45 life cycle of fungi diagram
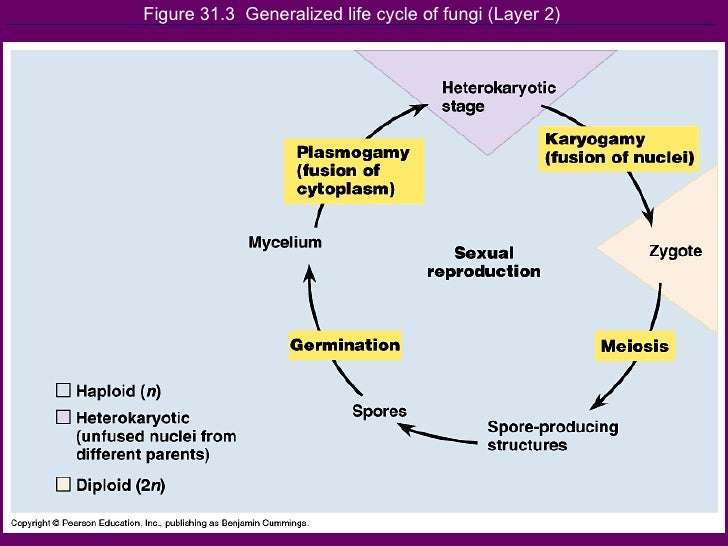
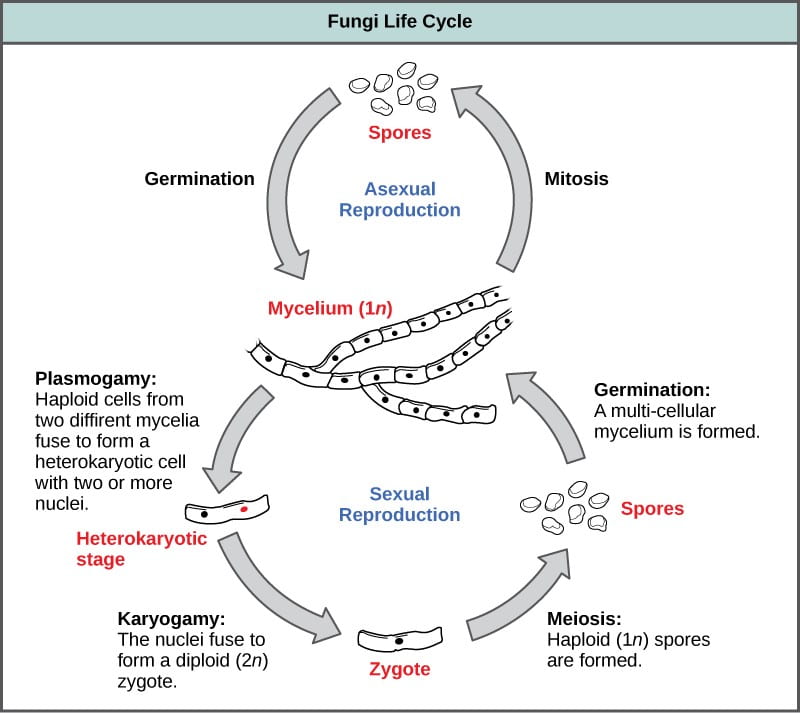
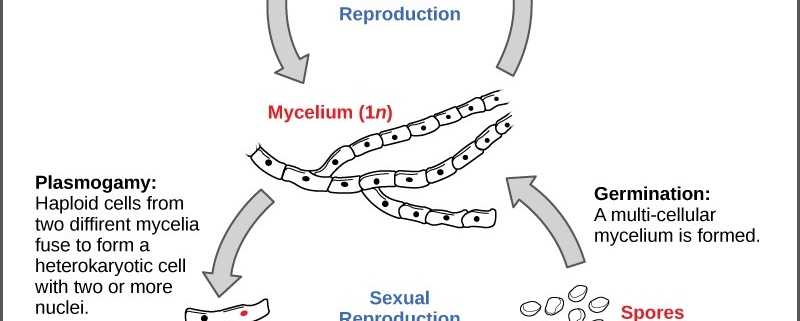
The diagram below shows the generalized life cycle of fungi. Spores are reproductive cells that are dispersed by wind. They are capable of germinating and producing a new mycelium. Ecology: Some Important Symbiotic Relationships . Lichens The life cycle of an ascomycete is characterized by the production of asci during the sexual phase. The haploid phase is the predominant phase of the life cycle. The Basidiomycota (basidiomycetes) are fungi that have basidia (club-shaped structures) that produce basidiospores (spores produced through budding) within fruiting bodies called ...
