43 Use The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To Determine Which Of The Following Are Paramagnetic.
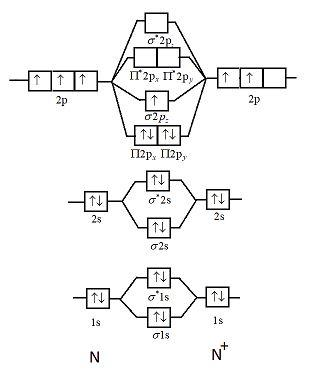
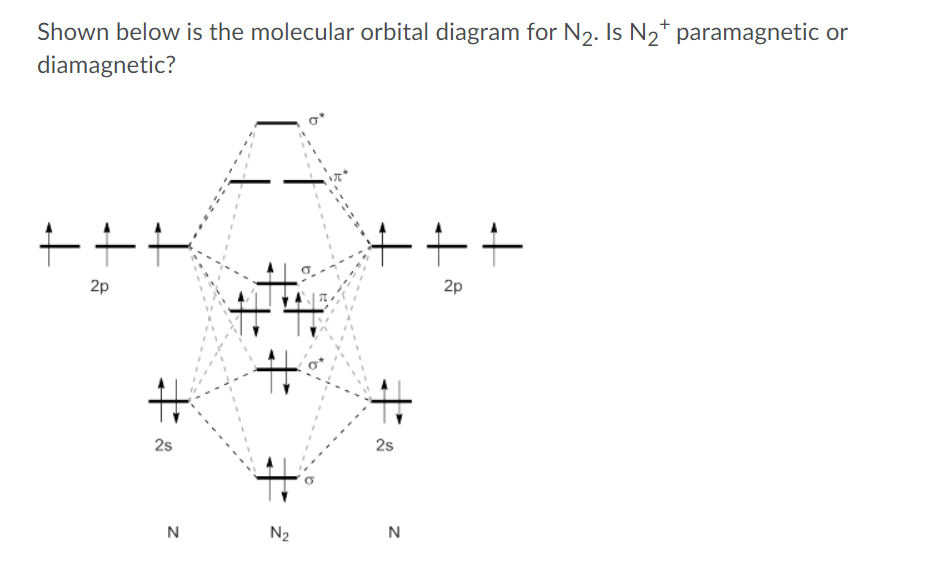
chem test 3 (ch 6&7) Flashcards - Quizlet Using molecular orbital theory, determine whether F2, F2−, or (F2)^2− would have the strongest bond. F2 Using molecular orbital theory, determine the magnetism of O2 and O2−. Both O2 and O2− are paramagnetic. Formaldehyde, an organic compound frequently used to preserve biological specimens, has the formula H2CO. Use molecular orbital diagrams to predict which of the ... asked Aug 5, 2019 in Chemistry by z1stxfile. general-chemistry. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. asked Jul 15, 2019 in Chemistry by brittanyr9777. general-chemistry. Nitrogen can lose an electron to form N2+. Given the molecular orbital configuration of N2 [core] (σ2s)2 (σ *2s)2 ...
