You know that A can undergo two reactions as shown in the below reaction coordinate diagram with one reaction pathway labeled in red and one reaction pathway labeled in blue. The red path leads to Product B, while the blue path leads to Product C. Assuming both reaction pathways occur simultaneously in competition with each other, what is the ... Question: Label the reactants, products, and energy changes in the reaction coordinate diagram below. Define the reaction as endothermic or exothermic. Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic? Reactants Activat energy Products Overall energy change Exothermic Reaction pathway Endothermic.
29.03.2021 · A. Red blood cells (RBC) or Erythrocytes. Red blood cells (RBCs) or erythrocytes are blood cells with terminally differentiated structures lacking nuclei and are filled with the O 2-carrying protein, hemoglobin.; Erythrocytes are the functional component of blood involved in the transportation of gases and nutrients throughout the human body.

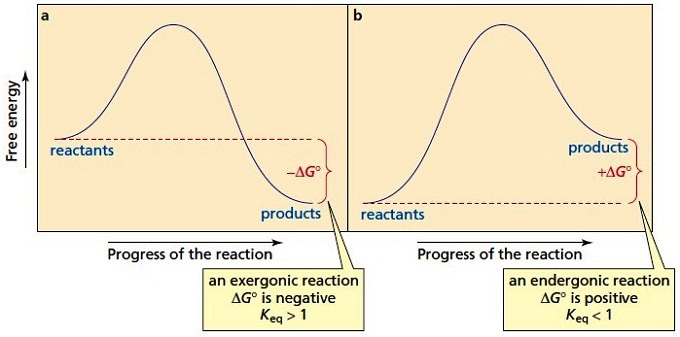
Labeled reaction coordinate diagram
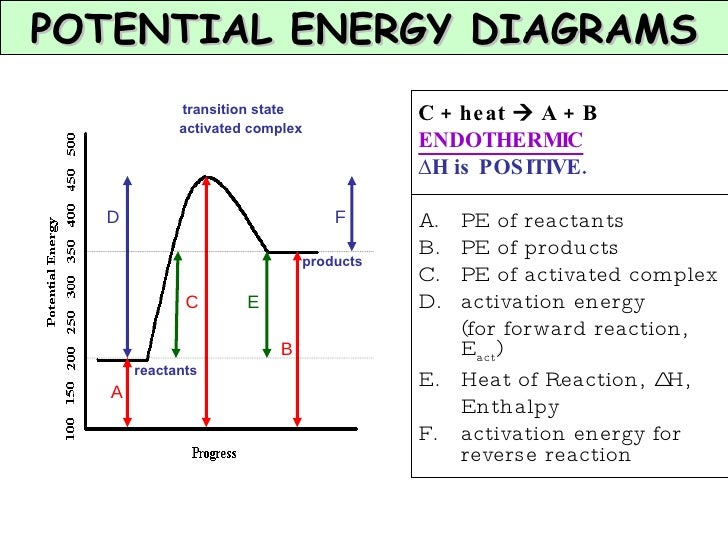
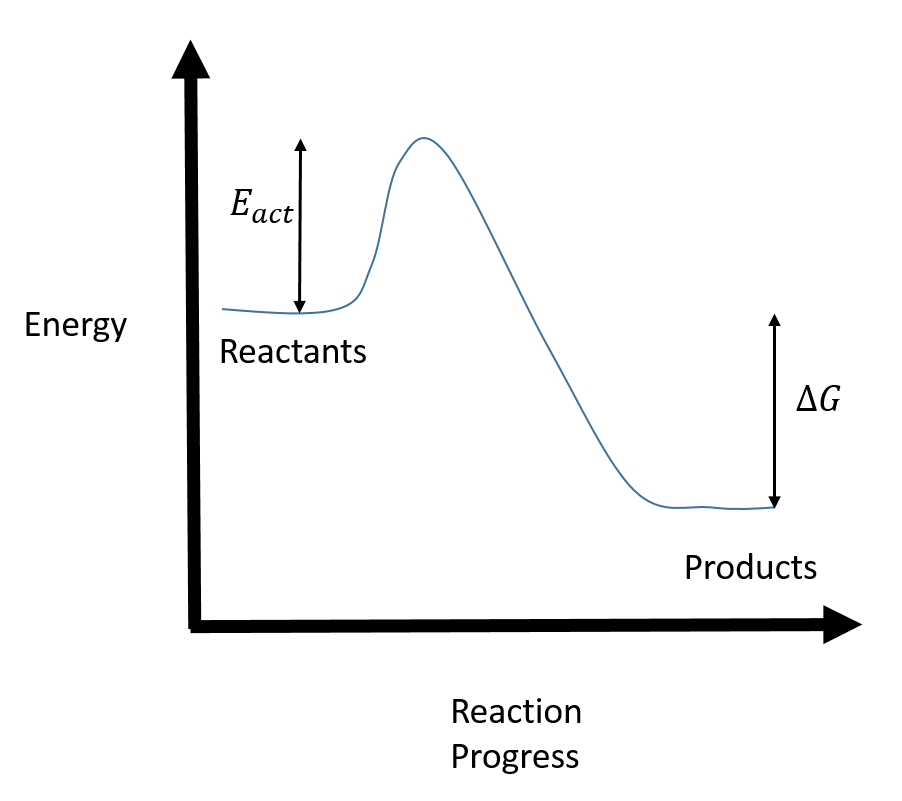
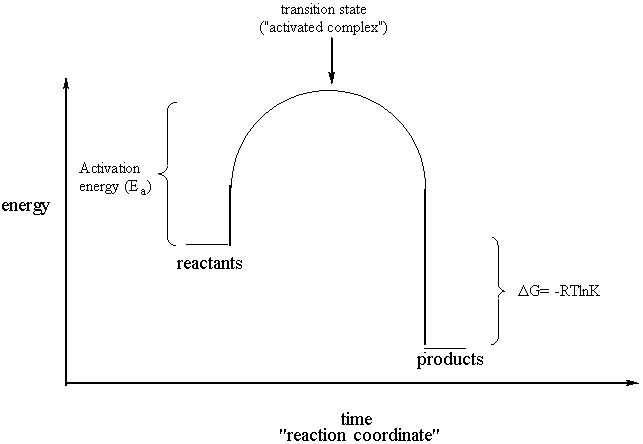
reaction coordinate Br Figure 9.11 Reaction free-energy diagram for the S N1-E1 solvolysis reaction of (CH 3) 3CBr with ethanol.The rate-limiting step,ionization of the alkyl halide (red curve),has the transition state of highest standard free energy.The transition state theory is given. A reaction energy diagram (Figure 1) is presented on the chalk