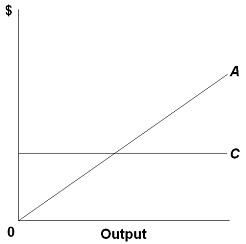
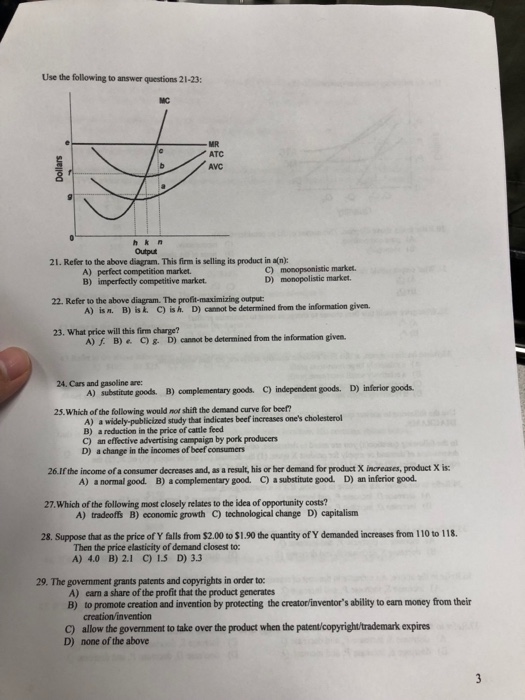
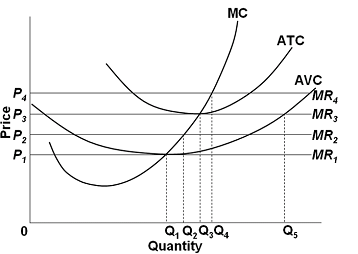
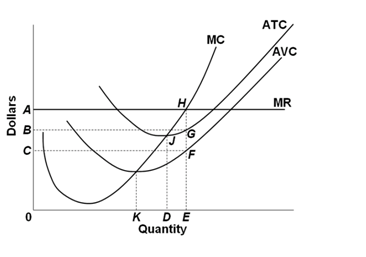
43 according to the information in the provided diagram, this firm is selling its product in a(n)
Solved 16.Balin's Burger Barn operates in a perfectly ... According to the information in the provided diagram, this firm is selling its product in a (n) monopolistic market. purely competitive market. oligopoly market. monopolistically competitive market. 20. . Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Answered: Refer to the information provided in… | bartleby Solution for Refer to the information provided in Figure below to answer the question that follow. P4 AS2 AS ASo B Aggregate output Y rice level
Marketing Chapter 2 Flashcards A portfolio-planning method that evaluates a company's strategic business units in terms of its market growth rate and relative market share. SBUs are classified as stars, cash cows, question marks, or dogs. Term Stars Definition high-growth, high-share businesses or products. They often need heavy investments to finance their rapid growth.

According to the information in the provided diagram, this firm is selling its product in a(n)
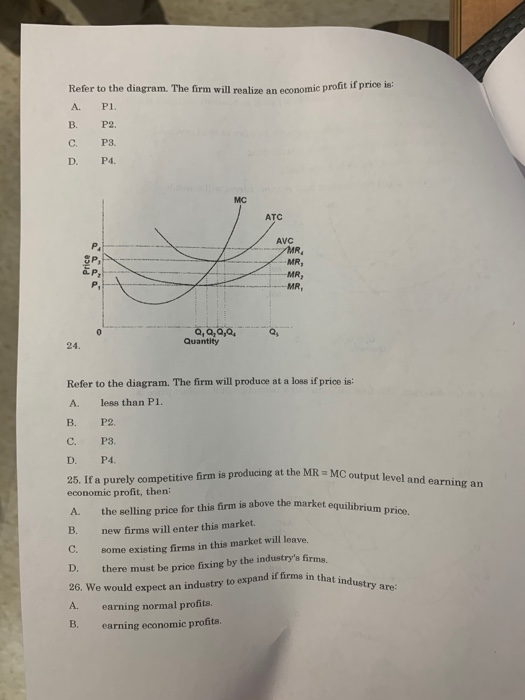
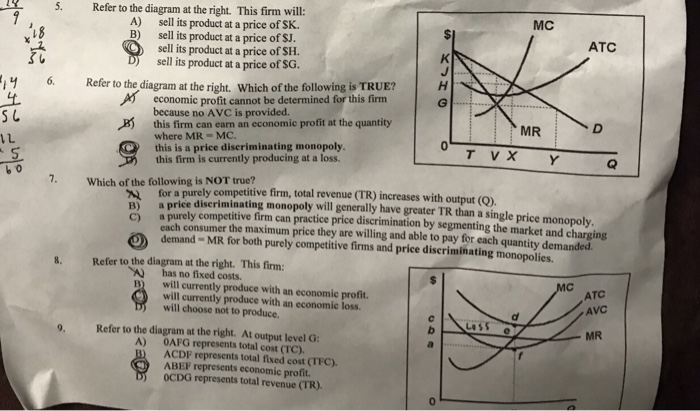
Chapter 10 Flashcards | Chegg.com If product price is $60, the firm will: A. shut down. B. produce 4 units and realize a $120 economic profit. C. produce 6 units and realize a $100 economic profit. D. produce 3 units and incur a $40 loss. C. produce 6 units and realize a $100 economic profit. 76. Refer to the above data. Answered: A firm sells its product in a perfectly… | bartleby A firm sells its product in a perfectly competitive market where other firms charge a price of $100 per unit. The firm estimates its total costs as C(Q) = 60 + 12Q+ 2Q?. a. How much output should the firm produce in the short run? units b. What price should the firm charge in the short run? 2$ c. What are the firm's short-run profits? $ d. 16.1 The Problem of Imperfect Information and Asymmetric ... Asymmetric information is the condition where one party, either the buyer or the seller, has more information about the quality or price of the product than the other party. In either case (imperfect or asymmetric information) buyers or sellers need remedies to make more informed decisions. "Lemons" and Other Examples of Imperfect Information
According to the information in the provided diagram, this firm is selling its product in a(n). TEST 3 Flashcards | Chegg.com A perfectly elastic demand curve implies that the firm: A. must lower price to sell more output. B. can sell as much output as it chooses at the existing price. C. realizes an increase in total revenue which is less than product price when it sells an extra unit. D. is selling a differentiated (heterogeneous) product. B Profit Maximisation - Economics Help Profit Maximisation. An assumption in classical economics is that firms seek to maximise profits. Profit = Total Revenue (TR) - Total Costs (TC). Therefore, profit maximisation occurs at the biggest gap between total revenue and total costs. A firm can maximise profits if it produces at an output where marginal revenue (MR) = marginal cost (MC) Solved 11. (B), output will be less than in diagram ... According to the information in the provided diagram, this firm is selling its product in a (n) monopolistic market. purely competitive market. oligopoly market. monopolistically competitive market. 20. . Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. Econ 202 Test 3 Questions Flashcards - Quizlet An industry comprising a very large number of sellers producing a standardized product is known as pure competition. An industry comprising a small number of firms, each of which considers the potential reactions of its rivals in making price-output decisions, is called oligopoly