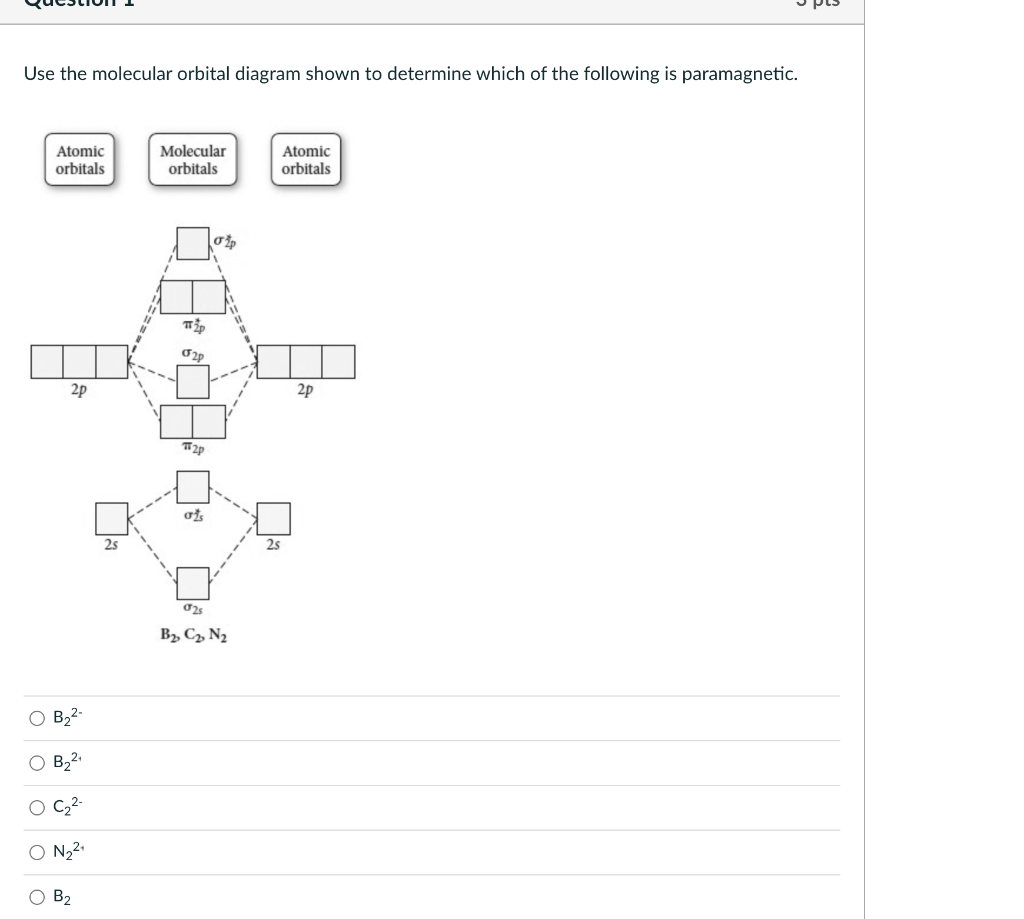
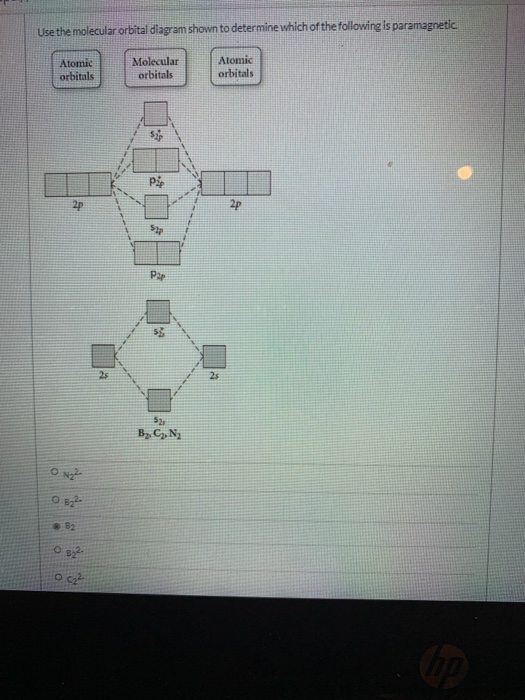
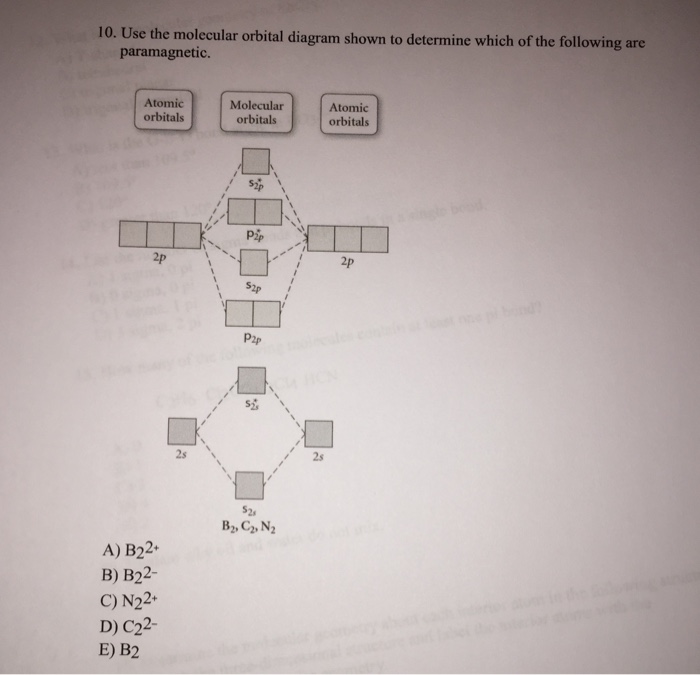
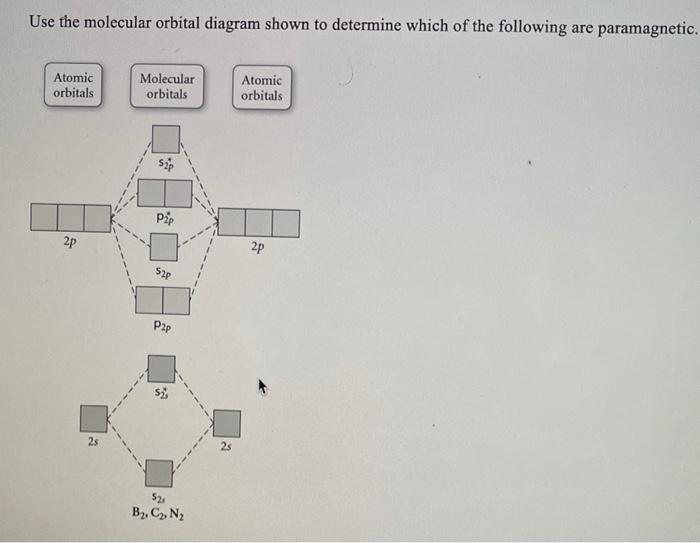
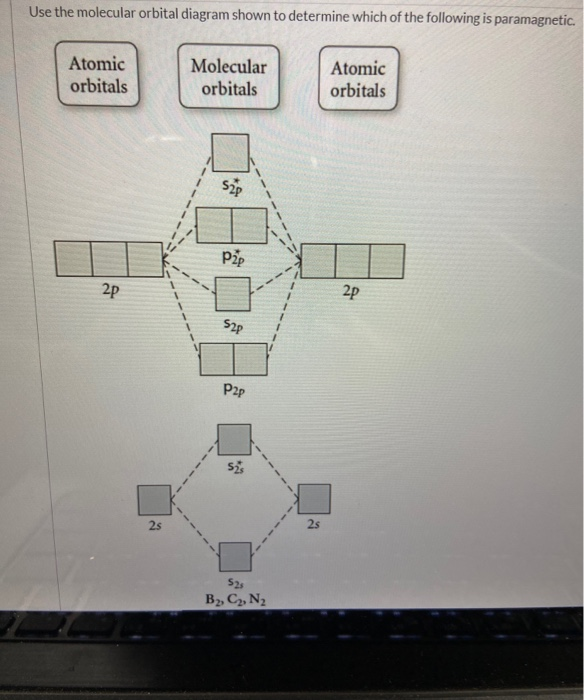