board (complete with axes labeled: potential energy vs. reaction coordinate (or reaction progress)). The activation energy, Ea, (the change in energy from reactants to the top of the "hill") is labeled. Provide a detailed reaction coordinate diagram consistent with this scenario; include as much detail as possible. 2f) Assume for the moment that it is not known which step of Mechanism 1 is rate-determining. Consider an experiment conducted using 18OH2 (oxygen-18 labeled water) and stopped prior to complete hydrolysis of the starting ester F.
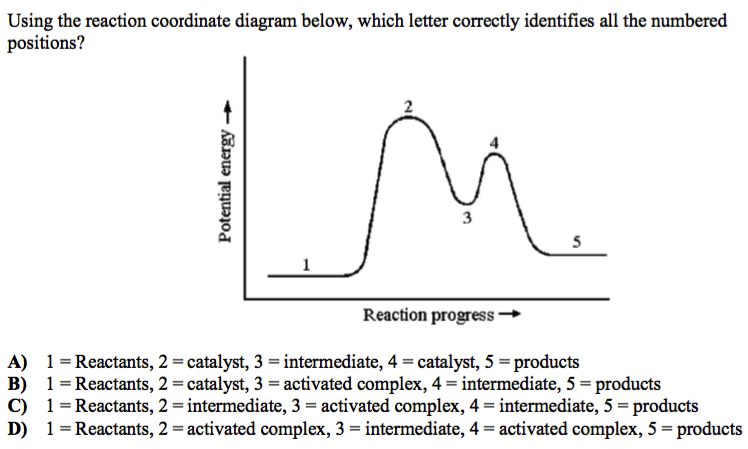
Labeled reaction coordinate diagram. Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Label the following reaction coordinate diagram by matching between letters and numbers: (diagram in kinetics pt 2 folder in energy diagram folder on desktop) 1- J ... -Label the multi-step reaction energy diagram below using the letters corresponding to the labels on the left. There are more labels than needed; each label can be used only once. You know that A can undergo two reactions as shown in the below reaction coordinate diagram with one reaction pathway labeled in red and one reaction pathway labeled in blue. The red path leads to Product B, while the blue path leads to Product C. Assuming both reaction pathways occur simultaneously in competition with each other, what is the ... Draw and correctly label reaction coordinate diagrams that represent each of the two situations and describe how each diagram reflects the thermodynamics and kinetics of the situation.
