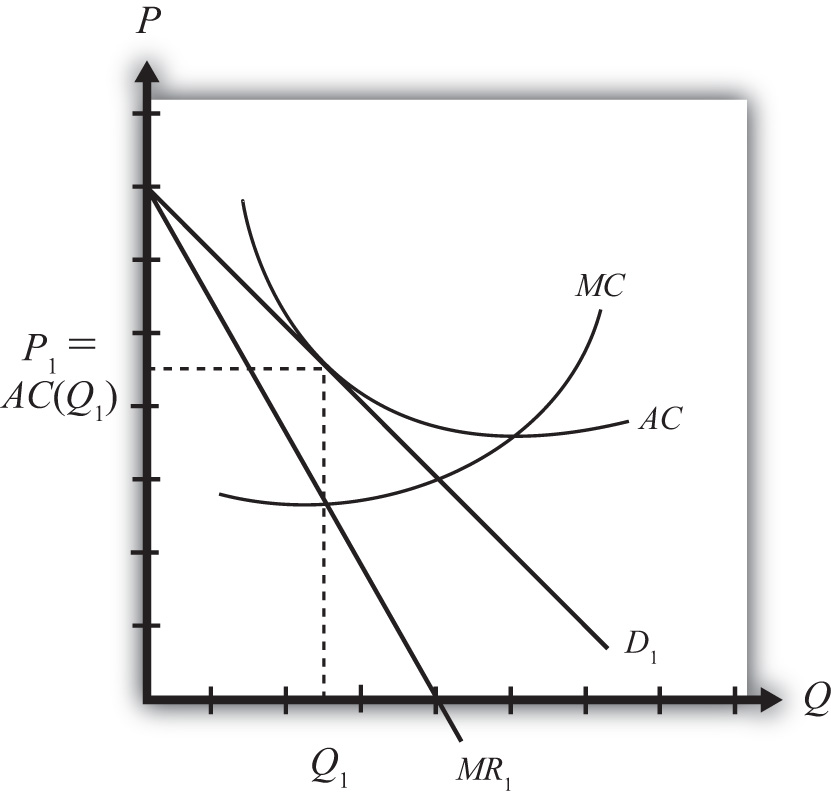
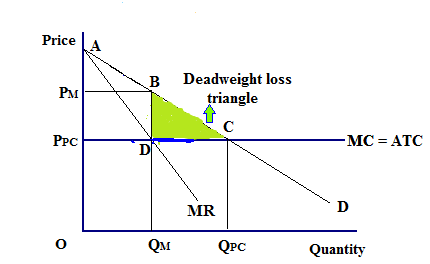
PDF ECO 211 Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 Use the cost and revenue curves to answer the questions that follow. Assume the firm is a profit maximizer. 1. Q = 250 2. P = $0.65 3. Will this firm produce this quantity? Yes 4. AR = $0.65 (same as price) 5. TR = P x Q = $0.65 x 250 = $162.50 6. ATC = $0.50 7. Chapter 11 Homework Flashcards - Quizlet If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will. ... Refer to the diagram. Line (1) reflects the long-run supply curve for: an increasing-cost industry. ... Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is correct? PDF Econ 1013 2nd MT F 2013 - Compiler Press 26) Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is P1, the profit-maximizing firm in the short run should A) produce output A. B) produce output B. C) produce output C. D) produce output D or shut down as it doesnʹt really matter which. Equilibrium of a Firm under Monopolistic Competition Long run equilibrium is achieved at point E where LMC equals MR (Fig. 5.16). The equilibrium output thus determined is OQ M. At this output, AR equals AC. The firm gets normal profit by selling OQ M output at the price OP M. Note that a monopolistically competitive firm always operates somewhere to the left of the minimum point of its AC curve.
Microeconomic Exam #2 Ch. 7/7A, 9, 10, 11, 12 Flashcards | Quizlet At the profit-maximizing level of output, a purely competitive firm will: ... If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will. 【Ap微观经济】04:不完全竞争 例题 - 哔哩哔哩 A monopolistically competitive firm sets a price higher than marginal cost because demand is higher than marginal revenue. Also, in the long run it produces a quantity where average total cost isn't minimized, so it has excess capacity. Finally, firm entry and exit leads to firms earning zero economic profits. 假装都会了 Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 - Harper ... Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Which of the following is ... The pre-merger competitive equilibrium involves 2 firms ... Download scientific diagram | The pre-merger competitive equilibrium involves 2 firms with average cost C f selling a combined output Q f at price P f . A merger can be pro-competitive even if the ...