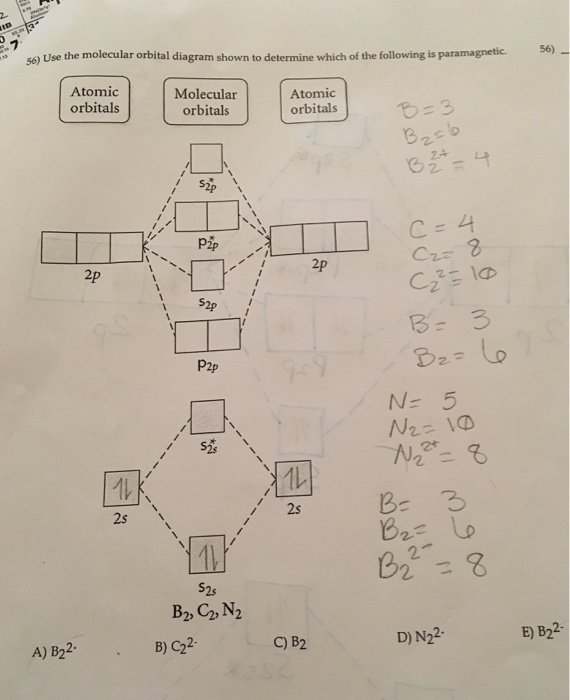
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. 10. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals pã µ 2p 2p P2p 2s /2s 2s A) B22 B) B22- C) N22 D) C22- E)...