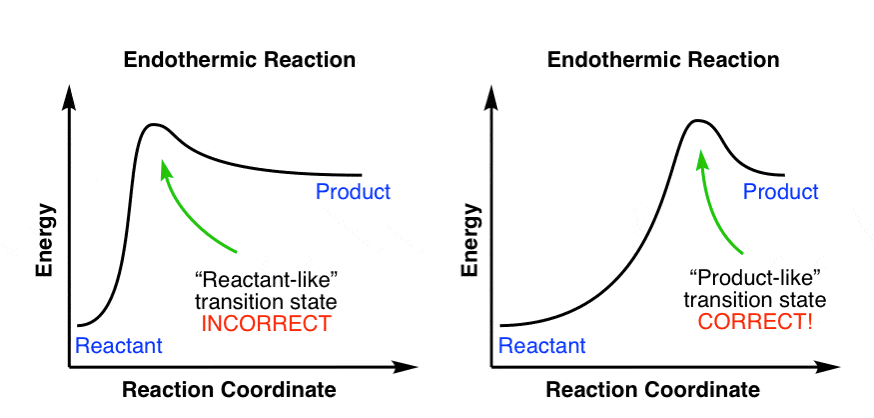
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (1 rating) A is activation energy B is …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: In the energy diagram shown below, the AH of the reaction is labeled by D. Energy Reaction coordinate True False. The diagram below shows us the IRC, or intrinsic reaction coordinate for the process (for definitions, see here), the reaction proceeding from left to right as shown in the scheme above, with a (free energy) barrier of 14.4 kcal/mol and exothermic by a similar amount (wB97XD/6-311G(d,p) with a continuum solvation correction for water). One first notices that it is not the smooth bell-shaped ... About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... c) Using a reaction coordinate diagram and the Hammond postulate, plot if you would expect an early or late transition state for the first step (A to B) of this reaction. Label this plot "C". (2 points) PE Reaction coordinate d) Based on your answer to part (c), what range would you expect the β LG values fall within? Explain your answer.
Chemistry questions and answers. Label the following reaction coordinate diagram. Energy Reactant (s) Transition State Product (s) Activation Energy (forward) Transition State Activation Energy (forward) Energy Enthalpy of Enthalpy of Reaction Product (s) Reaction AHrxn Reactant (s) Reaction Coordinate Reaction Coordinate Reset Zoom. We never include both forces of an action-reaction pair. Convert the free-body diagram into a more detailed diagram showing the x ... directed away from the interface. The source of this force is object B, and this normal force is labeled accordingly. Since object B has a tendency to slide down, object A has a tendency to slide up with respect to the interface, so the friction [latex]{f ... Explains the energy versus reaction coordinate diagram. Relates the activation energies for the forward and reverse reactions of an exothermic reaction to th... The reaction coordinate free energy profile of a typical reaction under Curtin-Hammett control is represented by the following figure: The ratio of products only depends on the value labeled ΔΔ G ‡ in the figure: C will be the major product, because the energy of …
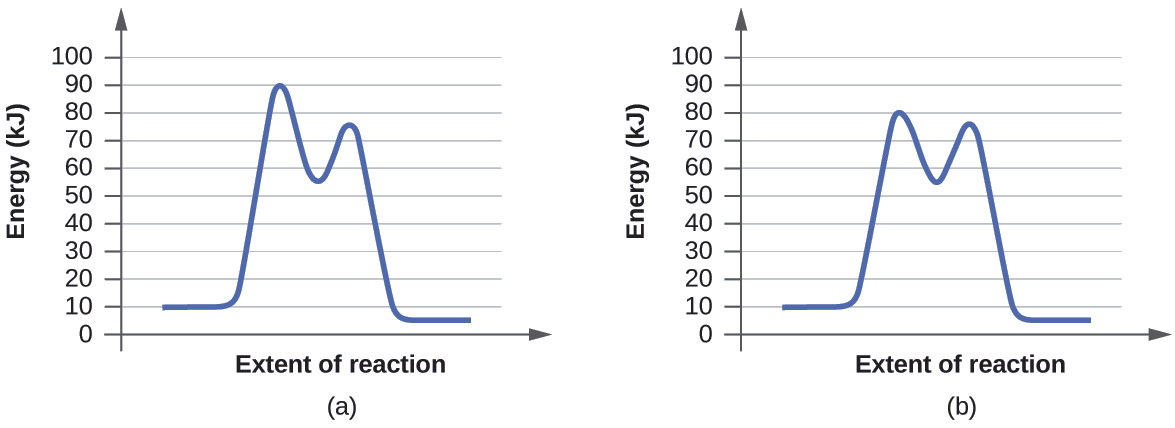
Typically, we envision reactions proceeding left to right along the reaction coordinate, so often, the activation energy is only noted for the forward reaction. The activation energy on the diagram below shows the barrier to be 102.6 kJ mol -1 .
