44 brain diagram reticular formation
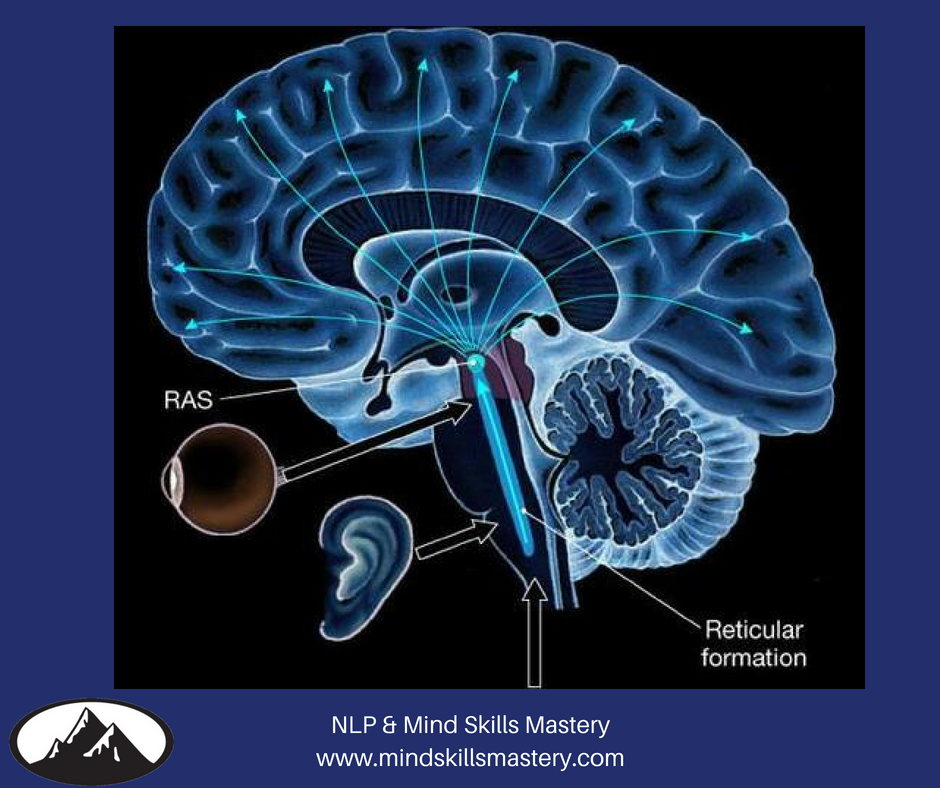
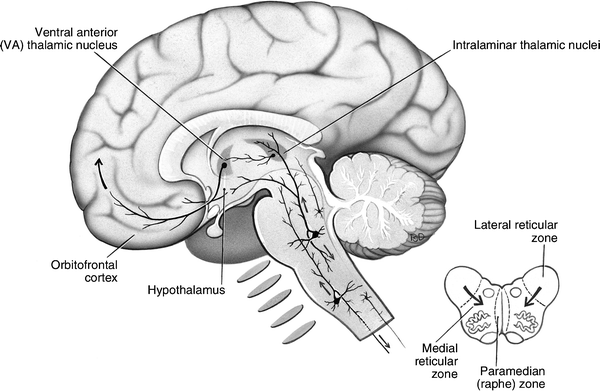
The above diagram illustrates the reticular nuclei in the brainstem in a tiered fashion ... Surrounding the previously discussed ridge of serotonergic cells, the medial reticular formation has many roles and functions. The medial reticular formation is filled with a mixture of large and small ... The reticular activating system (RAS) is a component of the reticular formation in vertebrate brains located throughout the brainstem. Between the brainstem and the cortex, multiple neuronal circuits ultimately contribute to the RAS.[1] These circuits function to allow the brain to modulate between slow sleep rhythms and fast sleep rhythms, as seen on EEG.
... midbrain, while the metencephalon and telencephalon develop to the hindbrain (which include the brainstem, cerebellum, and the reticular formation).