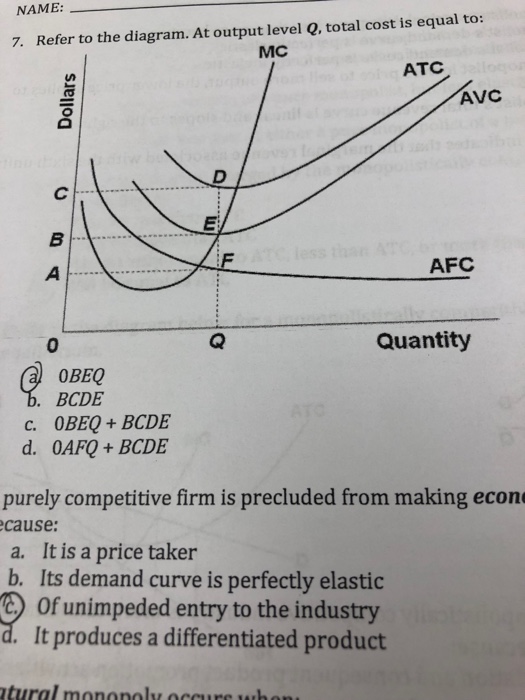
Solved MC ATC Firm Industry The accompanying graphs are for neither productive nor allocative efficiency is achieved MC ATC 0 MR Q, 2 Quantity If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will ...
Microeconomics, McGraw Hill, Assignment 6 - Quizlet The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, ... If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will.
Eco Quiz 8 Flashcards | Quizlet If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will suffer an economic loss. earn a normal profit. earn an economic profit. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. earn a normal profit. If the industry depicted in this graph were a pure monopoly, the product price would be lower than $8. $8. $14. $16.
L9(Ch8-Monopoly)-Q&A - Ch8 Monopoly Market structure 2 ... View L9(Ch8-Monopoly)-Q&A from BUSINESS 23706 at University of Technology Sydney. Ch8 Monopoly Market structure 2 Homework exercises for Lecture 9 Short Answer Questions : Use Figure 8.1, which
PDF Fall 2012 Economics 103h: Review questions for final exam ... A) A small number of firms compete. B) Firms produce identical products. C) Firms compete only on product price. D) Firms are free to enter and exit the market. Answer: D 2) In monopolistic competition, a firm has some ability to affect the price for its product because of A) easy entry and exit. B) economic profits. C) product differentiation.
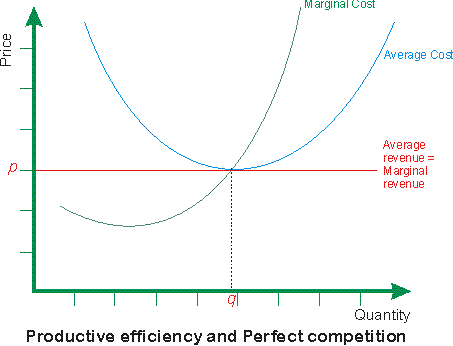
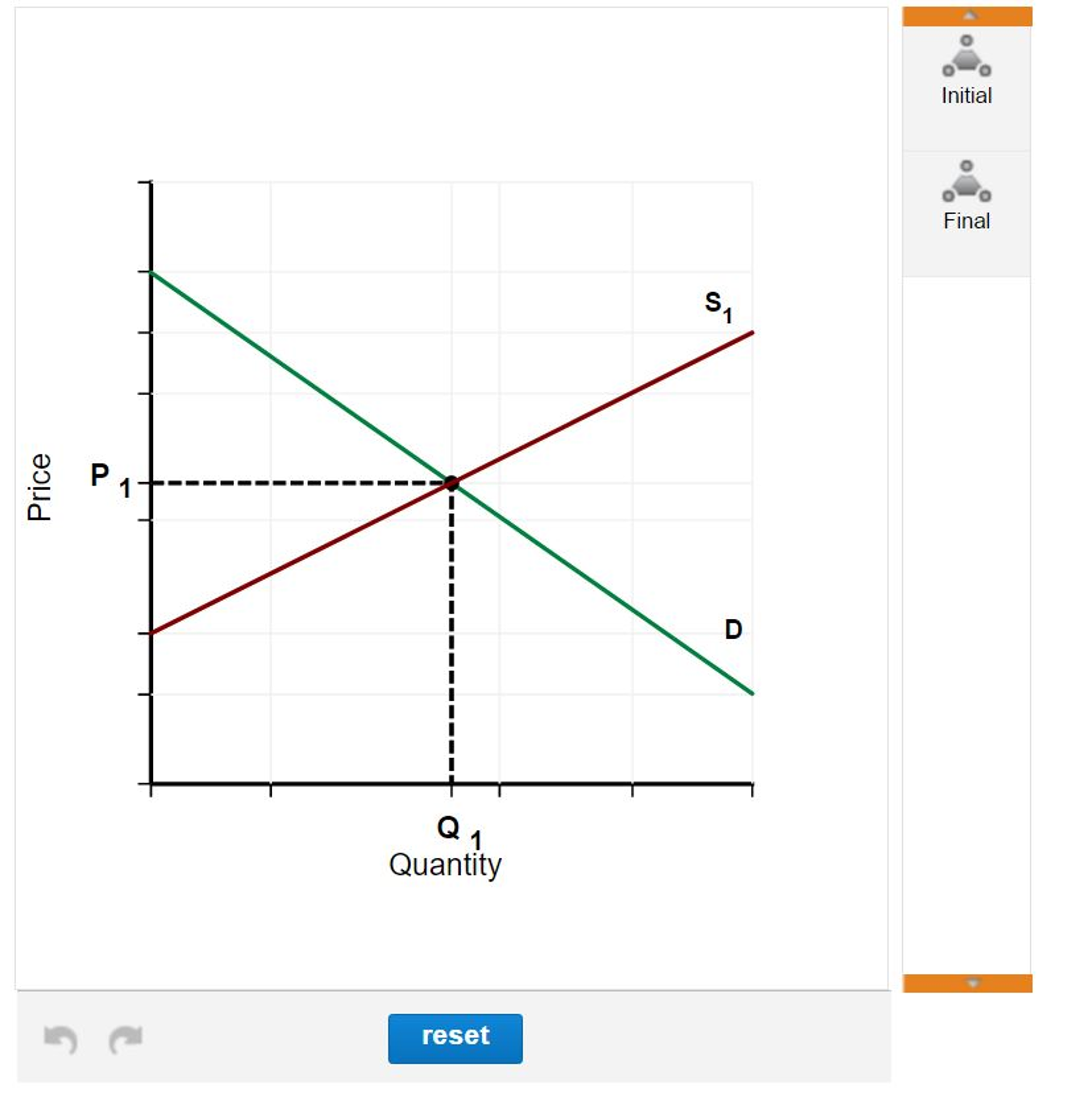