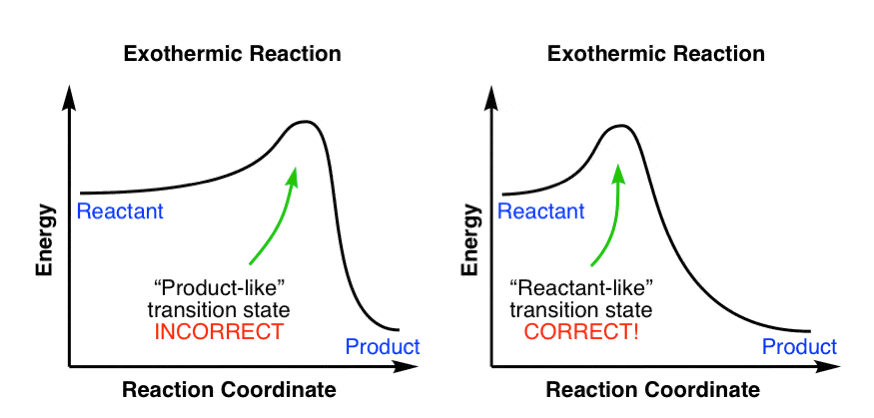
Start by drawing and labeling the reaction coordinate diagram. Since we know that is negative, the products must be lower in energy than the reactants. Now, the question wants you to find the activation energy if we were to reverse the reaction. In other words, we want to start at the products and end up with the reactants.
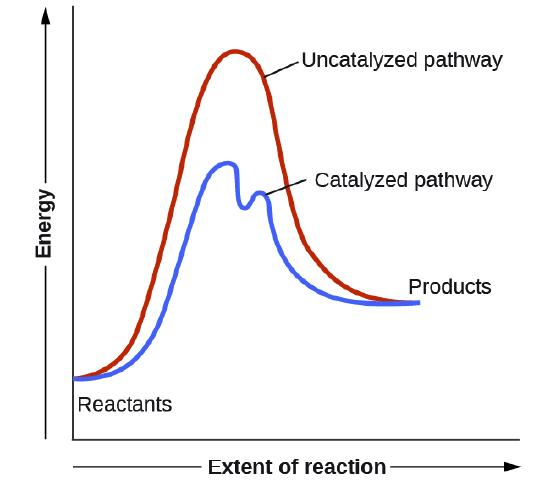