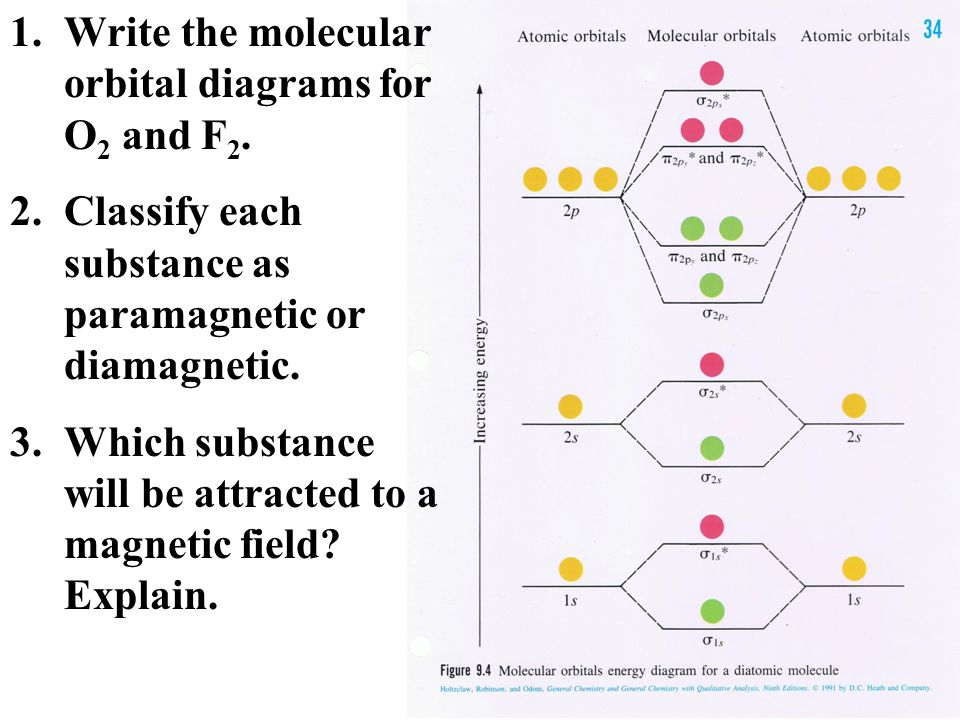
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic.
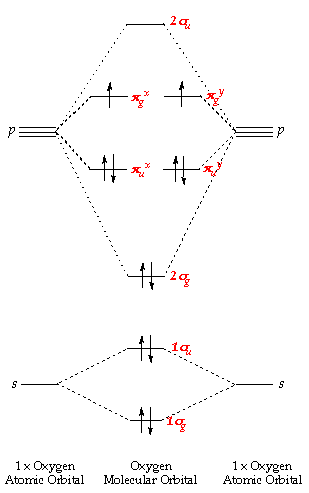
chemistry 1a Chapter 10 Flashcards | Quizlet Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable A) Ne2^2⁺ B) F2^2⁺ C) F2^2⁻ D) F2 E) O2^2⁺ E). O2^2⁺ Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2 2⁺ ... opentextbc.ca › 8-4-molecular-orbital-theory8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory – Chemistry Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Solution. We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 11. 9.10: Molecular Orbital Theory Predicts that Molecular ... To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for \(\ce{O2}\), we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in Figure 9.10.1 . We again fill the orbitals according to Hund's rules and the Pauli principle, beginning with the orbital that is lowest in energy.