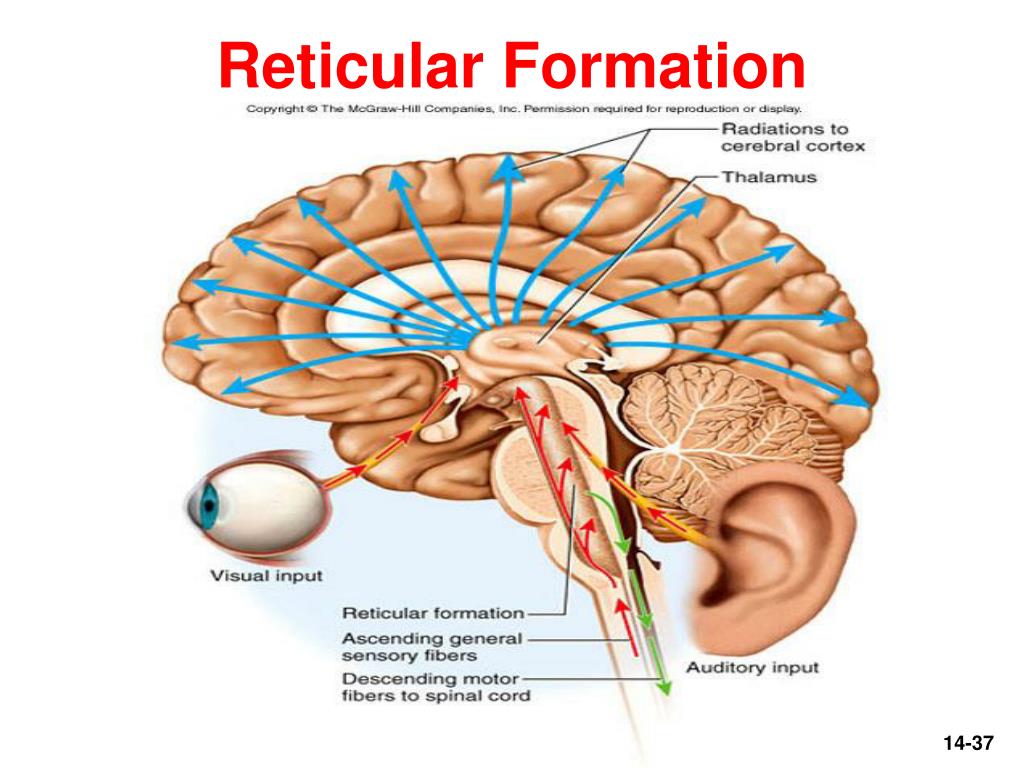
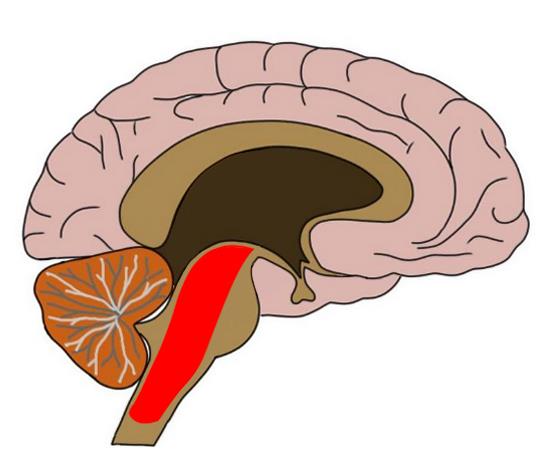
Brain diagram reticular formation
June 15, 2020 - Other articles where reticular formation is discussed: activation: …brain, but primarily from the reticular formation, the nerve network in the midbrain that monitors ingoing and outgoing sensory and motor impulses. Activation, however, is not the same as direct cortical stimulation by specific ... August 25, 2015 - The reticular formation is found in the brainstem, at the center of an area of the brainstem known as the tegmentum. The tegmentum is a heterogeneous section of neural tissue that extends vertically through the brainstem, making up the portion of the brainstem that sits between the ventricles ... Structure of Reticular Formation. The reticular formation is present in the brainstem with projections that ascend towards the cerebral cortex or descend towards the spinal cord.
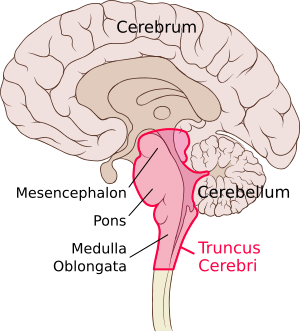
Brain diagram reticular formation. Hippocampus: Anatomy and functions. The hippocampal formation is an important component of the limbic system, along with the amygdala and septal area (although some also include the cingulate gyrus and prefrontal cortex as part of this system). The world "hippocampus" is derived from the Greek words "hippos" meaning horse and ... Movement: The substantia nigra and red nucleus in the midbrain interact with the basal ganglia in the cerebral hemispheres to help control movement.; Autonomic functions: The medulla contains nuclei that maintain functions like breathing and regulation of cardiovascular function.; Sleep and consciousness: The reticular formation, a group of nerves that extends throughout the brainstem ... Red nucleus. The anatomical structure and composition of the red nucleus has long been the source of debate among anatomist.This midbrain structure plays an important role in locomotion and several theories suggest that it has evolved dramatically with the advent of bipedalism.. Since there is still quite a bit of discord in the scientific community regarding this structure, this article will ... The brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata, situated in the posterior part of the brain. It is a connection between the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the spinal cord. Embryologically, it develops from the mesencephalon and part of the rhombencephalon, all of which originate from the neural ectoderm. The brainstem is organized internally in three laminae ...