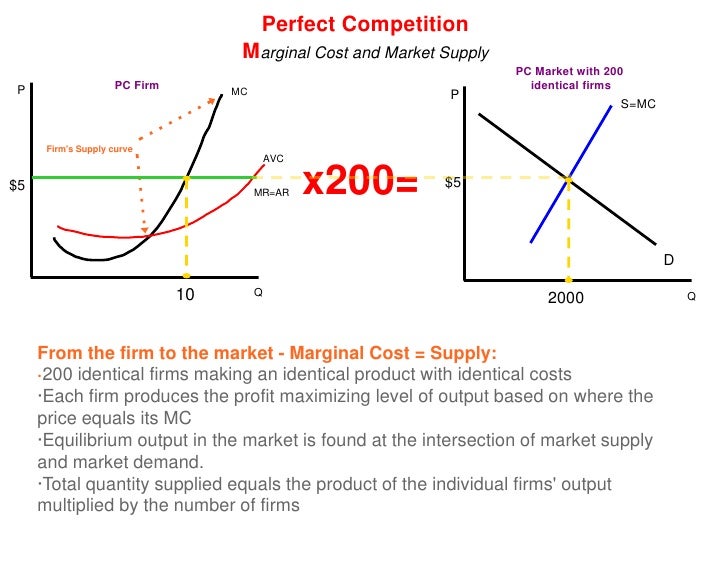
Competitive Firm's Short-Run Supply Curve (With Diagram) A supply curve, tells us how much output it will produce at every possible price. We have seen that competitive firms will increase output to the point at which P = MC, but they will shut down if P < AVC. Thus, for positive output the firm's supply curve is the portion of the MC curve that lies above the AVC curve. ADVERTISEMENTS:
ch12.docx - Refer to the two diagrams for individual firms ... If the industry depicted in the graph comprises only one seller, the profit-maximizing price and quantity will be P 3 and Q 3 . The supply curve for a monopolist is nonexistent. To maximize profit, a pure monopolist must maximize the difference between total revenue and total cost.
Answered: A competitive firm produces output… | bartleby A competitive firm produces output using three fixed inputs and one variable input. The firm's. short-run production function is q = 200x − 3x^2, where x is the amount of variable input used. The. price of the output is $5 per unit and the price of the variable input is $10 per unit. In the short run,
Solved 6 MC ATC Price MR 00:45:49 Q, Q Quantity If the ... Economics. Economics questions and answers. 6 MC ATC Price MR 00:45:49 Q, Q Quantity If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will Multiple Choice suffer an economic loss. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency. earn an economic profit. O earn a normal profit.