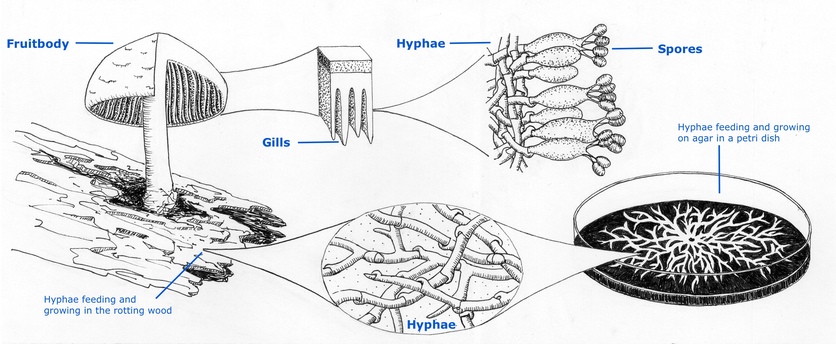
Mycelia in the Life Cycle of Fungi. The life cycle of most fungi starts with the production of spores that germinate to form hyphal threads. Given that most of these fungi are sessile, apical extension/growth of the hyphae ultimately results in the formation and growth of the mycelia (mycelial network).
.png?revision=1)
Life cycle of fungi diagram
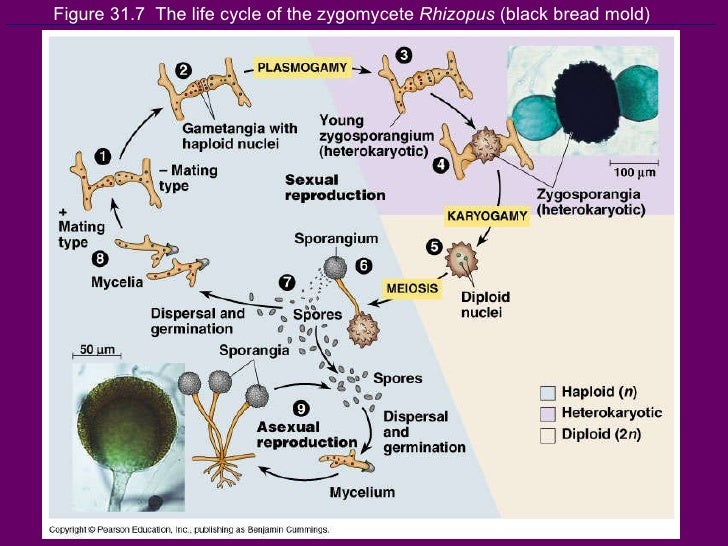
Life cycle of fungi. In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus, a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion, and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote (the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cells).Meiosis (reduction division) restores the haploid number of chromosomes and initiates the haploid ... The life cycle of fungi can follow many different patterns. For most of the molds indoors, fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle: spore, germ, hypha, mature mycelium. Brundrett (1990) showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould. Fungi are found everywhere from the air, soil, river, lakes and seas to plants, animals, clothing, etc. Let's look at the life cycle of fungi to get a better understanding. Life Cycle of Fungi: The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi. Not all fungi reproduce in the same way.
