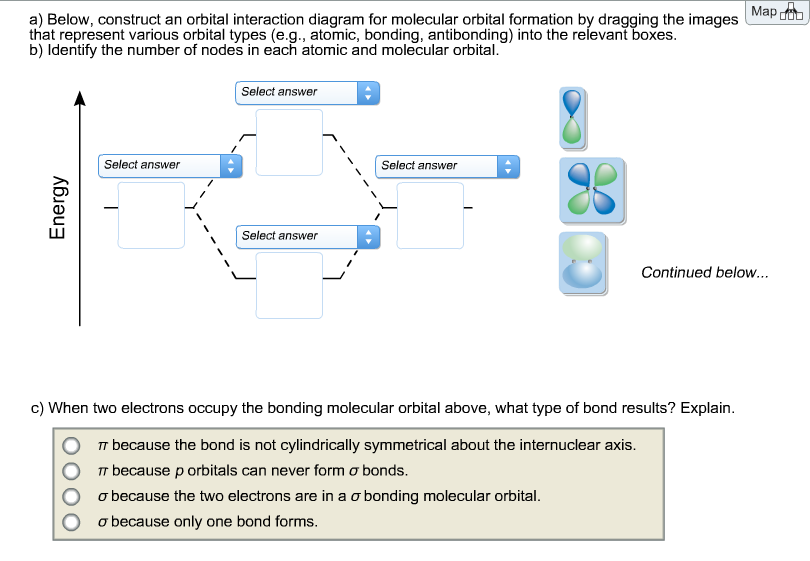
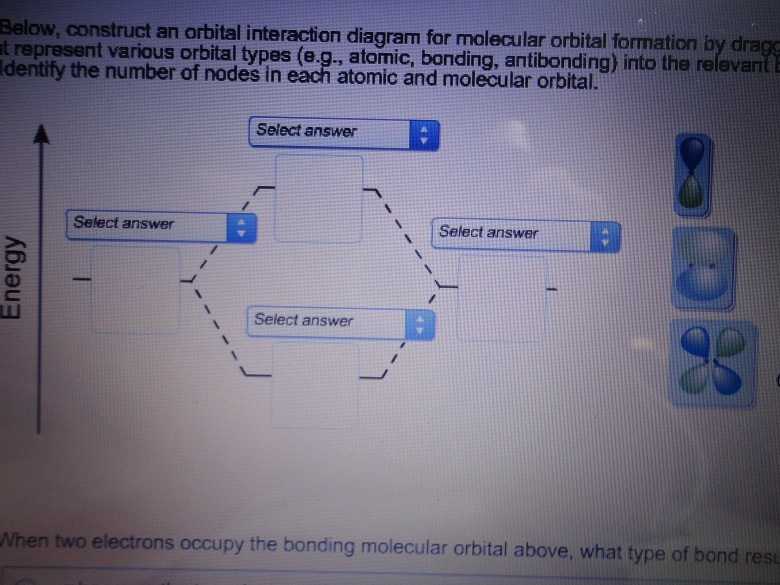
40 below construct an orbital interaction diagram
equivalent sp2 orbitals, leaving one p orbital untouched. The process is shown below. 2s 2p X 2p y 2p z Potential energy sp2 hybridization sp2 sp2 sp2 p In this top view, the unhybridized p orbital cannot be seen because it also arranges itself to be as far apart from the sp2 orbitals as possible. Below, construct an orbital interaction diagram for molecular orbital formation by dragging the image that represents various orbital types (e.g., atomic, bonding, antibonding) into the relevant boxes. b) Identify the number of nodes in each atomic and molecular orbital.
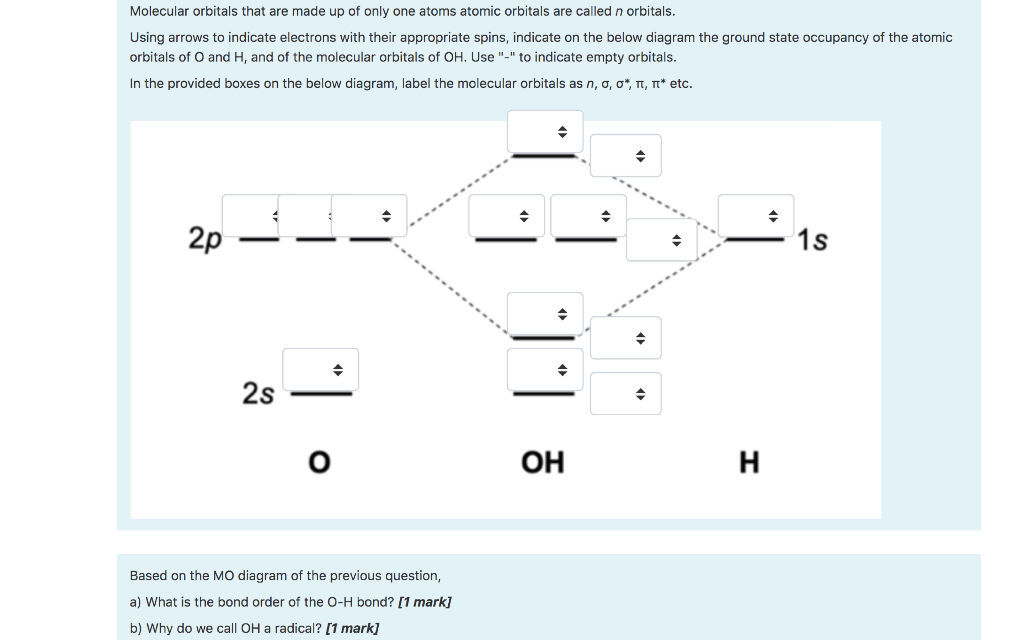
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Below construct an orbital interaction diagram
Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer. The interaction of the two bonded atoms with the bonding electrons produces a more stable arrangement for the atoms than when separated. Electrons usually occupy these orbitals. A sigma bonds