42 glycolysis diagram for kids
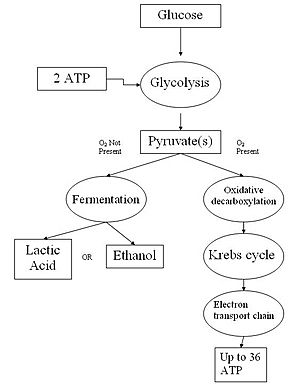
Cellular respiration introduction | Biology (video) | Khan ... But the first step of cellular respiration is glycolysis, breaking up of glucose. What it does is, it breaks up the glucose from a 6-carbon molecule-- so it literally takes it from a 6-carbon molecule-- let me draw it like this-- a 6-carbon molecule that looks like this. And it's actually a cycle. Glycolysis - Definition and Glycolysis Pathway - BYJUS Glycolysis is followed by the Krebs cycle during aerobic respiration. In the absence of oxygen, the cells make small amounts of ATP as glycolysis is followed by fermentation . This metabolic pathway was discovered by three German biochemists- Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas in the early 19th century and is known as the EMP ...
PDF Cellular Respiration - Henry County Public Schools 2. If oxygen IS present after glycolysis, what process occurs next? a) Electron Transport Chain b) Krebs Cycle c)Fermentation 3. A process that does NOT require oxygen is known as what? a) Aerobic b) Anaerobic 4. In glycolysis, glucose is broken into 2 molecules of _____ acid 5. Where does the Kreb's cycle occur? _____ 6.
Glycolysis diagram for kids
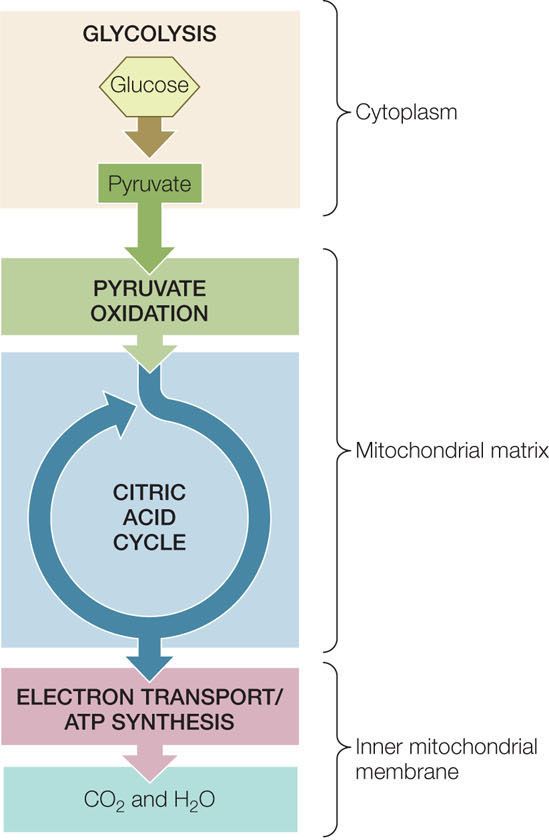
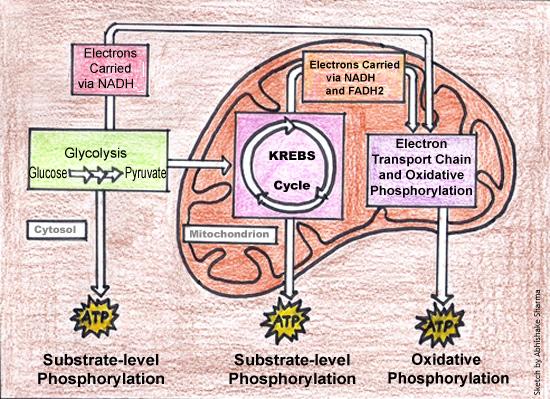
Cellular Respiration Lesson for Kids: Definition & Steps ... Glycolysis and the Krebs cycle each makes two molecules of ATP, and the ETC produces about 34 molecules of ATP. That is a total of about 38 ATP molecules from one glucose molecule. Where the ... PDF Cellular Respiration - Exploring Nature 1) Glycolysis 2) Krebs Cycle 3) The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) This is a very simple overview of these 3 stages: Glycolysis (Stage 1) Glycolysis is the process where 1 glucose molecule, in the cell's cytoplasm, is broken down (through several steps) into 2 molecules of pyruvate, which is then used in the Kreb's Cycle (stage 2). PDF The Krebs Cycle - Lake Washington Institute of Technology 46 Chapter 2 Cellular Respiration Copyright © 2003 Nelson Student Worksheet Solutions The Krebs Cycle, Solution LSM 2.2-4 Krebs Cycle Acetyl-CoA enters the cycle and ...