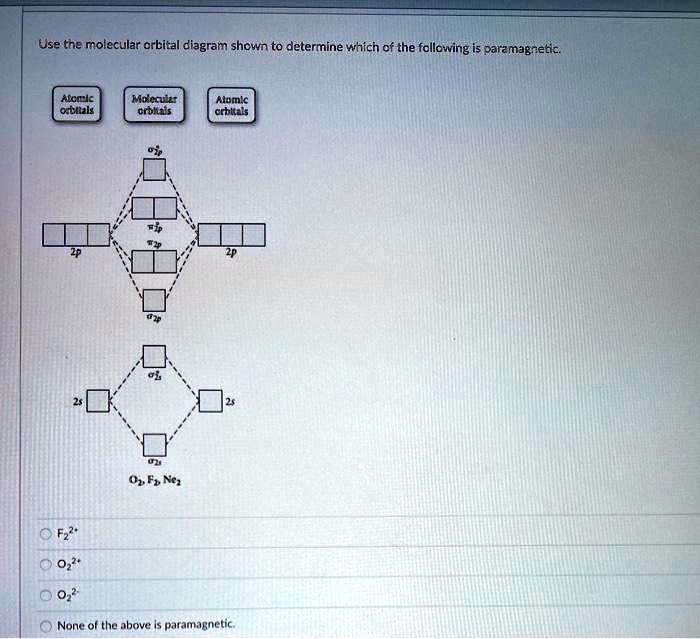
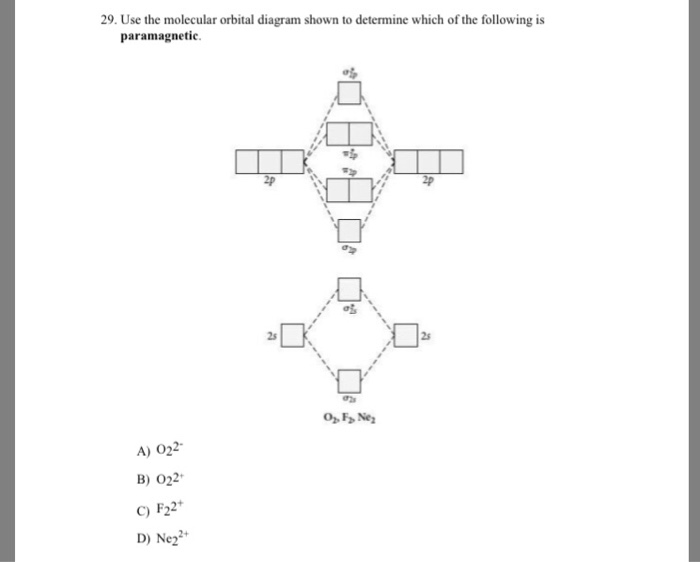
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic.. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to... | Clutch Prep Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A. Ne 22+ B. O 22+ C. F 22+ D. O 22- E. None of the above are paramagnetic. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Concept Videos. Recitation Week 10 (test 3 - Recitation 2) - GitHub Pages 2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) B2^2+ B) B2^2-C) N2^2+ D) C2^2-E) B2 en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Electron_paramagneticElectron paramagnetic resonance - Wikipedia Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) or electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy is a method for studying materials with unpaired electrons.The basic concepts of EPR are analogous to those of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), but the spins excited are those of the electrons instead of the atomic nuclei. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Electron_configurationElectron configuration - Wikipedia The form of the periodic table is closely related to the electron configuration of the atoms of the elements. For example, all the elements of group 2 have an electron configuration of [E] ns 2 (where [E] is an inert gas configuration), and have notable similarities in their chemical properties.
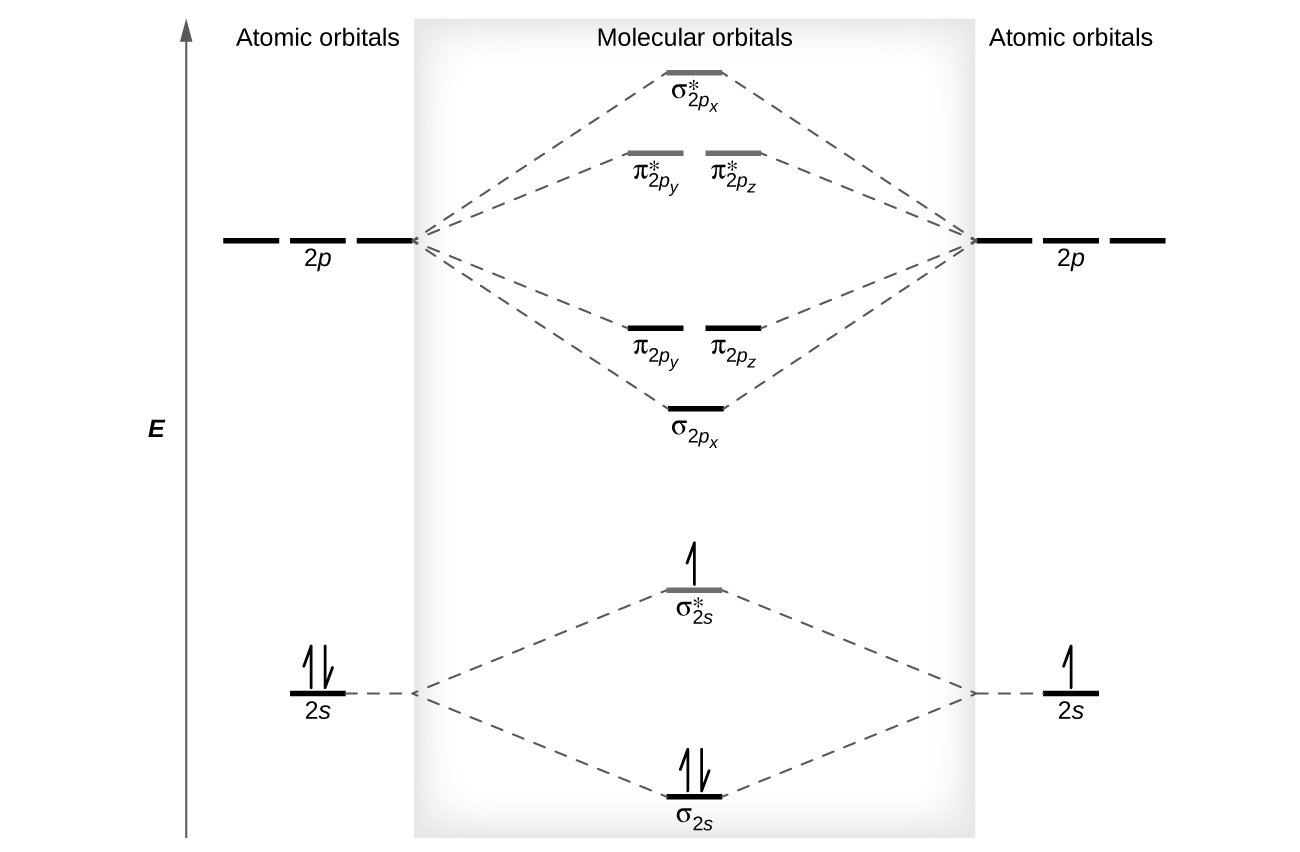
Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds. Answered: Draw the molecular orbital diagram… | bartleby Answered: Draw the molecular orbital diagram… | bartleby. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. B22+, B2, C22-, B22-, and N22+. Study Chapter 4 Pre-Exam Flashcards - Quizlet Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. O₂²⁺ Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to... | Clutch Prep Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine the bond order for NO +.Is NO+ paramagnetic or diamagnetic? In molecular orbital names, s = sigma and p = pi.a. 3, paramagneticb. 2, paramagneticc. 2.5, paramagneticd. 2, diamagnetice. 3, diamagnetic