is always the first bond formed between two atoms. Sigma star (σ*) antibonding molecular orbital - Normally this orbital is empty, but if it should In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
Below construct an orbital interaction diagram. Molecular Orbital Theory - Octahedral, Tetrahedral or Square Planar ... because it does not consider the interaction between the metal and ligand orbitals. The molecular orbital theory ... The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for σ-bonding in octahedral complexes can be shown as: Based on these values, we can construct the orbital interaction energy diagram shown on the right. The diagram highlights the interaction between the HOMO of the diene and the LUMO of the dienophile, which leads to the formation of a new bonding molecular orbital between the two molecules. What feature of the molecular orbital diagram allowed you to answer the previous question? A. All electrons are paired in the molecular orbitals. B. There are electrons in the antibonding orbitals that are formed for the mixing of the atomic p-orbitals. C. There are unpaired electrons. D. An orbital is characterized by a size, shape, and orientation in space below, construct an orbital interaction diagram for molecular Below, construct an orbital interaction diagram for molecular orbital formation by dragging the image that represents various orbital types (e.g., atomic, bonding, antibonding) into the relevant boxes.
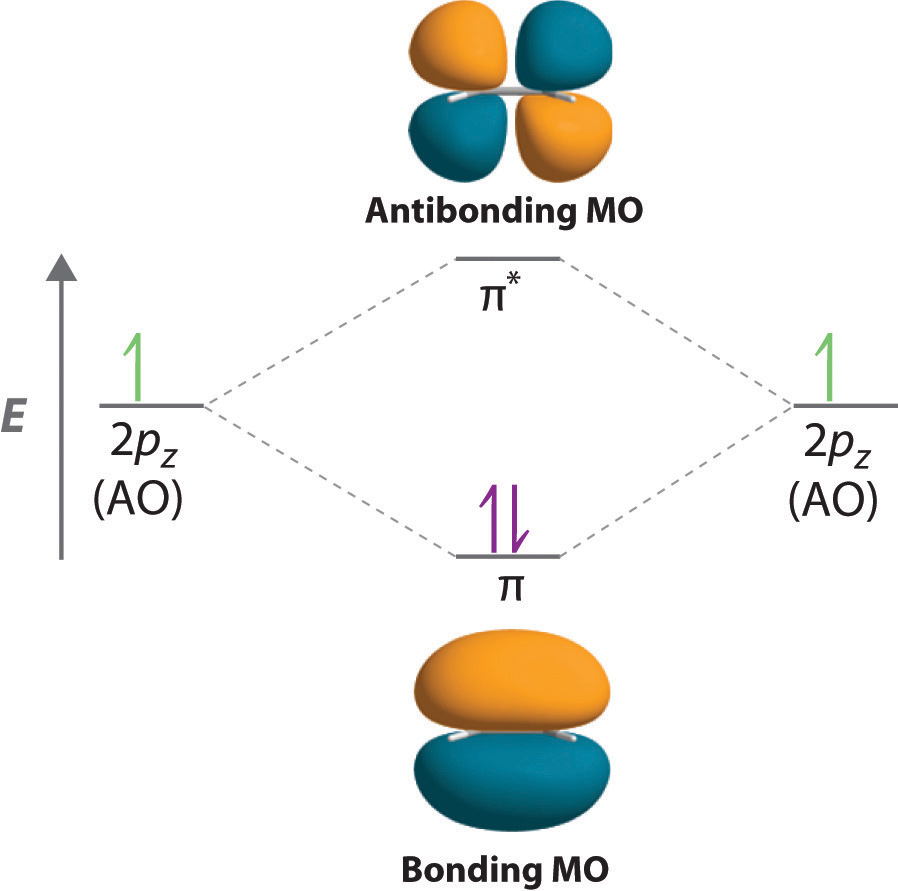
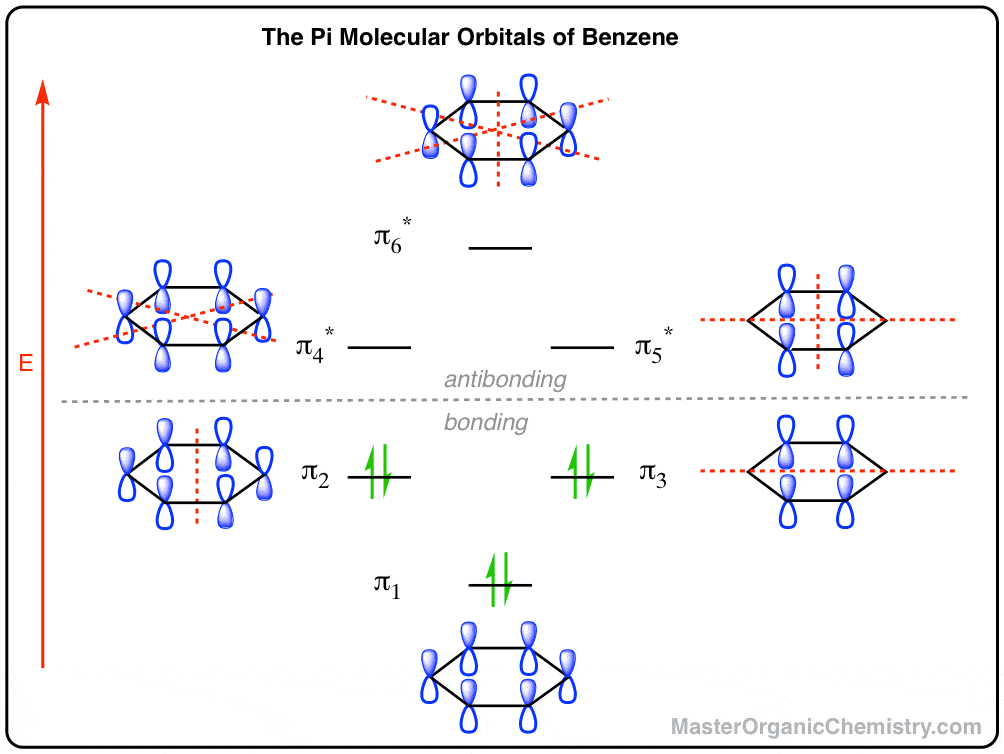
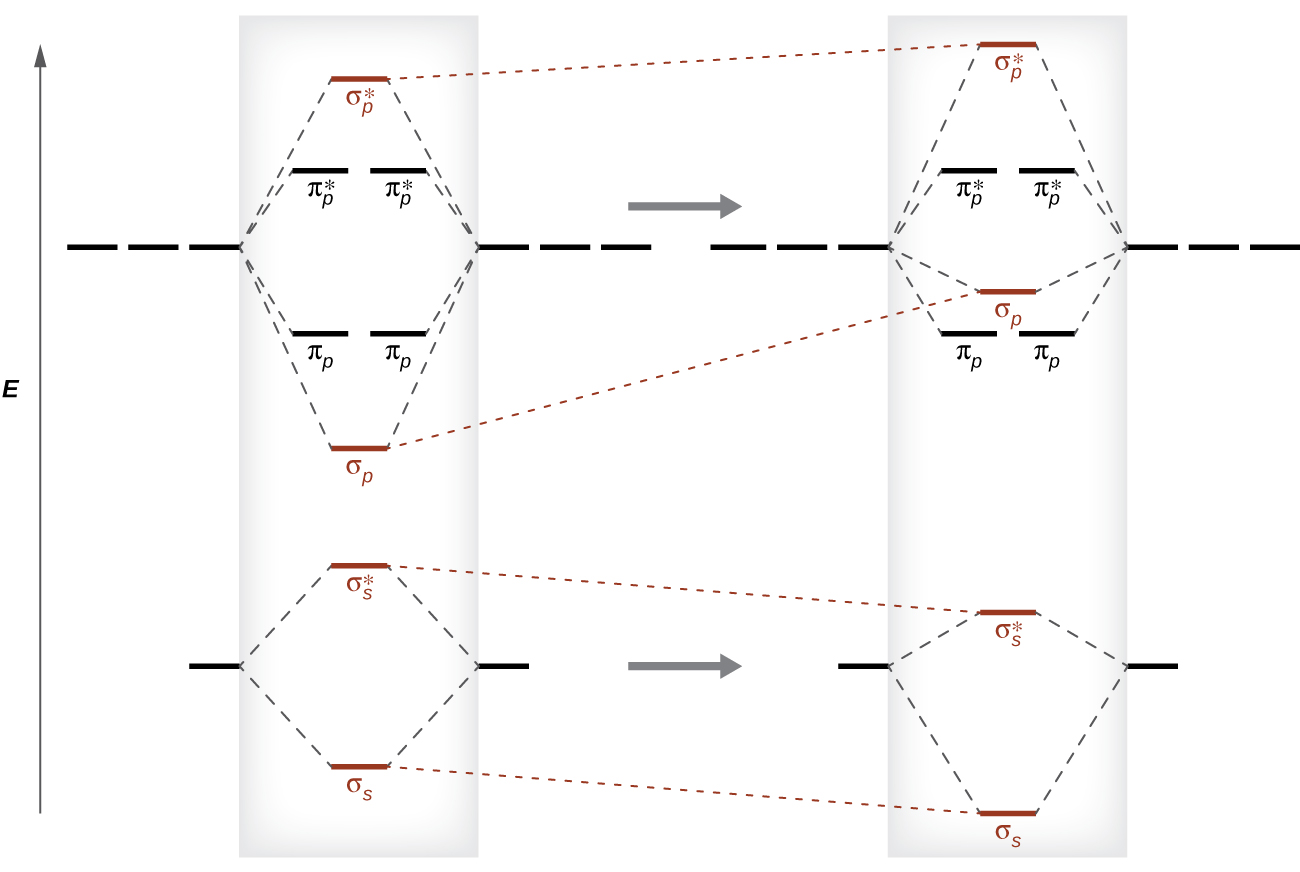
It is possible for the 2s orbital on one atom to interact with the 2p z orbital on the other. This interaction introduces an element of s-p mixing, or hybridization, into the molecular orbital theory. The result is a slight change in the relative energies of the molecular orbitals, to give the diagram shown in the figure below. Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics. In the diagram below we can see the energy differences mentioned above as well as other types of molecular orbitals that appear when the wave function of an atomic orbital of some of the atoms does not have