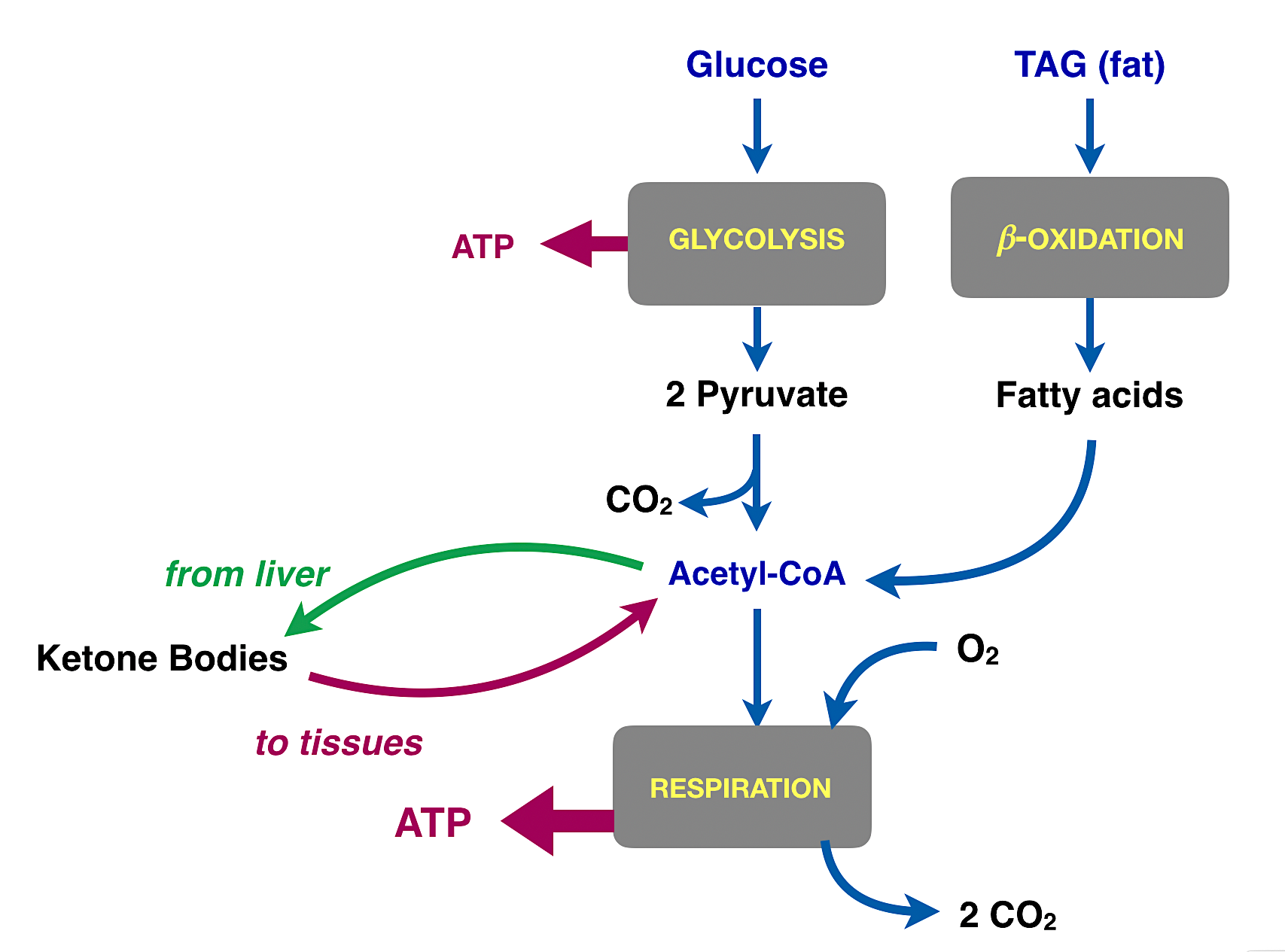
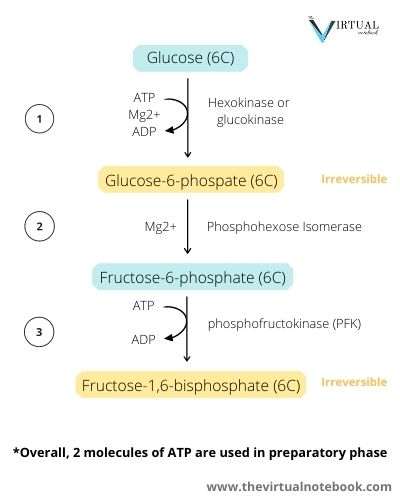
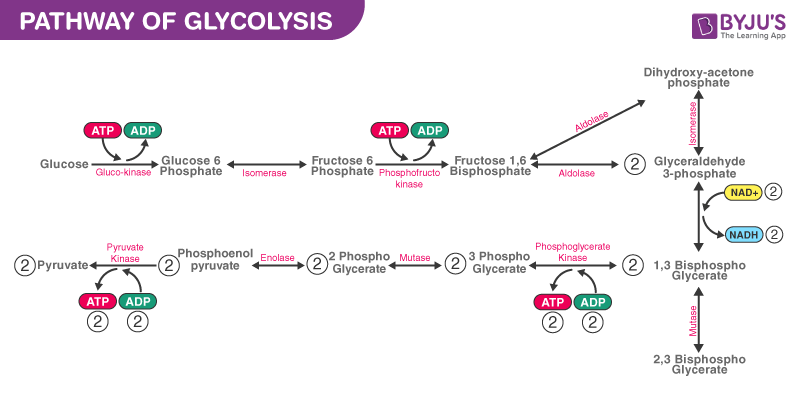
Glycolysis diagram for kids. PDF ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration Powerpoint Glycolysis Glucose 2 pyruvic acids 2 ATP Pyruvic acid conversion 2 Pyruvic acids 2 CO 2 2 Acetyl CoA 0 ATP Kreb Cycle 2 Acetyl CoA (1 per cycle) 4 CO 2 2 ATP (1 made per cycle) ETC 6O 2 FADH 2 Glycolysis ppt - SlideShare There are 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions in glycolysis. There are two stages Stage 1: (Reactions 1-5) A preparatory stage in which glucose is phosphorylated, converted to fructose which is again forphorylated and cleaved into two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. In this phase there is an investment of two molecules of ATP. Glycolysis - Cellular respiration - Higher Biology ... Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose into two pyruvate molecules. This process does not require oxygen (it is anaerobic). The production of pyruvate from glucose involves the production of... Carbohydrate Metabolism Notes: Diagrams & Illustrations ... GLYCOLYSIS osms.it/glycolysis Energy-producing breakdown of glucose into pyruvate Occurs in cytoplasm of all cells PROCESS Glucose transporter (GLUT) carries glucose into cell Kinases (hexokinase, glucokinase) phosphorylate glucose → conformational change, i.e. glucose can't diffuse out) → glucose-6-phosphate Uses one ATP molecule Glucose ...