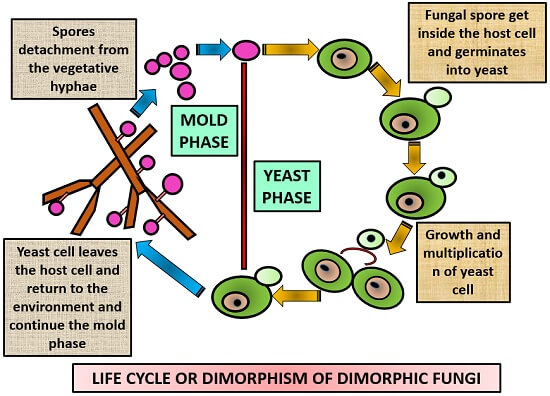
Life cycle of fungi diagram. Fungal life cycles - spores and more. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and include yeasts, moulds and mushrooms. Some fungi are multicellular, while others, such as yeasts, are unicellular. Most fungi are microscopic, but many produce the visible fruitbodies we call mushrooms. Fungi can reproduce asexually by budding, and many also have sexual ... Life Cycle of Fungus-like protists. A fungus-like protist lives a part of its life as a haploid cell and the other part as a diploid cell. The haploid cell will usually join with another haploid cell to make a diploid cell. This cell will continue to grow and will have many nuclei. Once the cell gets mature enough it will form sporangium. Most forms of indoor mold follow the same four-stage life-cycle: Hypae growth, Spore formation, Spore liberation (dispersal), and Spore germination. Without the ideal conditions for growth (source of moisture, nutrients, and oxygen) mold cannot grow. Mold is ubiquitous in that it has the ability to grow in both indoor and outdoor environments. The life cycle of fungi has a wide range of examples dependent on the types of the fungi. Not all fungi imitate similarly. While a few fungi recreate sexually, others duplicate asexually. Hence, we are going to take a gander at the life cycle of fungi in the asexual and sexual stage.
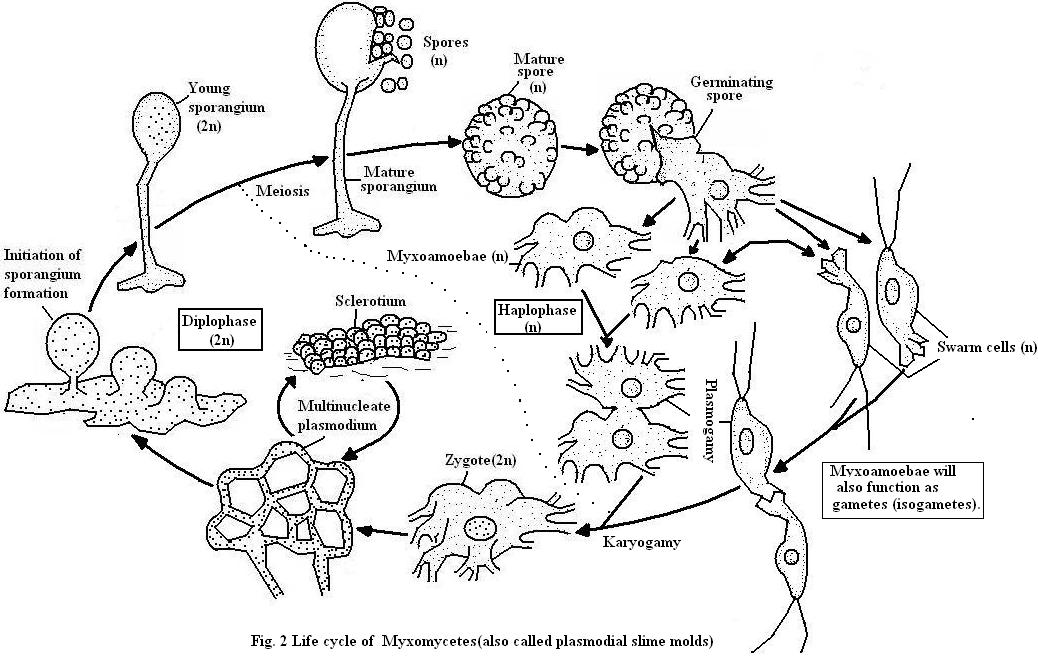
Life Cycle of Plasmodiophora Brassicae (With Diagram) | Fungi. In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of plasmodiophora brassicae with the help of suitable diagrams. Cook and Swartz (1930) showed that the life cycle of P. brassicae comprises two distinct phases, the haplophase (primary phase) and the diplophase (secondary phase). II. LIFE CYCLE OF A 'TYPICAL' FUNGUS. Generalized Life Cycle of Fungi. REFER TO DIAGRAM FROM CLASS NOTES OR TO THE FOLLOWING: . Also visit the following links for additional information: The life cycle of fungi can follow many different patterns. For most of the molds indoors, fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle: spore, germ, hypha, mature mycelium. Brundrett (1990) showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould. Alternation of generations is a term applied to a reproductive cycle (a diplobiontic life cycle) of certain vascular plants, fungi, and protists.The term is a bit confusing for people familiar only with the life cycle of a typical animal. A more understandable name would be "alternation of phases of a single generation" because we usually consider a generation of a species to encompass one ...