adequate symmetry to be combined linearly with any of the Wave functions of the remaining atoms of the molecule. book I will usually draw pi bonds this way in 3D structures. p orbital lobes are in the plane of the paper. p orbital lobe is in back of the paper. p orbital lobe is in front of the paper. H C C H Each line represents a bond. While the three simple lines of the triple bond appear equivalent,
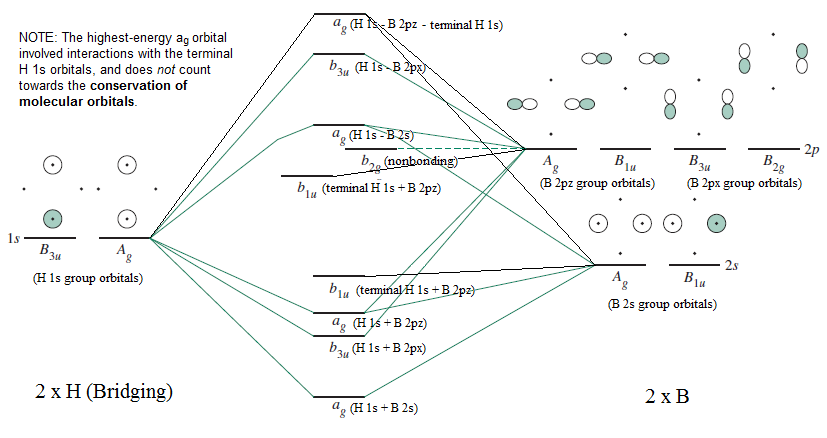
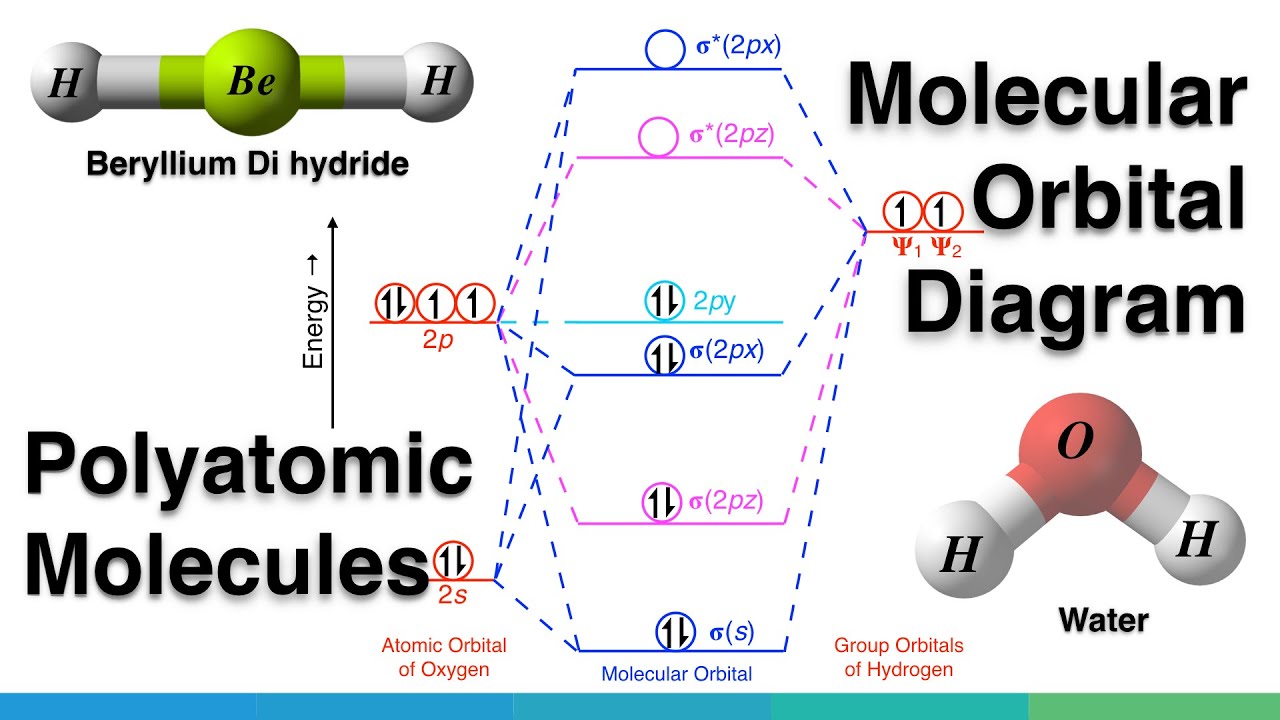
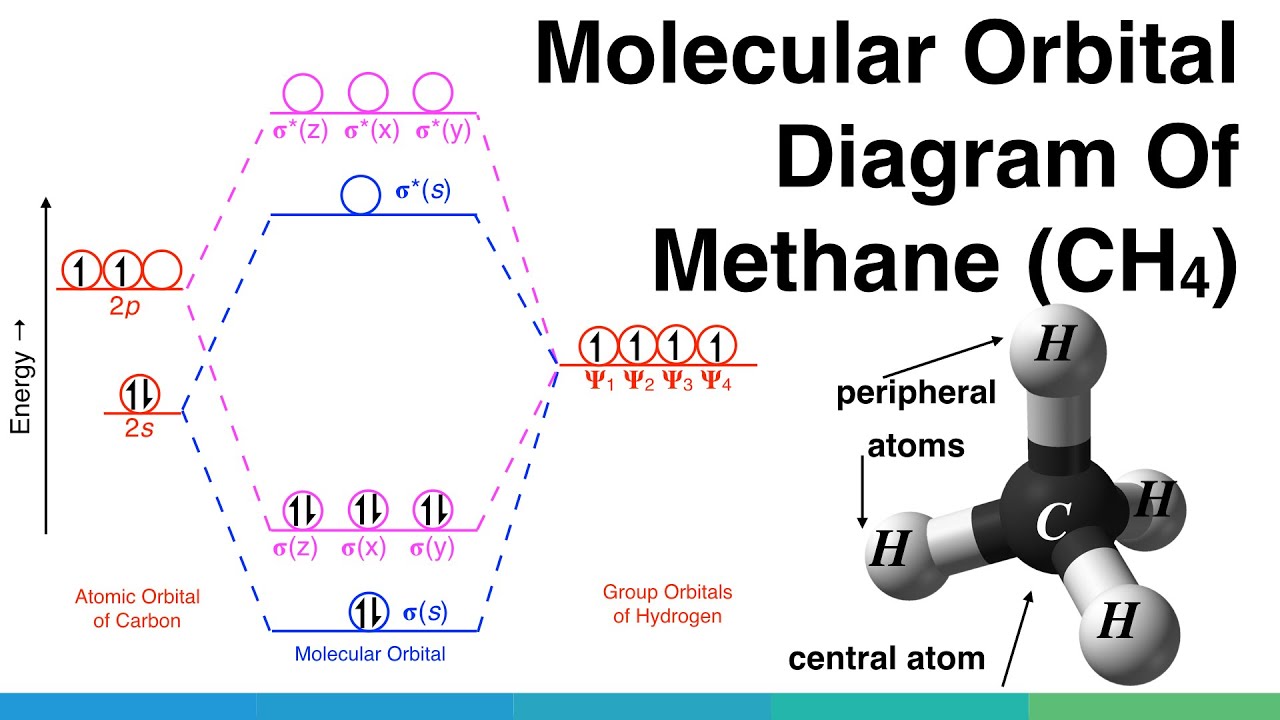
Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules (MO Theory) When two different atoms are bonded together, their molecule is called heteronuclear molecule. where C1 and C2 are two constants having different values for different atoms. Also the molecular orbitals formed are unsymmetrical due to difference in electronegativities. Construct SALCs and the molecular orbital diagram for NH\(_3\). This is the first example so far that has more than two pendant atoms and the first example in which the molecule has atoms that lie in three dimensions (ie it is not flat). Ammonia is a trigonal pyramidal molecule, with three pendant hydrogen atoms. Draw an MO diagram for the reaction above. In other words, start from the one frontier MO on each reactant to build the MO's of the new sigma bond in the product. o Draw the orbital from the base (hydroxide) that is likely to donate its electrons. o Draw the orbital from the acid (aluminum chloride) that is likely to accept electrons. Thus we may construct a molecular orbital energy level diagram, similar to the one used to build up the electronic configurations of the atoms in the periodic table. The molecular orbital energy level diagram (Fig. 8-4) is as fundamental to the understanding of the electronic structure of diatomic molecules as the corresponding atomic orbital ...
#1. Draw the MO diagram for `B_2`. First step is to determine which MO diagram we're using. In this case, we're using the standard one. Draw out the MO diagram and label in the valence electrons. Boron has 2 electrons in the `2s` orbitals and 1 electron in the `2p` orbital. That's it for the MO diagram of `B_2`!