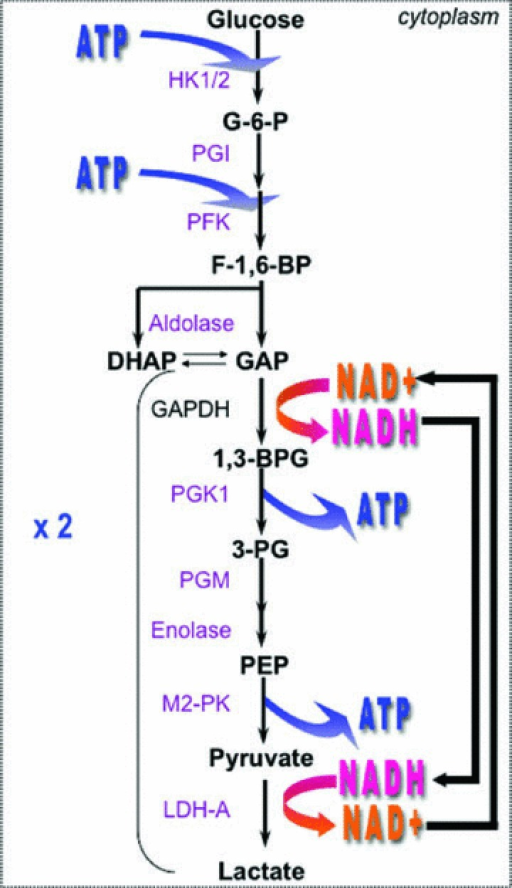
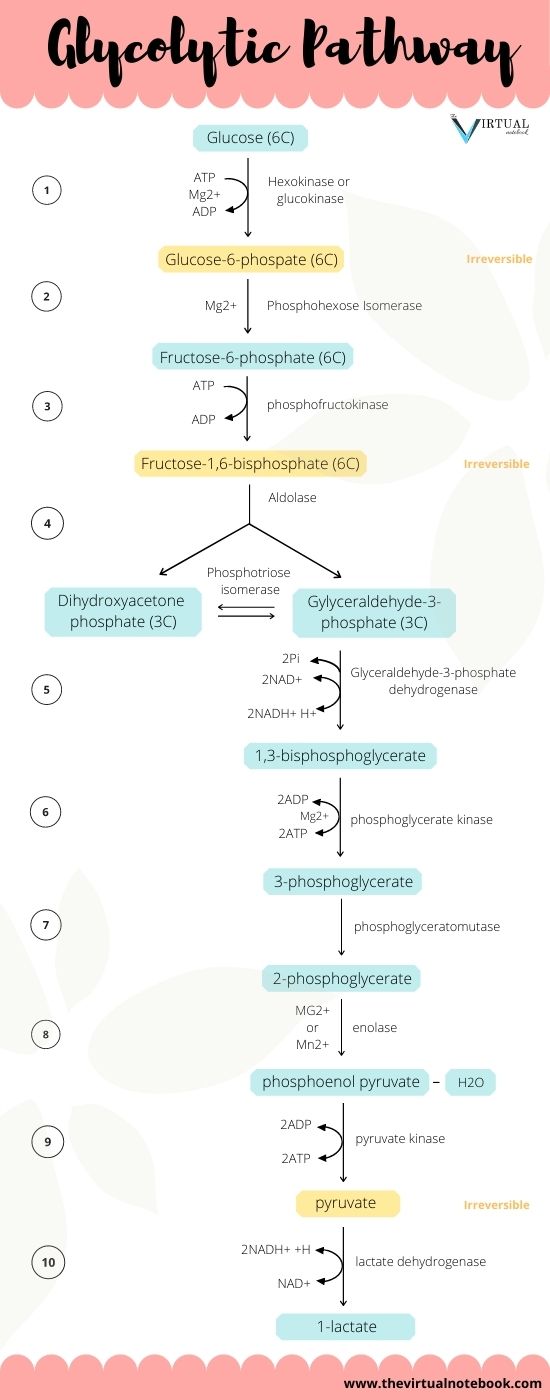
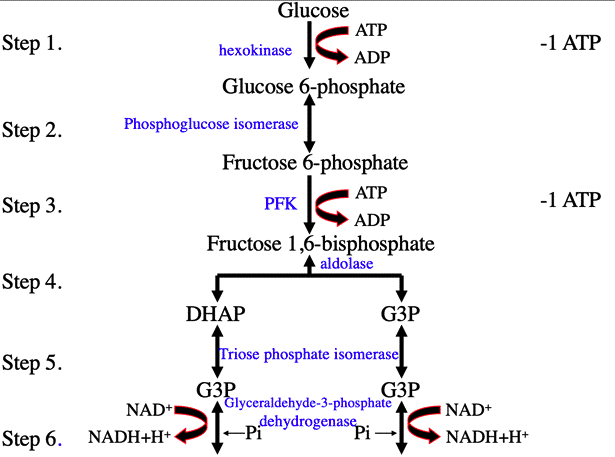
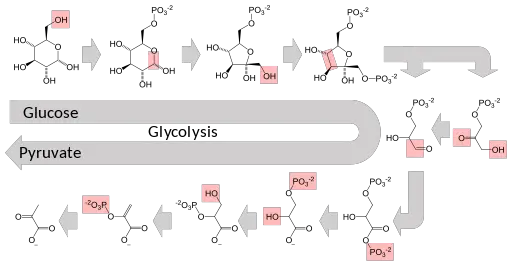
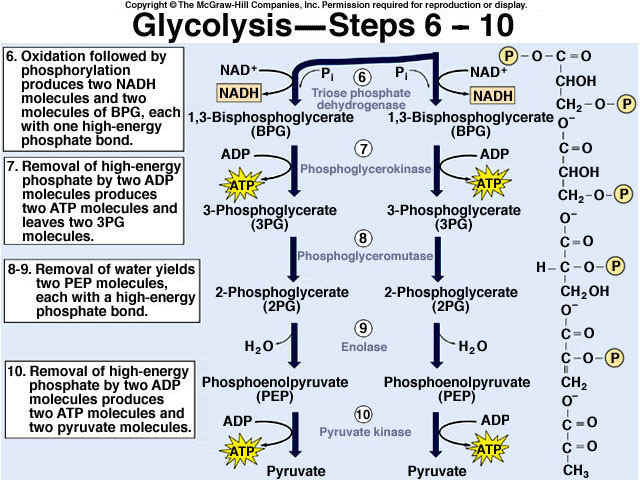
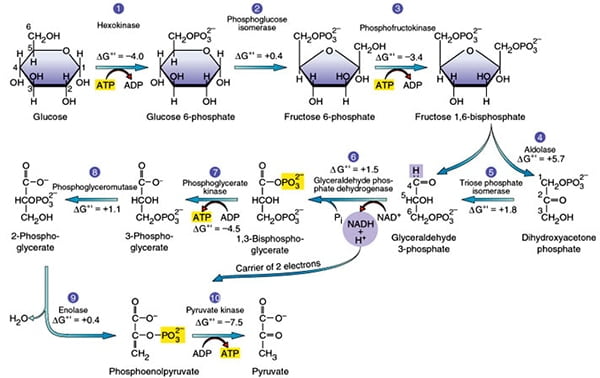
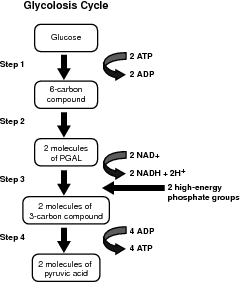
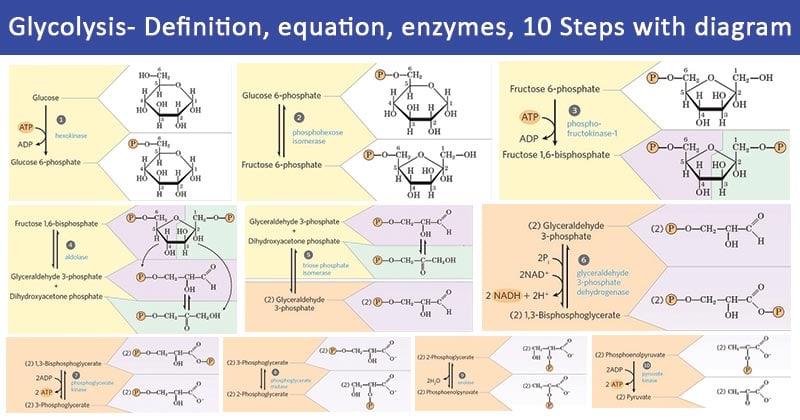
Glycolysis Explained in 10 Easy Steps (With Diagrams) Glycolysis is the metabolic process that serves as the foundation for both aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration. In glycolysis, glucose is converted into pyruvate. Glucose is a six- memebered ring molecule found in the blood and is usually a result of the breakdown of carbohydrates into sugars. The 10 Steps of Glycolysis - ThoughtCo Glycolysis, which translates to "splitting sugars", is the process of releasing energy within sugars. In glycolysis, a six-carbon sugar known as glucose is split into two molecules of a three-carbon sugar called pyruvate. This multistep process yields two ATP molecules containing free energy, two pyruvate molecules, two high energy, electron-carrying