Quiz 1 Flashcards | Quizlet 2. The bond order of a homonuclear diatomic molecule can be decreased by. removing electrons from a bonding MO or adding electrons to an antibonding MO. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) N2^2+. B) B2^2+. C) B2^2-. D) C2^2-. E) B2. quizlet.com › 538030724 › module-two-chem-101Module Two Chem 101 Problems Flashcards - Quizlet Complete the MO diagram (below) to determine if NO is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. NO is paramagnetic NO has 11 electrons in the valence shell. This means that there is an unpaired electron in a π* antibonding orbital. Solved Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to ... Chemistry questions and answers. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals 2p 2P קני 25 02 02, F2 Nez F2 None of the ions are paramagnetic. 2+ 02 2-. sansona.github.io › articles › mo-diagramsMO Diagrams - GitHub Pages #1. Draw the MO diagram for `B_2`. First step is to determine which MO diagram we're using. In this case, we're using the standard one. Draw out the MO diagram and label in the valence electrons. Boron has 2 electrons in the `2s` orbitals and 1 electron in the `2p` orbital. That's it for the MO diagram of `B_2`!
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which ... 55) Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O 2 2 ⁻ B) Ne 2 2 ⁺ C) O 2 2 ⁺ D) F 2 2 ⁺ E) None of the above are paramagnetic. Answer: D Diff: 4 Page Ref: 10.8
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to... | Clutch Prep Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.a.F22+b. Ne22+c. F22-d. O22+e. F2
› 44472489 › Physical_Chemistry_a(PDF) Physical Chemistry a molecular approach ... - Academia.edu Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. Electron configuration of - Answered by a verified Tutor We use cookies to give you the best possible experience on our website.