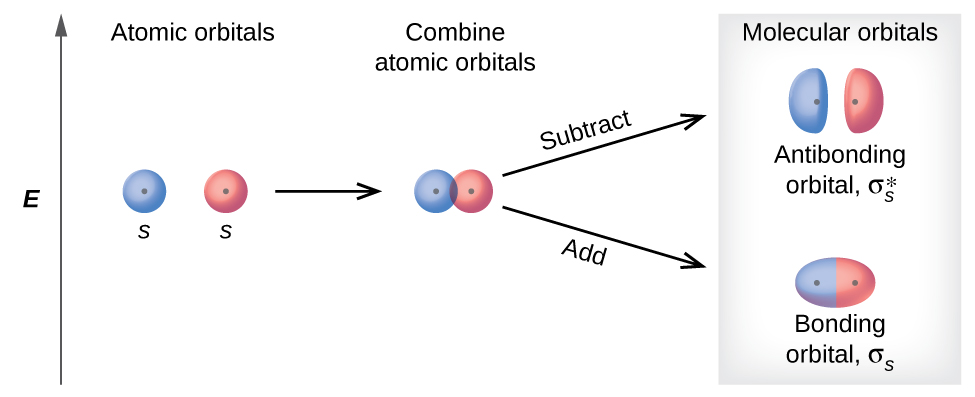
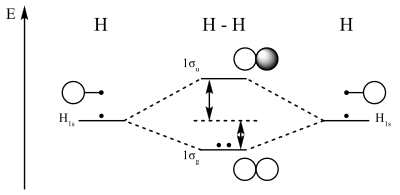
Energy-Level Diagrams. Because electrons in the σ 1 s orbital interact simultaneously with both nuclei, they have a lower energy than electrons that interact with only one nucleus. This means that the σ 1 s molecular orbital has a lower energy than either of the hydrogen 1s atomic orbitals. Conversely, electrons in the \( \sigma _{1s}^{\star } \) orbital interact with only one hydrogen ...
A schematic molecular orbital diagram for the Fe-Fe interaction in an S = I valence-delocalized Fe Fe pair based on effective C v symmetry at the Fe sites and the observed electronic transitions for the valance-delocalized [Fe2S2l cluster is shown in Fig. 15. The dominant interaction (responsible for the S = ground state) is the a overlap between the pair of orbitals, with progressively ...
Construct a "molecular orbital diagram" of the kind shown in this lesson for a simple diatomic molecule, and indicate whether the molecule or its positive and negative ions should be stable. A molecule in which all the electrons are paired, is called diamagnetic while molecule which has one or more unpaired electron is called paramagnetic.
Below, construct an orbital interaction diagram for molecular orbital formation by dragging the image that represents various orbital types (e.g., atomic, bonding, antibonding) into the relevant boxes. b) Identify the number of nodes in each atomic and molecular orbital.
Below, construct an orbital interaction diagram for molecular orbital formation by dragging the images that represent various orbital types (e.g., atomic, bonding, antibonding) into the relevant boxes. Identify the number of nodes in each atomic and molecular orbital.
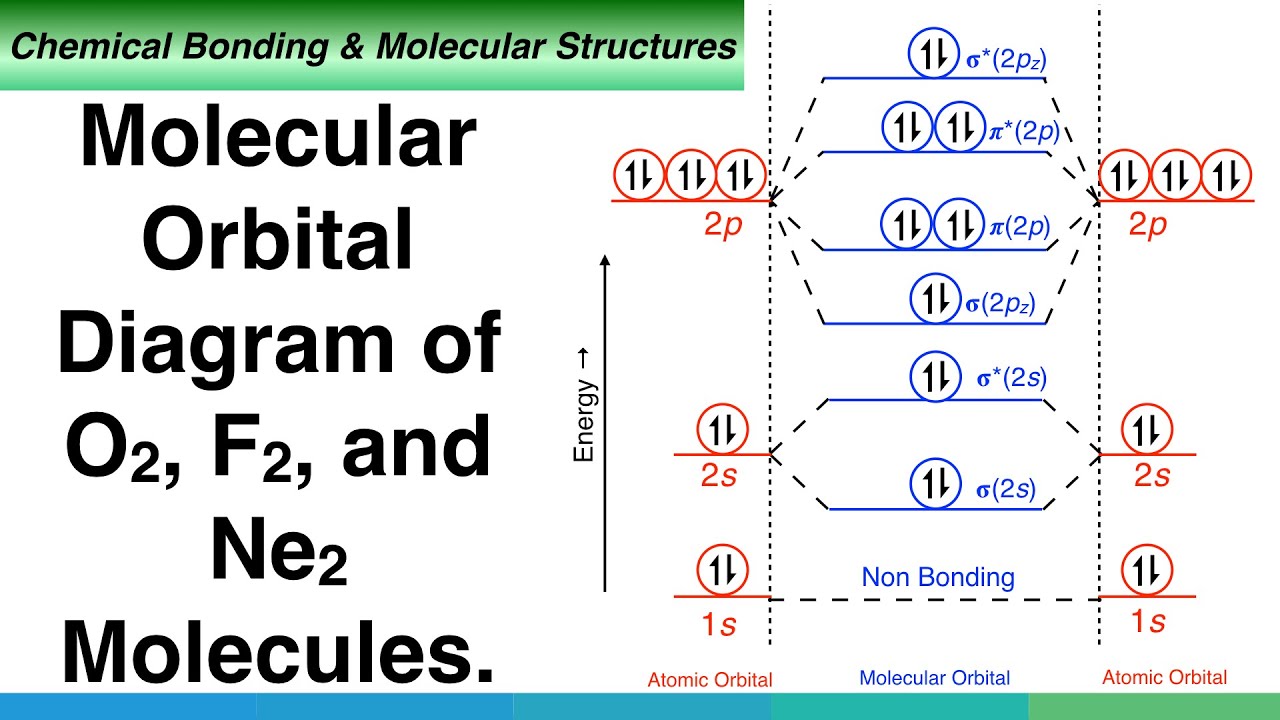
Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Solution We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 8.37.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Solution. We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 11.