Dead man's fingers undergoes the alternation of generations life cycle of most fungi (also seen in all plants; e.g. Ananas comosus) 19. Although this is true, Xylaria fungi have complicated life cycles, switching between asexual and sexual stages multiple times 10. O n this web page, a general lifecycle of fungi will be covered to help the ... † Premise of the study: The life histories of lichen fungi are not well known and cannot be readily studied in laboratory culture. This work documents in situ the complete life cycle of the widespread crustose lichen Calopadia puiggarii, which reproduces sexually and asexually on the surfaces of leaves. The life cycle of fungi can follow many different patterns. For most of the molds indoors, fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle: spore, germ, hypha, mature mycelium. Brundrett (1990) showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould. In general, fungi have a very short life span, though it differs greatly from species to species. Some types may live as short as a day, while others survive anywhere between a week and a month. The life cycle of a fungus begins as a spore and lasts until germination.
Download scientific diagram | (a) Life cycle of fungi, asexual and sexual reproduction of fungi. Most fungi in the class of Zygomycetes reproduce asexually. (b) Microscopic observation of ...
The basic life cycle of Fungi--You can edit this template on Creately's Visual Workspace to get started quickly.Adapt it to suit your needs by changing text and adding colors, icons, and other design elements. Easily export it in PNG, SVG, PDF, or JPEG image formats for presentations, publishing, and printouts.
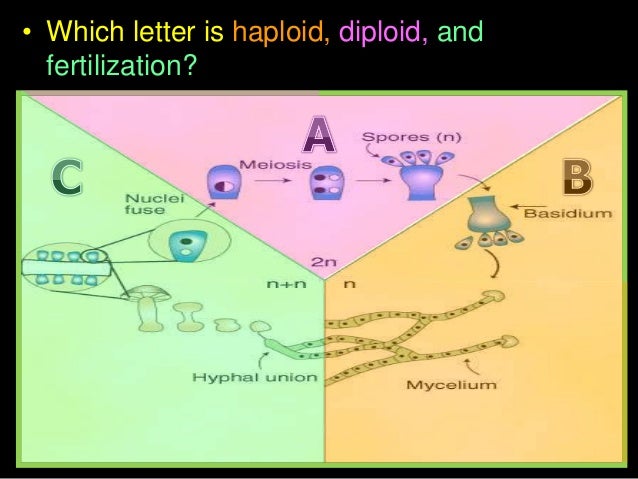
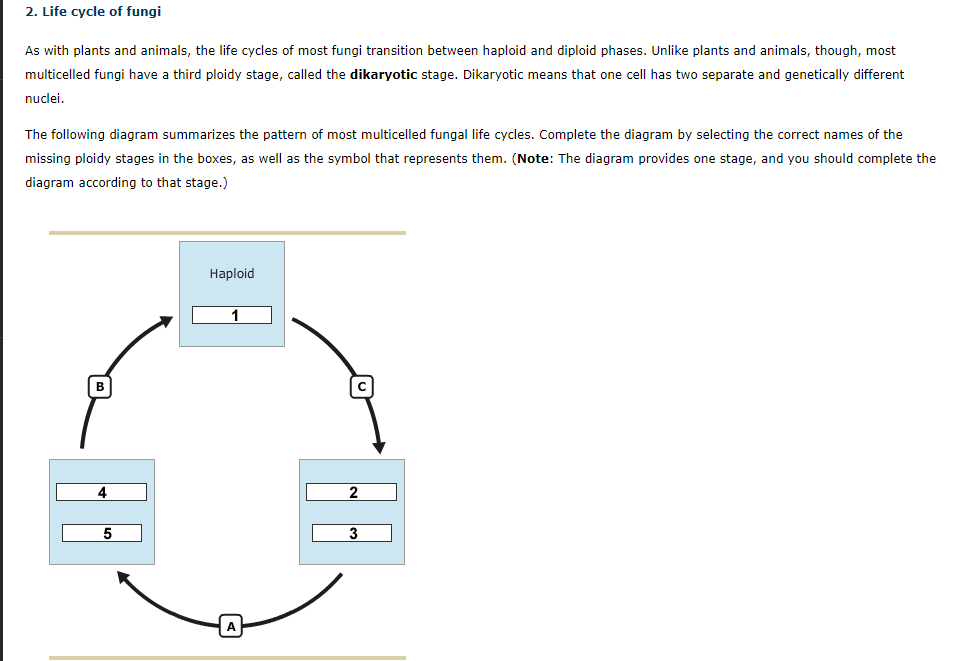
Investigating life 20.8: fungi reproduction ... Drag and drop each label into the correct location within the diagram of the basidiomycete life cycle. Drag and drop continued. In this diagram of the basidiomycete life cycle, click all the boxes that label dikaryotic structures.