PDF Final Exam Economics 101 Fall 2003 Wallace Final Exam ... B) a firm that purchases its resources from only one supplier. C) an industry that sells all its output to one buyer. D) a firm that sells all its output to one buyer. Answer: A Use the following information to solve the next 4 questions about a monopolistic market. The demand for a good is given by: P = 10 - Q. Microeconomics Chapter 10-12 Flashcards | Quizlet Firms seek to maximize total profit. A competitive firm in the short run can determine the profit-maximizing (or loss-minimizing) output by equating marginal revenue and marginal cost. In the short run, a purely competitive firm that seeks to maximize profit will produce where total revenue exceeds total cost by the maximum amount. Chapter 10 | Business Quiz - Quizizz Price is constant to the individual firm selling in a purely competitive market because answer choices the firm's demand curve is downsloping. of product differentiation reinforced by extensive advertising. each seller supplies a negligible fraction of total supply. marginal costs are constant. Question 13 120 seconds Q. PDF Suggested Solutions to Assignment 3 (Optional) - Queen's U (a) If two firms compete in this market with constant marginal and average costs, c =10 , find the Cournot equilibrium output and profit per firm. Suppose firm 1 takes firm 2's output choice q2 as given. Then firm 1's problem is to maximize its profit by choosing its output level q1. If firm 1 produces q1 units and firm 2
Circular Flow | Principles of Macroeconomics In the diagram, firms produce goods and services, which they sell to households in return for revenues. This is shown in the outer circle, and represents the two sides of the product market (for example, the market for goods and services) in which household's demand and firms supply. Pricing Decisions: Influencing Factors, Methods and ... Selling price is the amount for which customers are charged for some product manufactured or for a service provided by the firm. The pricing decisions are influenced by both internal and external factors. Needles, Anderson and Caldwell have suggested external factors and internal factors to be considered for setting a price by a business firm. PDF MCQ: Unit-1: introduction to Operations and Supply Chain ... A product-based definition of quality 2. According to the manufacturing-based definition of quality quality is the degree of excellence at an acceptable price and the control of variability at an acceptable cost quality depends on how well the product fits patterns of consumer preferences intro to micro chapter 10 quiz Flashcards | Quizlet A perfectly elastic demand curve implies that the firm a) must lower price to sell more output b) can sell as much output as it chooses at the existing place c) realizes an increase in total revenue that is less than product price when it sells an extra unit d) is selling a differentiated (heterogeneous) product c
ECONHW11SolS31.pdf - 85. Award: 1.00 point According to ... Award: 1.00 point According to the information in the provided diagram, this firm is selling its product in a (n) purely competitive market. oligopoly market. monopolistically competitive market. monopolistic market.
