45 consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide.
Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide, CO2. 730 In what phase is CO2 at 4 bar and -10°C? Solid Liquid liquid Pressure (bar) gas solid Gas 5.11 10 31.1 78.5564 Temperature (°C) Starting from 4 bar and -10°C, what phase change would eventually result from an increase in pressure? deposition melting condensation sublimation O vaporization Carbon dioxide is a one-carbon compound with formula CO2 in which the carbon is attached to each oxygen atom by a double bond.A colourless, odourless gas under normal conditions, it is produced during respiration by all animals, fungi and microorganisms that depend directly or indirectly on living or decaying plants for food.
Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide.In what phase is CO2 at 72 atm and 0 °C?a) solidb) liquidc) gas Starting from the point described above, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure?a) condensationb) depositionc) sublimationd) vaporizatione) meltingf) freezing.
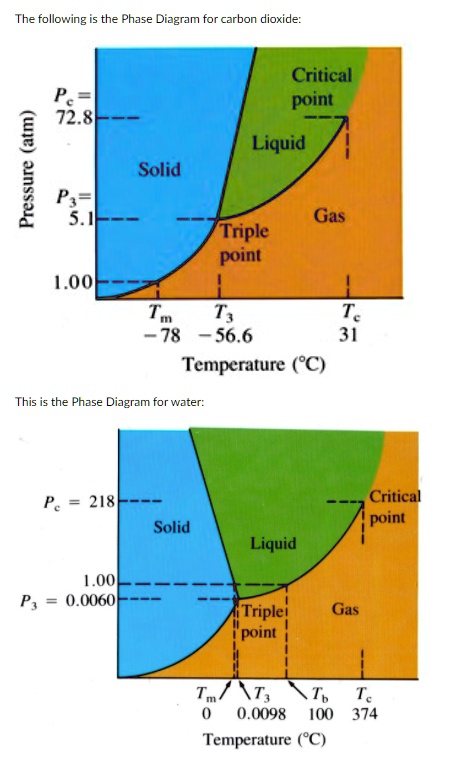
Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide.
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide. 73.0F In what phase is CO, at 72 atm and 0 °C? solld iquid liquid solid gas 5.11 gas 1.0 Incorrect -78.5 -56.4 31.1 Temperature ("C) Starting from the same point, 72 atm and 0 °C, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure? sublimation freezing melting deposition vaporization condensation Pressure (atm) Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page - find all choices before answering. 001 10.0 points Consider the phase diagrams for water and carbon dioxide. Explain the following observations: A thin wire with weights attached is draped over a block of "dry ice" and a second wire with weights is draped over a block of ice. Problem: Consider this phase diagram for carbon.Which phases are present at the lower triple point?a) diamond b) graphite c) gas d) liquid Which phase is stable at 105 atm and 1000 K?a) gas b) liquid c) diamond d) graphite Starting from the lower triple point, what action(s) would produce liquid carbon?a) raise the temperature b) raise the pressure c) lower the pressured) lower the temperature ...
Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide.. Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide, CO_2, below. In what is CO_2 at 4 bar and -10^degree C? solid liquid gas Starting from the point described above, what phase change would eventually result from an increase in pressure? freezing vaporization deposition sublimation melting. Question: Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide ... Problem: Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide in what phase is CO 2 at 4 atm and -10 °C? a. Solid b. Gas c. Liquid. Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide. In what phase is CO2 at 72 atm and 0 degree C? Starting from the point described above, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure? Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ...
The phase diagram for carbon dioxide. The only thing special about this phase diagram is the position of the triple point which is well above atmospheric pressure. It is impossible to get any liquid carbon dioxide at pressures less than 5.11 atmospheres. That means that at 1 atmosphere pressure, carbon dioxide will sublime at a temperature of ... Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide, 73.0 In what phase is Co, at 72 atm and 0 °C? solid liquid solid Pressure (atm) gas liquid 5.11 gas 1.0 -78,5 -56.4 Temperature ("C) 31.1 Starting from the same point, 72 atm and 0 °C, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure? Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide. 73.0 In what phase is Co, at 72 atm and 0 °C? solid liquid liquid Pressure (atm) gas O solid gas 5.11 1.0 31.1 -78.5 -56.4 Temperature (°C) Starting from the same point, 72 atm and 0 °C, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure? Q. Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide in what phase is CO 2 at 4 atm and -10 °C? a. Solid b. Gas c. Liquid. Q. The direct change of a substance from a solid to a gas is called ____.a. evaporationb. sublimationc. condensationd. solidification. Q. Complete this table describing the shape and volume of each phase.
Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide. In what phase is CO_2 at 72 atm and 0 degree C? solid gas liquid Starting from the point described above, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure? condensation deposition sublimation freezing vaporization melting ; Question: Consider this phase diagram for carbon ... Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide. In what phase is CO2 at 72 atm and 0 degree C? Starting from the point described above, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure? Question: Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide. In what phase is CO2 at 72 atm and 0 degree C? 4) Consider the phase diagrams for water and carbon dioxide given in the text on page 315. Explain the following observations: A thin wire with weights attached is draped over a block of "dry ice," a second wire with weights is draped over a block of ice. The wire cuts through the ice but not through the "dry ice." Answer Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in [link] as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously).
View Adobe Scan Feb 22, 2021 (9).pdf from CHM 112 at Mercer University. Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide. Phase changes in carbon dioxide 10,000 1,000 Liquid S
Problem Details. Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide. In what phase is CO2 at 4 atm and -10 °C? a) liquid b) gas c) solid Starting from the same point, 4 atm and -10 °C, what phase change would eventually result from an increase in pressure? a) sublimation b) melting c) freezing d) condensation e) vaporization f) deposition.
Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide. In what phase is CO 2 at 72 atm and 0°C?. a. solid. b. liquid. c. gas. Starting from the point described above, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure?
Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide In what phase is CO2 at 4 atm and -10 Degree C ? Solid Gas Liquid Starting from the point described above what phase change would eventually result from an increase in pressure? Melting freezing deposition sublimation vaporization condensation.
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide. 73.0 In what phase is CO, at 25 atm and -65 °C? solid liquid liquid gas solid gas 5.11 1.0 3D -78.5 -56.4 31.1 Temperature (°C) Starting from the same point, 25 atm and -65 °C, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure? freezing sublimation melting vaporization condensation deposition Pressure (atm)
Compare and contrast the phase diagrams of water and carbon dioxide. a) why doesn't CO 2 have a normal boiling point and normal melting point, whereas water does?. b) The slopes of solid-liquid lines in the phase diagram of H 2 O and CO 2 are different. What do the slopes of solid-liquid lines indicate in terms of the relative densities of the solid and liquid states for each substance?
Which phases are present at the upper triple point? solid I diamond liquid gas graphite Which phase is stable at loo atm and 6000 K? graphite gas diamond liquid Starting from the lower triple point, what action(s) would produce liquid carbon? Consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide. In what phase is CO2 at 4 atm and -10 degree C?
(b) With the decrease in pressure, both the fusion and boiling point of carbon dioxide will decrease. (c) For carbon dioxide, the critical temperature is 3 1. 1 o C and critical pressure is 73.0 atm. If the temperature of carbon dioxide is more than 3 1. 1 o C, it can not be liquefied, however large pressure we may apply.
Problem: Consider this phase diagram for carbon.Which phases are present at the lower triple point?a) diamond b) graphite c) gas d) liquid Which phase is stable at 105 atm and 1000 K?a) gas b) liquid c) diamond d) graphite Starting from the lower triple point, what action(s) would produce liquid carbon?a) raise the temperature b) raise the pressure c) lower the pressured) lower the temperature ...
Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page - find all choices before answering. 001 10.0 points Consider the phase diagrams for water and carbon dioxide. Explain the following observations: A thin wire with weights attached is draped over a block of "dry ice" and a second wire with weights is draped over a block of ice.
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide. 73.0F In what phase is CO, at 72 atm and 0 °C? solld iquid liquid solid gas 5.11 gas 1.0 Incorrect -78.5 -56.4 31.1 Temperature ("C) Starting from the same point, 72 atm and 0 °C, what phase change would eventually result from a decrease in pressure? sublimation freezing melting deposition vaporization condensation Pressure (atm)

0 Response to "45 consider this phase diagram for carbon dioxide."
Post a Comment