The lithium 1s orbital is the lowest-energy orbital on the diagram. Because this orbital is so small and retains its electrons so tightly, it does not contribute to bonding; we need consider only the 2 s orbital of lithium which combines with the 1 s orbital of hydrogen to form the usual pair of sigma bonding and antibonding orbitals.
When two carbons atoms bond, the pi(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals.C2(2-) has a bond order of 3, so i...
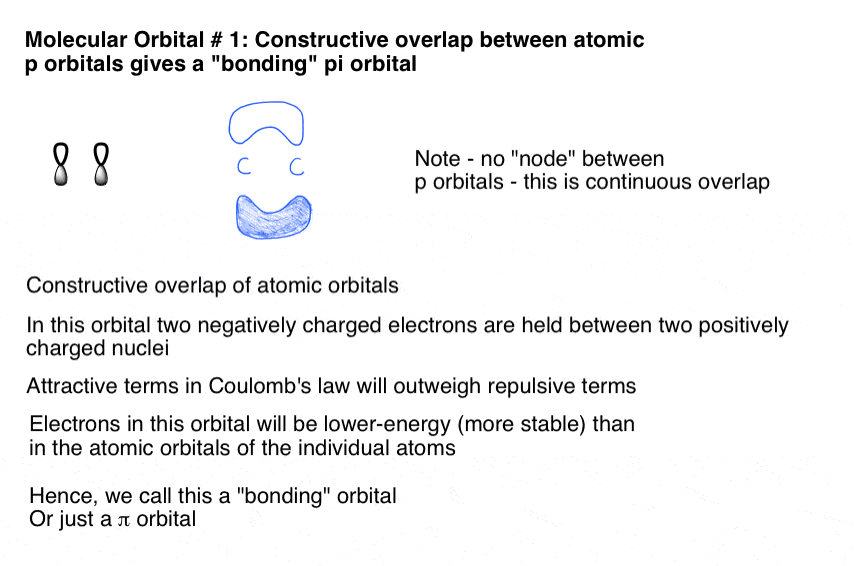
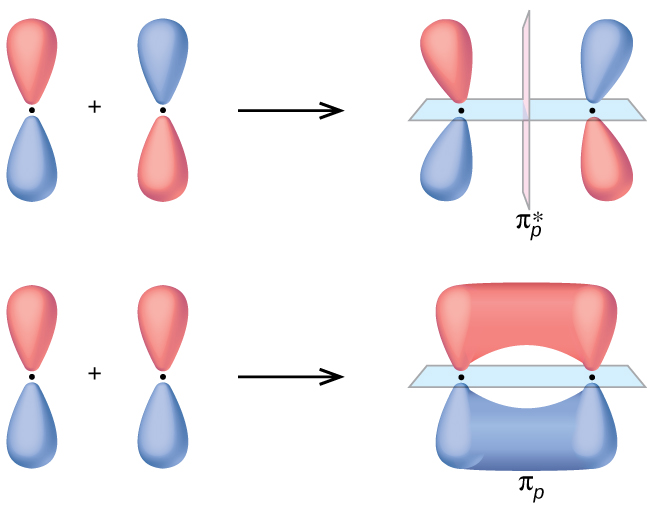
Sigma molecular orbitals formed by p orbitals are often differentiated from other types of sigma orbitals by adding the subscript p below it. So the antibonding orbital shown in the diagram below would be σ* p. Figure 4: The formation of a σ bonding and antibonding orbital using p-orbitals.
In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of F2. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals, which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms, in red and green gradients. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding. σ z y x σ* x y z Construct the molecular orbital diagram for ...
The interaction of the two bonded atoms with the bonding electrons produces a more stable arrangement for the atoms than when separated. Electrons usually occupy these orbitals. A sigma bonds is always the first bond formed between two atoms. Sigma star (σ*) antibonding molecular orbital - Normally this orbital is empty, but if it should
Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer.