Reticular formation, as the name suggests, is a network of neurons and nerve fibers, present in the brain. Earlier, no particular function was known to be associated with the reticular formation. Today, the reticular formation is considered to play a very important role in different activities of the brain and the nervous system. Midbrain reticular formation. The reticular formation is a network of phylogenetically old nuclei that is in charge of regulating basic and vital autonomic functions. The reticular formation is spread throughout the whole brainstem. The mesencephalic part of the reticular formation lies within two clusters that are found anterolateral to the ... C4 ET neurons terminate in midbrain (that is, midbrain reticular nucleus (MRN), superior colliculus (SC), anterior pretectal nucleus (APN) and periaqueductal grey (PAG)) and pons (that is, pontine ... Our brain can be broken down into a variety of structures, the oldest of which is made up of the brainstem, thalamus, and the cerebellum.. The brainstem gives us our most basic functions like consciousness💭 (reticular formation), breathing and heartbeat ️ (medulla), and coordination of movement🏃 (pons).
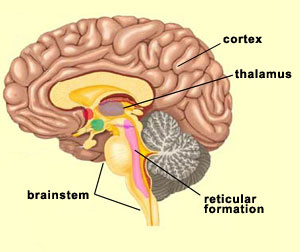
January 23, 2015 - EXTENT OF RETICULAR FORMATION: The reticular formation is situated in brain stem, and extends downwards into spinal cord and upwards up to thalamus and sub thalamus. 6. NEURONAL AGGREGATES. RETICULAR NUCLEI. The entire reticular formation is broadly arranged into three columns: Median ... The pons is a major structure in the upper part of your brainstem. It is involved in the control of breathing, communication between different parts of the brain, and sensations such as hearing ... The pons is responsible for several vital functions in addition to housing the reticular formation, which contains the neurons responsible for arousal and consciousness, and four cranial nerve nuclei. Brain Stem. The brain stem is a stalk-like structure that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord and consists of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. The brain stem contains many nerves, pathways, reflex centers, and nuclei and serves as a major relay station for sensory, motor, and autonomic information.
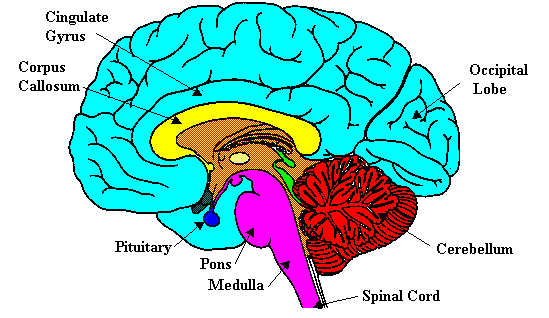
Brain Stem (Medulla Oblongata, Pons, and Midbrain), Reticular Formation, Cerebellum, Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Pituitary Gland, Corpus Collosum, and ...
A schematic diagram of the brain, with the lateral ventricles labeled. ... Reticular Formation: Definition & Functions 3:56 What Is Synovial Fluid? - Definition & Function ...
The Reticular Formation. The reticular formation is found in the anterior portion of the brainstem and is composed of multiple tracts that have a large number of connections. The reticular formation extends from the spinal cord through the brainstem to the diencephalon.
A diagram depicting the main subdivisions of the embryonic vertebrate brain. ... brain are also characteristic of animals with more advanced brains.
The reticular formation is found bilaterally in the brain and is therefore able to provide motor control to both sides of the brain when a person laughs or smiles. Since these fibers do not integrate with the corticobulbar fibers (also involved in facial expression), a patient may still smile symmetrically even if they have suffered a ...
License Image The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. ... nervous system is made up of the nerves which connect the brain ...
19.2 Schematic diagram to show the reticular nuclei in the brainstem. ... reticular formation, generate a continuous flow of impulses unless they are ...

Structure And Functions Of The Reticular Activating System Reticular Activating System Reticular Formation How To Memorize Things
Reticular Formation Diagram. angelo. July 3, 2021. Pin By Jason Sun On Projets A Essayer Cholinergic Gene Therapy Hypothesis. Reticular Activating System Cholinergic Slow Wave Sleep. Reticular Formation The Reticular Formation Extends Through The Central Core Of The Medulla O Reticular Formation Brain Anatomy And Function Brain Anatomy ...