The life cycle of fungi can follow many different patterns. For most of the molds indoors, fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle: spore, germ, hypha, mature mycelium. Brundrett (1990) showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould.
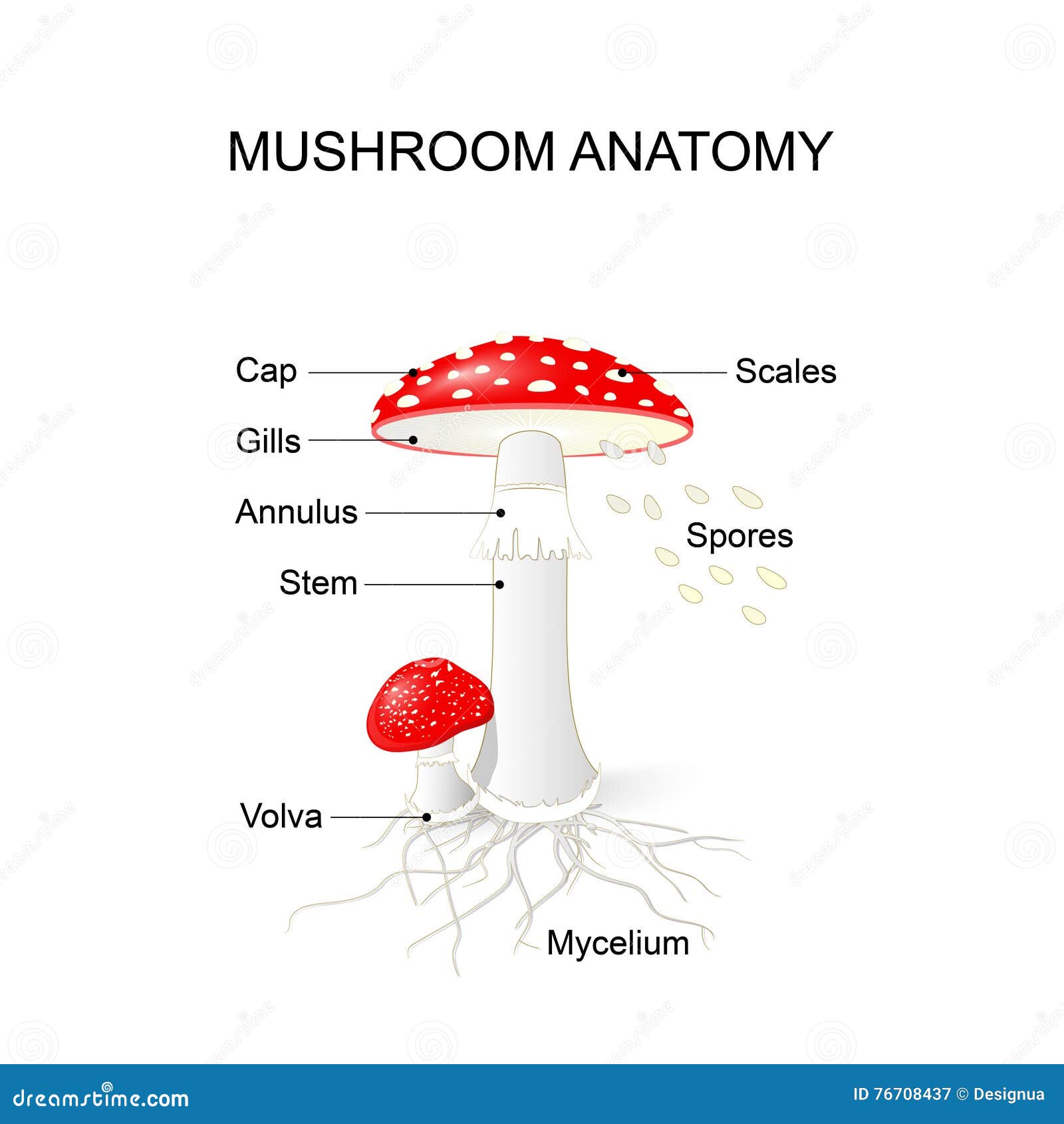
Mushroom Life Cycle Stock Illustrations 35 Mushroom Life Cycle Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
Mushrooms have a unique life cycle that all depends on the size of the mushroom as well as the environment in which the mushroom lives. Small mushrooms can grow in about 1 day while medium to larger sized mushrooms can grow in about 3-4 days. In order for the mushroom to grow steadily, the environment needs to provide steady moisture so that ...