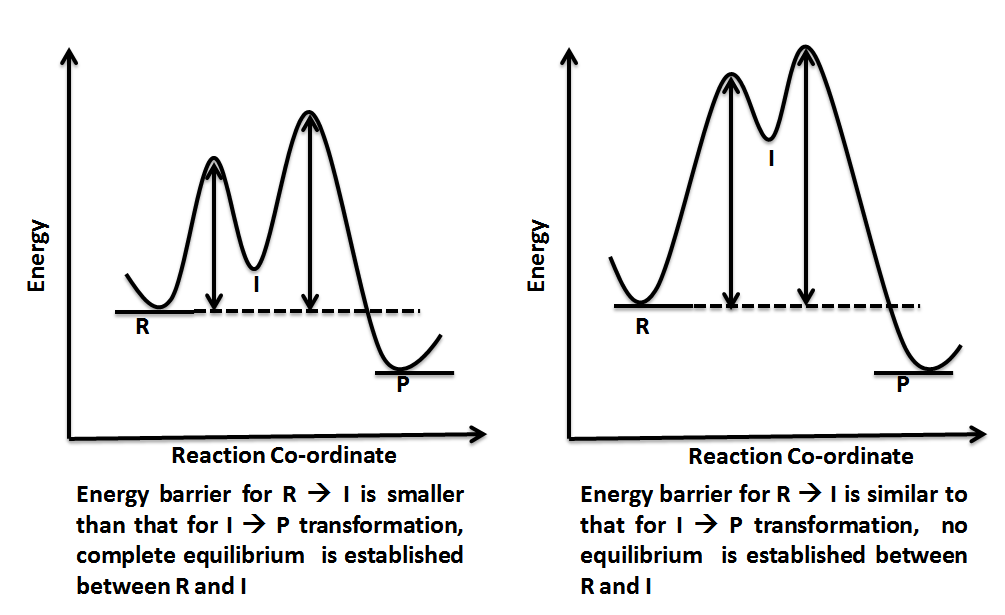
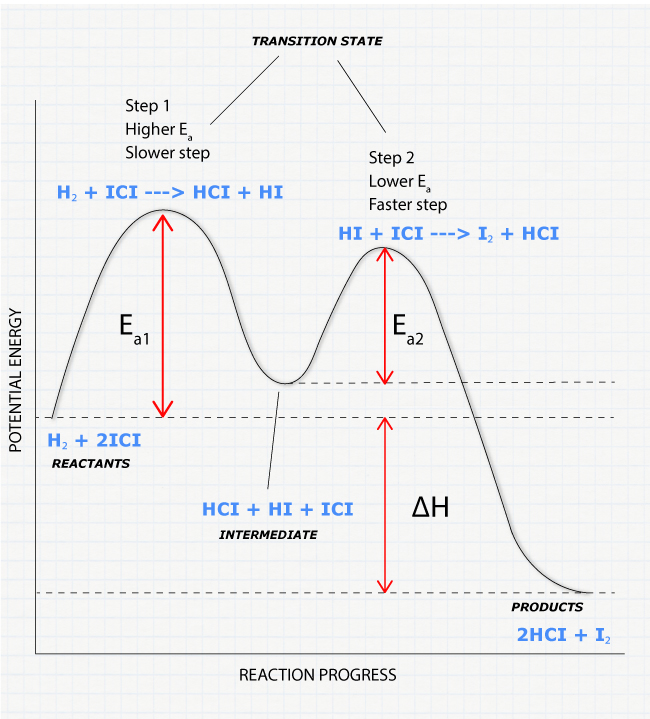
One such reaction is catalytic hydrogenation, the process by which hydrogen is added across an alkene C=C bond to afford the saturated alkane product. A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1.
Label the reactants, products, and energy changes in the reaction coordinate diagram below. Define the reaction as endothermic or exothermic.