The reticular formation is a complex network of brainstem nuclei and neurons that serve as a major integration and relay center for many vital brain systems to coordinate functions necessary for survival. The structure of the reticular formation forms a net-like connection of nuclei and neurons, hence its name "reticular," which correlates to its function of integrating, coordinating, and ...
June 8, 2020 - The reticular formation is a neuron network in the brainstem that enables consciousness, sensory and motor function, and endocrine and neurotransmitter regulation. This part of the central nervous system, spread in three main columns from one end of the brainstem to the other, is a core relay ...
The reticular formation is a nerve network of nuclei clusters found in the human brain stem. The dorsal tegmental nuclei are in the midbrain, the central tegmental nuclei are in the pons, and the ...
FIGURE 23-1 Position of the reticular formation in the brainstem. Diagrams illustrate the approximate positions of the reticular formation within the (A) midbrain, (B) pons, and (C) medulla as indicated by the dotted areas. Larger-sized dots represent magnocellular (large-celled regions), and ...
The Reticular formation is a set of neurons that extend from the spinal cord to the thalamus. This structure allows the body to wake up after a long sleep and stay awake during the day. Today's blog I've pointed out reticular formation facts (function, anatomy and diseases).
The reticular formation of the midbrain forms the core of this brain region across mammals. This region is bordered rostrally by the ascending medial lemniscus and caudally by the decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle. Across mammals in general, the reticular formation is bordered ...
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem. It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain. The neurons of the reticular formation make up a complex set of networks in the core ...
August 14, 2020 - The original functional differentiation was a division of caudal and rostral, based on the observation that damage to the rostral reticular formation induces a hypersomnia in the cat brain. In contrast, damage to the more caudal portion of the reticular formation produces insomnia in cats.

Human Anatomy Exam 3 Central Nervous System Limbic System Reticular Formation Spinal Cord Lecture 36 Flashcards Quizlet
The reticular formation is a vast network of neurons that are involved in maintaining consciousness and initiating arousal. This neuronal tract extends from the spinal cord to the diencephalon and occupies different parts of the brainstem throughout. The nuclei of the reticular formation are situated deep within the brainstem along its vertical ...
Brain diagram reticular formation. The reticular formation. In reality, if you look at its physiology, the reticular formation is a multineuronal post-synaptic formation. It has axons that are transversely and longitudinally arranged. However, it doesn't transmit any specific messages, such as sensitive, regional, or motor.

Reticular Formation Of Brain Stem Spirituality Soul And Consciousness Simon Cyrene The Bearer Of The Cross
This article is about the brains of all types ... The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article.
July 23, 2020 - There is enough information to ... been asked to use or relate a structure of the brain in five different FRQs. In 2009, students were asked to relate several factors, including the cerebellum and the reticular formation, to someone taking a driver’s education ...
... caudal and rostral , this was based upon the observation that the lesioning of the rostral reticular formation induced a hypersomnia in the cat brain ...
The reticular formation. In reality, if you look at its physiology, the reticular formation is a multineuronal post-synaptic formation. It has axons that are transversely and longitudinally arranged. However, it doesn't transmit any specific messages, such as sensitive, regional, or motor.
May 29, 2019 - The brainstem reticular formation (RF) represents the archaic core of those pathways connecting the spinal cord and the encephalon. It subserves autonomic, motor, sensory, behavioral, cognitive, and mood-related functions. Its activity extensively modulates cortical excitability, both in ...
A net-like structure of mixed gray and white matter known as the reticular formation is found in all three regions of the brainstem.
1. Stimulation of the reticular formation of the brain stem evokes changes in the EEG, consisting of abolition of synchronized discharge and introduction of low voltage fast activity in its place, which are not mediated by any of the known ascending or descending paths that traverse the brain stem.
August 26, 2008 - Compact literature review to provide basic knowledge of the reticular formation (RF) for clinicians. United Kingdom. The anatomical findings were collected from very recently published and well-edited books on neuroscience instead of hundreds of articles that contain materials still requiring ...
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system.The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum.It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the ...
Brainstem Thalamus Reticular Formation Cerebellum The Old Brain Simply Behaviour Applied Behaviour Analysis
Reticular formation: This highly diverse and integrative area contains a network of nuclei responsible for many vital functions including arousal, consciousness, sleep-wake cycles, coordination of certain movements, and cardiovascular control.; Periaqueductal gray (PAG) matter: This area plays a primary role in processing pain signals, autonomic function, and behavioral responses to fear and ...