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. a. f22+ b. ne22+ c. f22- d. o22+ e. f2
CH 101, exam #4 Flashcards - Quizlet use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. F2 ^2+ how many of the following ionic compounds are insoluble in water? NaCl KI Mg(NO3)2 CaCO3 PbI2. 2. give the theoretical yield, in moles, of CO2 from the reaction of 4.00 moles of C8H18 with 4.00 moles of O2
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine ... Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.A) N22+ B) B2C) B22+D) C22-E) C22+
Answered: Draw a molecular orbital diagram and… | bartleby Question. Draw a molecular orbital diagram and use it to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. F 22+. Ne 22+. O 22-. O 22+. None of the above is paramagnetic. check_circle.
is b22+ paramagnetic or diamagnetic Paramagnetic species use molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic ( \ce { }! At least one unpaired electron and diamagnetic is the only paramagnetic species is not supported by inbox API.
Which of the following is paramagnetic? (use the mole... Which of the following is paramagnetic? (use the molecular orbital diagram) a) Li 2. b) Be 2. c) B 2. d) C 2. e) N 2. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules Concept Videos.
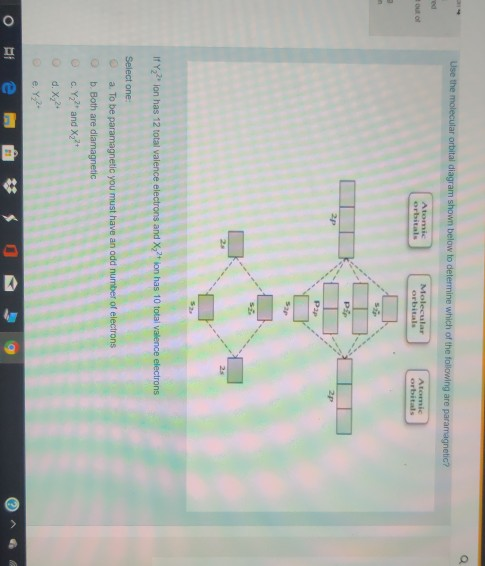
Solved Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to ... Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following ions is fare paramagnetic. X 2+ , Y22+ Consider that Y22+ ion has 12 total valence electrons, and X 2+ ion has 10 total valence electrons Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals PSP 2P 2p PP 2 23 52 Select one: a. Both ions are diamagnetic b.
Solved Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to ... This problem has been solved! See the answer. See the answer See the answer done loading. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. Ne 22 ⁺. O 22 ⁻.
OneClass: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to ... Use molecular orbital theory to describe the bonding in the following. For each one, find the bond order and decide whether it is stable. Is the substance diamagnetic or (a) Be_2 bond order Is it stable? stable unstable Is it diamagnetic or paramagnetic? diamagnetic paramagnetic (b) Ne_2 bond order Is it stable? stable unstable Is it diamagnetic or paramagnetic? diamagnetic paramagnetic
Solved Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to ... We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: 10. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals pふ 2p 2p P2p 2s /2s 2s A) B22 B) B22- C) N22 D) C22- E) B2.
9.10: Molecular Orbital Theory Predicts that Molecular ... To obtain the molecular orbital energy-level diagram for \(\ce{O2}\), we need to place 12 valence electrons (6 from each O atom) in the energy-level diagram shown in Figure 9.10.1 . We again fill the orbitals according to Hund's rules and the Pauli principle, beginning with the orbital that is lowest in energy.
opentextbc.ca › 8-4-molecular-orbital-theory8.4 Molecular Orbital Theory – Chemistry Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Solution. We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 11.

Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.A) N22+ B) B2C) B22+D) C22-E) C22+
chemistry 1a Chapter 10 Flashcards | Quizlet Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable A) Ne2^2⁺ B) F2^2⁺ C) F2^2⁻ D) F2 E) O2^2⁺ E). O2^2⁺ Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2 2⁺ ...
















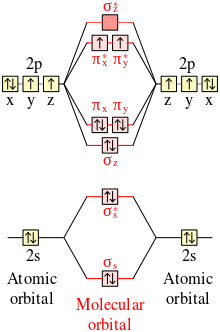
0 Response to "43 Use The Molecular Orbital Diagram Shown To Determine Which Of The Following Are Paramagnetic."
Post a Comment