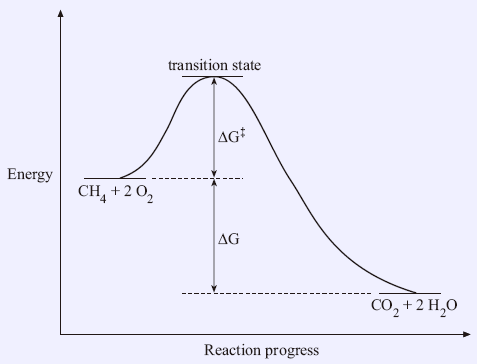
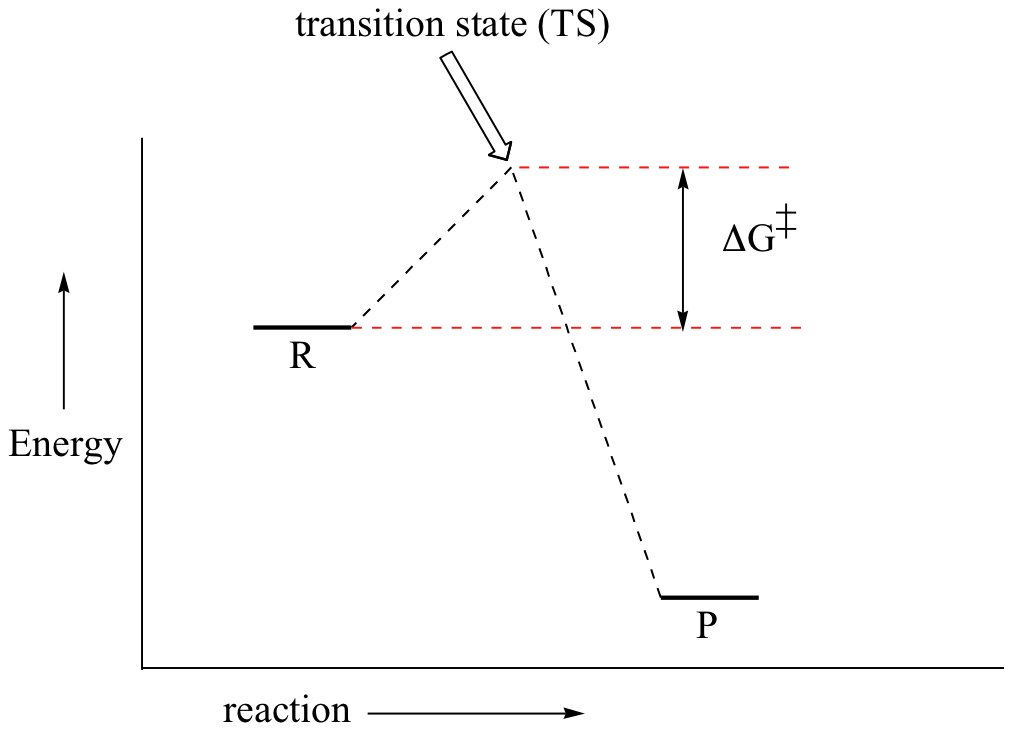
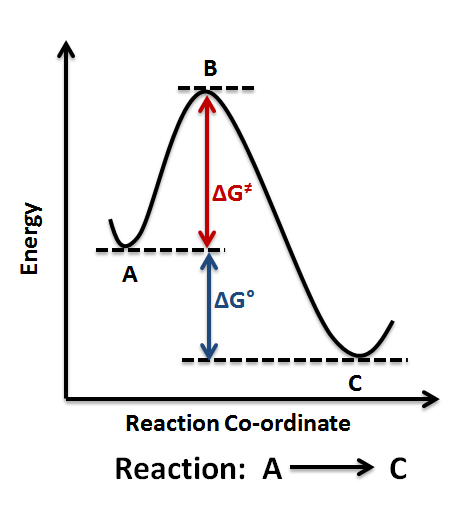
Figure 2: Reaction coordinate diagram for the bimolecular nucleophilic substitution (\(S_N2\)) reaction between bromomethane and the hydroxide anion. from Wikipedia. The activation energy (\(E_a\)), labeled \(\Delta{G^{\ddagger}}\) in Figure 2, is the energy difference between the reactants and the activated complex, also known as transition ...
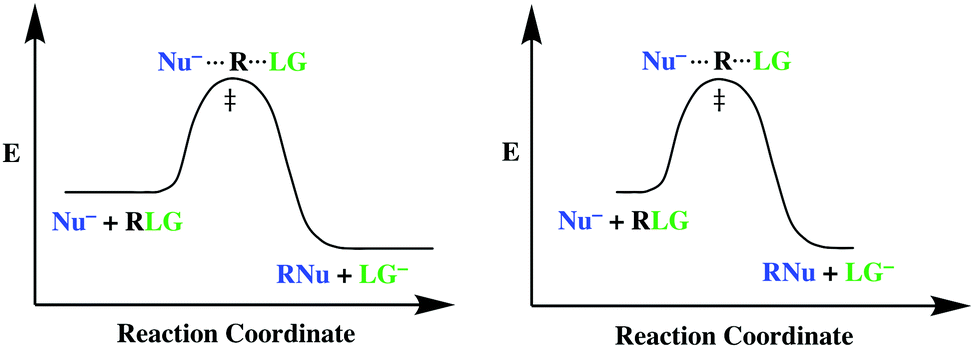
Figure 9.3 shows the reaction coordinate diagram in the S N 2 reaction of hydroxide ion with chloromethane to give methanol and chloride ion. We see that the transition state contains both hydroxide ion and the substrate. As the reaction proceeds through the transition state, a bond forms between carbon and hydroxide ion, and the bond between carbon and chlorine breaks.