Learn the ventricles of the brain along with their definition, function, location, anatomy, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow using labeled diagrams. The ventricular system contains the lateral, third, and fourth ventricles whose function is to produce cerebrospinal fluid. Learn where CSF is found,
The Brain Stem. PIXOLOGICSTUDIO/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY / Getty Images. The brainstem is an area located at the base of the brain that contains structures vital for involuntary functions such as the heartbeat and breathing. The brain stem is comprised of the midbrain, pons, and medulla. 3.
The reticular formation is a complex network of brainstem nuclei and neurons that serve as a major integration and relay center for many vital brain systems to coordinate functions necessary for survival. The structure of the reticular formation forms a net-like connection of nuclei and neurons, hence its name "reticular," which correlates ...
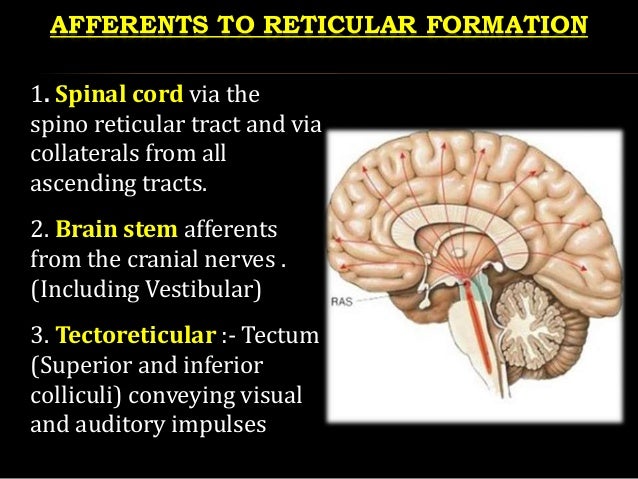
The network known as reticular formation is spread throughout the spinal cord, the midbrain, the pons, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus. The majority of structures within the brain sends and accepts fibers which ascend and descend throughout the reticular formation.
PLAY. -group of brain structures including the amygdala, hippocampus, and hypothalamus that are involved in processing and regulating emotions, memory, sexual arousal, and response to stress. is a complex brain structure that is particularly involved in processing emotions and fear-learning. -the main limbic structure involved in fear/threat ...
Will you need to label diagrams such as the brain / know where everything is? Will their be questions such as “Where is the reticular formation located” etc.. I know the functions of everything but sometimes get confused on the exact locations
January 1, 1958 - Dell, P. Humoral effects on the brain stem reticular formation. In: Henry Ford Hospital International Symposium. The reticular formation of the brain. Boston, Mass.: Little, Brown & Co., 1957. (In press) Dell, P. Humoral effects on the brain stem reticular formation.
Structure of Reticular Formation. The reticular formation is present in the brainstem with projections that ascend towards the cerebral cortex or descend towards the spinal cord.
August 25, 2015 - The reticular formation is found in the brainstem, at the center of an area of the brainstem known as the tegmentum. The tegmentum is a heterogeneous section of neural tissue that extends vertically through the brainstem, making up the portion of the brainstem that sits between the ventricles ...
June 15, 2020 - Other articles where reticular formation is discussed: activation: …brain, but primarily from the reticular formation, the nerve network in the midbrain that monitors ingoing and outgoing sensory and motor impulses. Activation, however, is not the same as direct cortical stimulation by specific ...


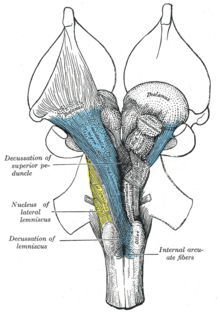
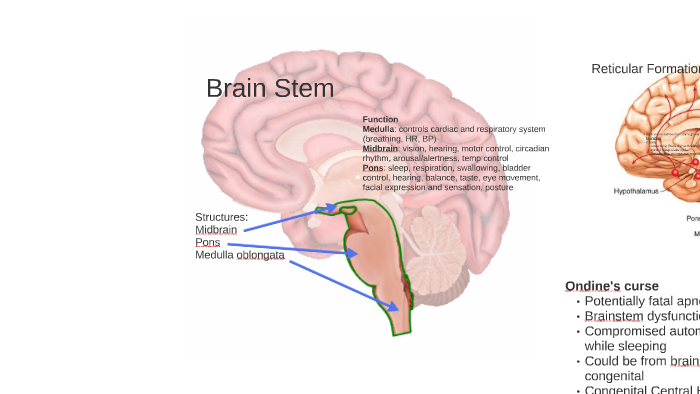













:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/2444/VPK1y7MWwZT5SHvHTAQA_nucleus_reticularis_lateralis_01-3.png)





0 Response to "44 brain diagram reticular formation"
Post a Comment