/chapter2/pages17and18/page17and18_files/moconnoncon.png)


/chapter2/pages17and18/page17and18_files/connoncon.png)

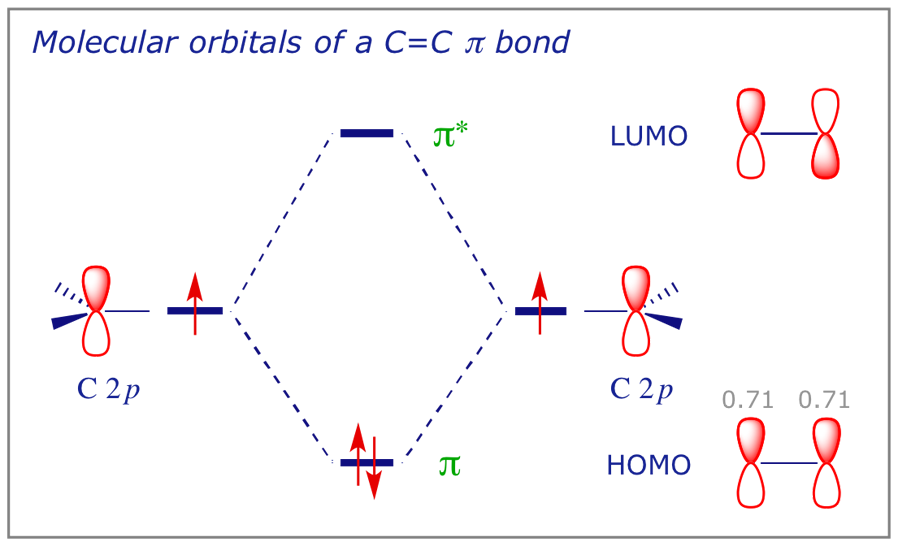

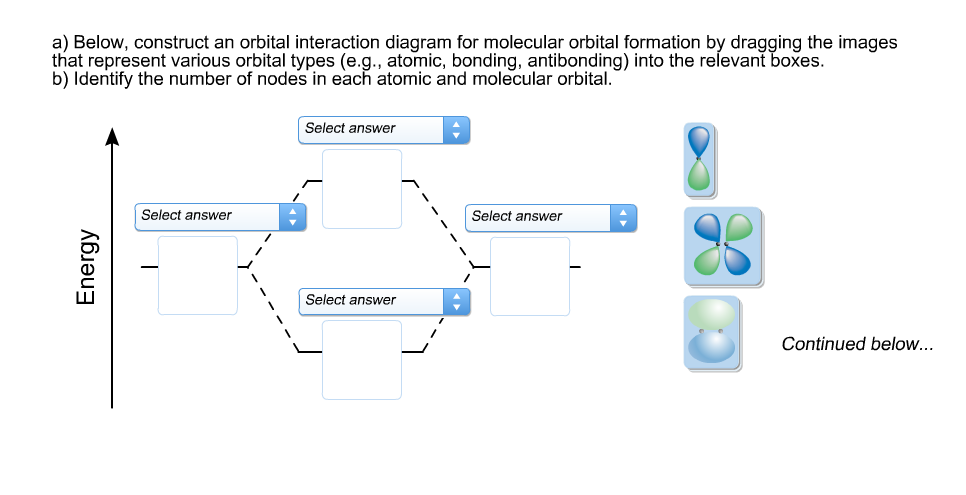

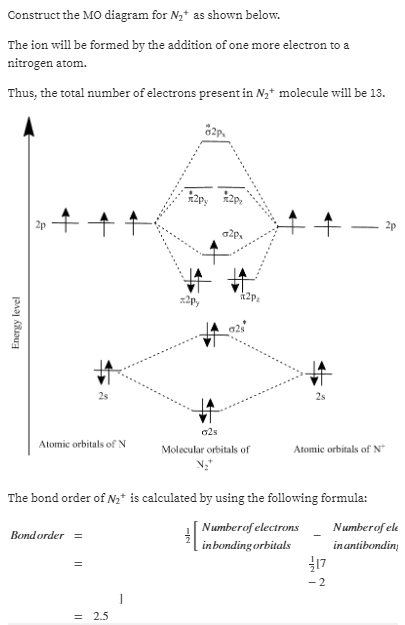

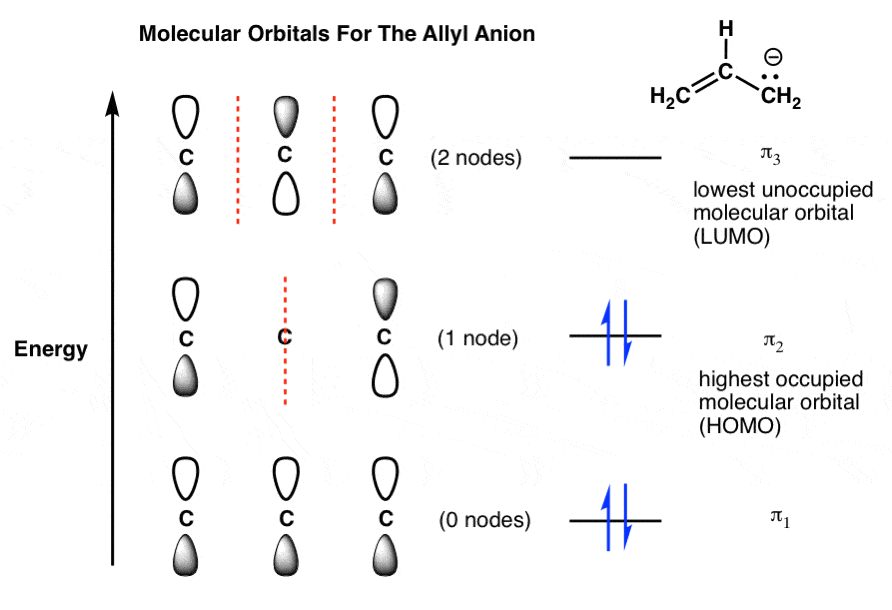



0 Response to "40 below construct an orbital interaction diagram"
Post a Comment