Complete Life Cycle Of The Lichen Fungus Calopadia Puiggarii Pilocarpaceae Ascomycetes Documented In Situ Propagule Dispersal Establishment Of Symbiosis Thallus Development And Formation Of Sexual And Asexual Reproductive Structures Semantic
Complicated Life Cycle . Fungi are an extremely diverse and complicated group of organisms. While we have just started to scratch the surface of the many complex fungi life cycles, these basic tenents will hold true for most fungi. Next time you open a bag of moldy bread, think of the life cycle of the fungi that you see!
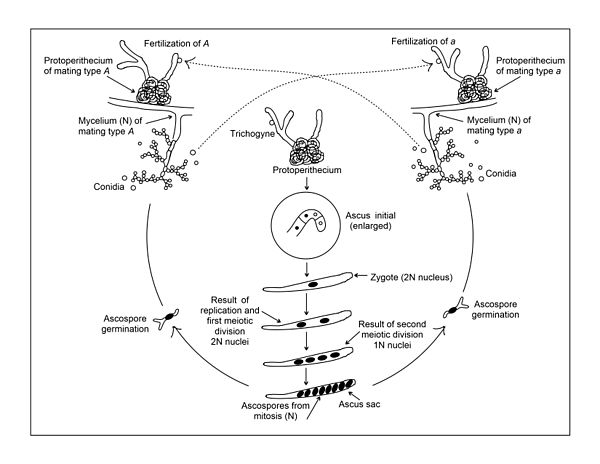
5. Motile structures do not occur in the life cycle. 6. In yeasts, asexual reproduction occurs through budding and fission. Oidia stage, similar to yeast, is found. In some other ascomycetes as well. 7. In majority of ascomycetes, the common mode of asexual reproduction is through the formation of conidia (singular-conidium).
ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of aspergillus with the help of suitable diagrams. Mycelium of Aspergillus: It is well developed and made up of a loosely interwoven mass of hyaline, bright or pale coloured, extensively branched, septate hyphae. Some of the hyphae ramify superficially upon the substratum. Others penetrate […]
ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of taphrina, explained with the help of suitable diagrams. The genus Taphrina (old generic name Exoascus still in use by many authors) contains several' species which are very important pathogens. They induce hypertrophic malformations of buds, leaves, twigs, flowers and fruits producing diseases known […]
ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of penicillium with the help of suitable diagrams. Mycelium of Penicillium: The mycelium is well developed and copiously branched. It is composed of colourless, slender, tubular, branched and septate hyphae. The hyphae run in all directions on the substratum and become intertwined with one […]
• example of fungal life cycle with dikaryotic hyphae: mushroom dikaryotic mycelium is major phase only when mushroom is formed does karyogamy occur, followed by meiosis Complete the life cycle to explain the generalized life cycle of fungi (use textbook Figure 31.5): D. Fungal phylogeny Five phyla plus "imperfect fungi"
Fungi are found everywhere from the air, soil, river, lakes and seas to plants, animals, clothing, etc. Let's look at the life cycle of fungi to get a better understanding. Life Cycle of Fungi: The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi. Not all fungi reproduce in the same way.
The life cycle of fungi can follow many different patterns. For most of the molds indoors, fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle: spore, germ, hypha, mature mycelium. Brundrett (1990) showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould.
Life cycle of fungi. In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus, a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion, and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote (the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cells).Meiosis (reduction division) restores the haploid number of chromosomes and initiates the haploid ...
.png?revision=1)

























0 Response to "45 life cycle of fungi diagram"
Post a Comment