Label the following reaction coordinate diagram. enthalpy of reaction, reactant(s), reaction coordinate, activation energy (reverse), transition state, < 0, > 0, activation energy (forward), = 0, product(s), energy
Solution for Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for a fast, stepwise, exothermic reaction. Label reactants, products, intermediate(s), transition state(s),…
The diagram shows that the vector is first drawn to scale in the indicated direction; a parallelogram is sketched about the vector; the components are labeled on the diagram; and the result of measuring the length of the vector components and converting to m/s using the scale. (NOTE: because different computer monitors have different resolutions, the actual length of the …
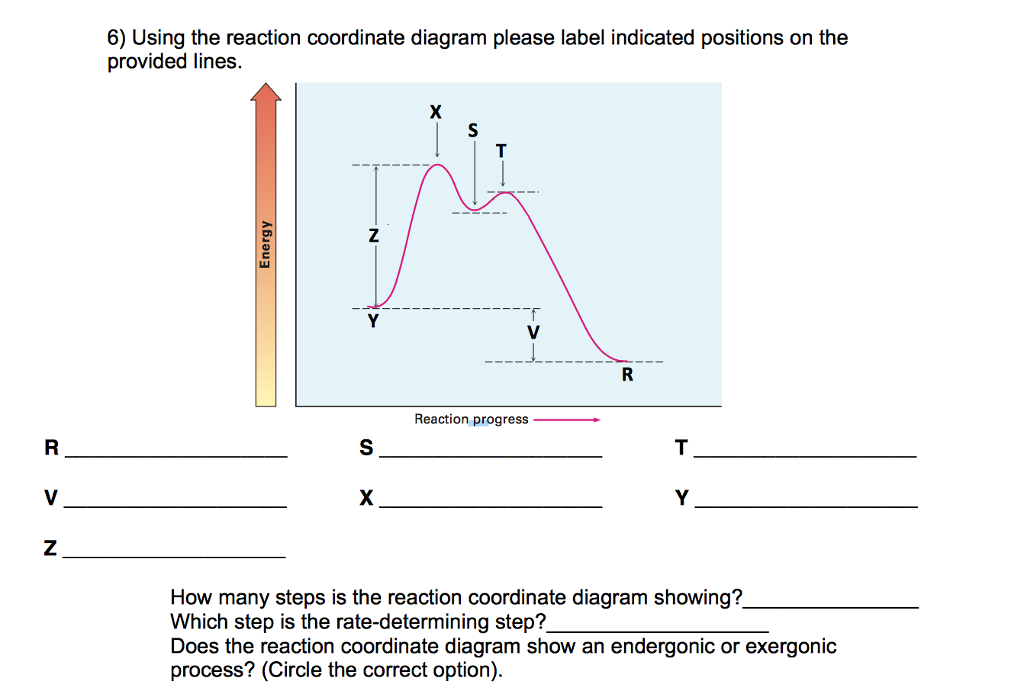
Label the energy diagram for a two‑step reaction. January 7, 2022 thanh. Label the energy diagram for a two-step reaction. enthalpy change transition state starting materials RX+H products rate-limiting transition state intermediates activation energy reaction coordinate.
Construct the gas phase Reaction Coordinate Diagram for the Cl + CH3Cl SN2 reaction by plotting the relative energy in kJmol 1 versus Cl + C | {z} Distance H3 Cl. Place the Reaction Coordinate Diagram on the graph provided below and plot the energies on a relative energy scale. Label the various species along the reaction pathway. 0 5 10 15 20 ...
Problem Details. Label the following reaction coordinate diagram by matching between letters and numbers: All Chemistry Practice Problems Energy Diagram Practice Problems. Q. A reaction coordinate diagram is shown below for the reaction of A to form E. Answer the following questions.i) Identify the transition state (s)?ii) W...