ECONHW12Sols19.pdf - 60. Award: 1.00 point ... - Course Hero Award: 1.00 point If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will suffer an economic loss. earn a normal profit. earn an economic profit. achieve productive efficiency but not allocative efficiency.
Chapter 11 Study Questions ( Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. The predicted long-run adjustments ...
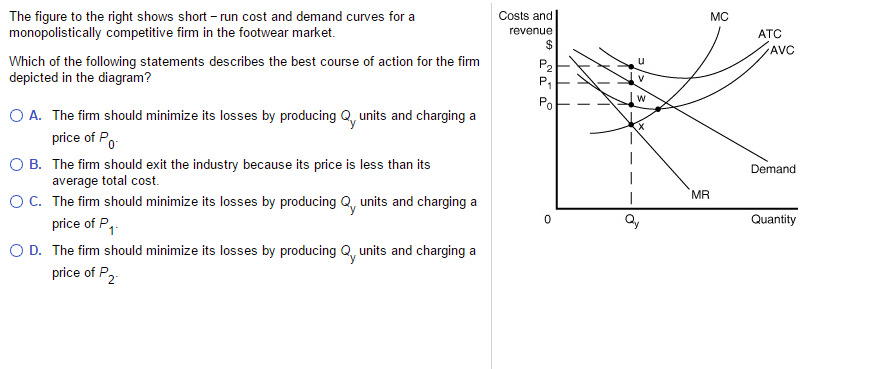
3 refer to table 13 2 what is the output q that - Course Hero Figure 13-7 Figure 13-7 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the footwear market. 5) Refer to Figure 13-7. Which of the following statements describes the best course of action for the firm depicted in the diagram? A) The firm should exit the industry because its price is less than its average total cost.
PDF Marginal Cost Total Cost P5 B - Grafton School District 2. Assume that a firm produces output using one fixed input, capital, and one variable input labor. The firm can sell all of the output it produces at a market price of $3, can hire all the workers it wants at a market wage rate of $11, and has a fixed cost of $10. It faces the following production schedule. Number of Total Employees Output 0 0
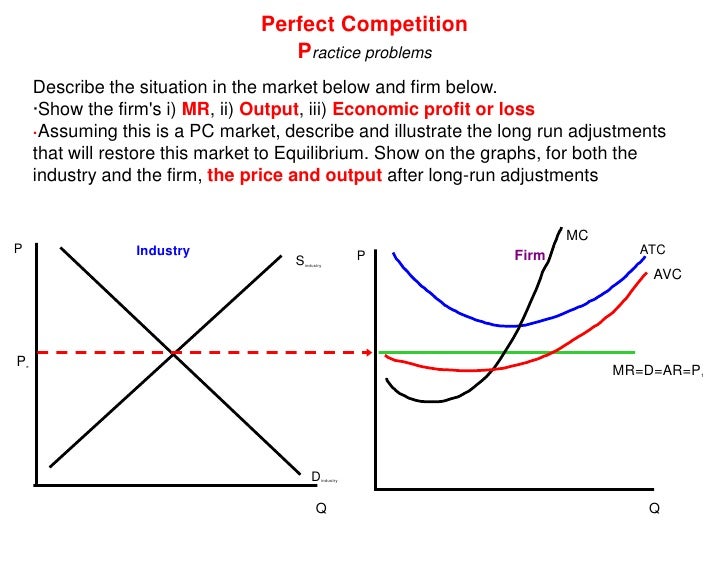
PDF Perfect Competition Questions Question 1 Perfect Competition Questions Question 1 Suppose there is a perfectly competitive industry where all the firms are identical with identical cost curves. Furthermore, suppose that a representative firm's total cost is given by the equation TC = 100 + q2 + q where q is the quantity of output produced by the firm.
econ 202 -- test 3 Flashcards | Quizlet If the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output Q, it will earn a normal profit. Marginal cost is ________. (TVC+TFC)/Q The diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total revenue is $400
Long-Run Equilibrium (With Diagram)| Economics In order to ascertain this, let us suppose that the firm produces an output q = q*. It is seen in Fig. 11.14 that at q = q*, the consumer is willing to pay p*, i.e., the value of the marginal unit of the good to the consumer is p* which is greater than the cost of production of the marginal unit, Eq*.
ECON FINAL Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve A represents ... If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will:.










0 Response to "41 if the competitive firm depicted in this diagram produces output q, it will"
Post a Comment