Econ final Flashcards - Quizlet 14) Which of the following is NOT true about Opportunity Cost. A) Opportunity Cost can involve non-monetary exchanges. B) Opportunity Cost can be illustrated using a Production Possibilities Model. C) Opportunity Cost can be used in International Trade. D) Opportunity Cost is always assoicated with a monetary value. D
Solved According to the information in the provided ... See the answer According to the information in the provided diagram, this firm is selling its product in a (n) a) purely competitive market. b) oligopoly market. c) monopolistically competitive market. d) monopolistic market. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (4 ratings) a) purely competitive market. … View the full answer
PDF CHAPTER 22 The Costs of Production - Fulk's Economic Website 18. Assume that a firm has a plant of fixed size and that it can vary its output only by varying the amount of labor it employs. The table below shows the relationships between the amount of labor employed, the output of the firm, the marginal product of labor, and the average product of labor. (a) Assume each unit of labor costs the firm $20.
Selling Costs: Definitions, Assumptions, Equilibrium (With ... The curve of selling cost is a tool of economic analysis. It is a curve of average selling cost per unit of product. It is akin to the average cost curves. In other words, like the cost curves, selling costs are also of U-shape. Moreover, there are two terms according to which the curve of selling cost is drawn.
ECON 202S Final Exam Flashcards - Quizlet According to the information in the provided diagram, this firm is selling its product in a(n) A. purely competitive market. At P3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will. C. produce 40 units and incur a loss. Refer to the accompanying diagram. The firm's supply curve is the segment of the.
PDF Chapter 6. Data-Flow Diagrams Data-flow diagrams (DFDs) model a perspective of the system that is most readily understood by users - the flow of information through the system and the activities that process this information. Data-flow diagrams provide a graphical representation of the system that aims to be accessible to computer specialist and non-specialist users alike.
Top 3 Theories of Firm (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion Total revenue is maximum when MR = 0, and MR = 0 when the demand for a company's product is unitary elastic. In Figure 7.4 we observed that if the firm wishes to maximize total revenue (without profit constraint) it will choose output Q's, where TR is maximum (i.e., the slope of the TR curve is zero or MR = 0).
Productive Efficiency - definition and diagrams ... To be productively efficient means the economy must be producing on its production possibility frontier. (i.e. it is impossible to produce more of one good without producing less of another). Points A and B are productively efficient. Point D is inefficient because you could produce more goods or services with no opportunity cost
The Circular-Flow Model of the Economy - ThoughtCo The outer lines on the diagram (the lines labeled "Labor, capital, land, etc." and "Finished product") also form a closed loop, and this loop represents the fact that firms use factors of production to create finished products and households consume finished products in order to maintain their ability to provide factors of production.
16.1 The Problem of Imperfect Information and Asymmetric ... Asymmetric information is the condition where one party, either the buyer or the seller, has more information about the quality or price of the product than the other party. In either case (imperfect or asymmetric information) buyers or sellers need remedies to make more informed decisions. "Lemons" and Other Examples of Imperfect Information
Answered: A firm sells its product in a perfectly… | bartleby A firm sells its product in a perfectly competitive market where other firms charge a price of $100 per unit. The firm estimates its total costs as C(Q) = 60 + 12Q+ 2Q?. a. How much output should the firm produce in the short run? units b. What price should the firm charge in the short run? 2$ c. What are the firm's short-run profits? $ d.
Chapter 10 Flashcards | Chegg.com If product price is $60, the firm will: A. shut down. B. produce 4 units and realize a $120 economic profit. C. produce 6 units and realize a $100 economic profit. D. produce 3 units and incur a $40 loss. C. produce 6 units and realize a $100 economic profit. 76. Refer to the above data.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_How_Does_Price_Elasticity_Affect_Supply_Feb_2020-03-8039eb24253f4fb18a337a1c0dd355ba.jpg)












/dotdash_Final_Analyzing_Starbucks_Value_Chain_Oct_2020-01-d263a993151e430f95fccd3898dfbd6a.jpg)


0 Response to "43 according to the information in the provided diagram, this firm is selling its product in a(n)"
Post a Comment