Three additional examples of the Hunsdiecker reaction and a proposed mechanism for the transformation will be shown above by clicking on the diagram. Note that the meta- dihalobenzene formed in reaction 4 could not be made by direct halogenation reactions, since chlorine and bromine are ortho/para-directing substituents. Also, various iodide derivatives …
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
UML state machine, also known as UML statechart, is an extension of the mathematical concept of a finite automaton in computer science applications as expressed in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) notation.. The concepts behind it are about organizing the way a device, computer program, or other (often technical) process works such that an entity or each of its …
Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction as above but add the activation energy, E a, for the catalyzed reaction on the appropriate curve in this diagram and label it. This is a bit more subtle since .Types of catalysts (article) | Kinetics | Khan AcademySection The Rate of a Reaction
8. A lit fuse was required to initiate the reaction in the flare. Use this information, along with your previous results to correctly label the reaction coordinate diagram shown below. Use these symbols to label each item in your diagram: reactants (R), products (P), reaction enthalpy (AH), and activation energy (Ea).
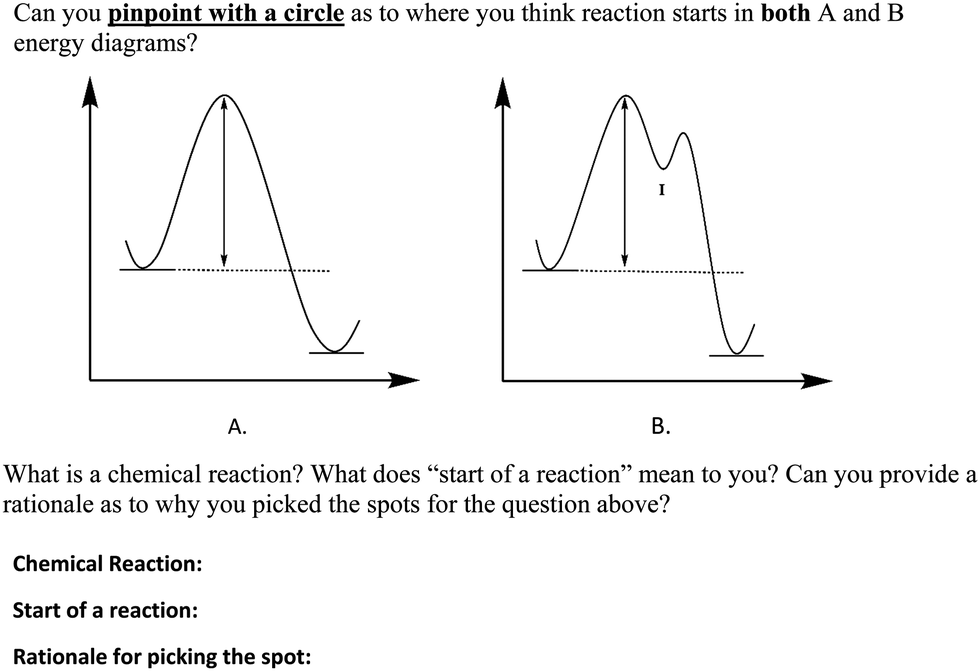
The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a chemical reaction. In this example, B is at a lower total energy than A. This is an exothermic reaction(heat is given off) and should be favorable from an energy standpoint. The energy difference between A and B is E in the diagram.
Provide a detailed reaction coordinate diagram consistent with this scenario; include as much detail as possible. 2f) Assume for the moment that it is not known which step of Mechanism 1 is rate-determining. Consider an experiment conducted using 18OH2 (oxygen-18 labeled water) and stopped prior to complete hydrolysis of the starting ester F.
transition state theory is given. A reaction energy diagram (Figure 1) is presented on the chalk board (complete with axes labeled: potential energy vs. reaction coordinate (or reaction progress)). The activation energy, Ea, (the change in energy from reactants to the top of the "hill") is labeled.
reaction coordinate Br Figure 9.11 Reaction free-energy diagram for the S N1-E1 solvolysis reaction of (CH 3) 3CBr with ethanol.The rate-limiting step,ionization of the alkyl halide (red curve),has the transition state of highest standard free energy.The
















0 Response to " "
Post a Comment