molecules of NADH, and two molecules of water. Aerobic Glycolysis Explained - Sport Science Insider The presence, or lack, of oxygen. Glycolysis via aerobic glycolysis occurs when oxygen and hydrogen atoms bond together to break down glucose, and facilitate an exchange of energy. Anaerobic glycolysis, on the other hand, occurs when glucose is broken down without the presence of oxygen. 2. The by-products created. Glycolysis Overview & Steps | What is the First Step of ... Glycolysis starts in the cytoplasm with stage 1, or early glycolysis, which encompasses reaction 1 through reaction 3. Early glycolysis is the investment phase where two molecules of ATP are ...
Krebs / citric acid cycle (video) - Khan Academy Krebs / citric acid cycle. Overview of the Krebs or citric acid cycle, which is a series of reactions that takes in acetyl CoA and produces carbon dioxide, NADH, FADH2, and ATP or GTP. Created by Sal Khan. Review of aerobic glycolysis and its key enzymes - new ... the whole pathway of glycolysis, containing 10 steps of chemical reactions with each catalyzed by a specific enzyme, was elucidated by the 1940s. 5 figure 1 shows the 10 steps and 10 specific enzymes, which are hexokinase (hk), phosphoglucose isomerase (pgi), phosphofructokinase (pfk), aldolase, triosephosphate isomerase (tpi), glyceraldehyde 3 … Teaching Photosynthesis and Cell Respiration with Activities In these activities, students create their own diagram for each process: Glycolysis, Citric Acid Cycle, Oxidative Phosphorylation, Light Reactions, and Light Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle). Each of these activities was designed to allow students to color or cut-and-paste while they read a 2 page reading and answer some questions. Glycolysis | Cellular respiration | Biology (article ... Glycolysis. Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism. Glycolysis consists of an energy-requiring phase followed by an energy-releasing phase. This is the currently selected item.
Glycolysis Diagram For Kids - schematron.org Feb 04, · Glycolysis: All Steps with Diagram, Enzymes, Products, Energy Yield and Significance. By Editorial Team on February 4, in Biochemistry. Glycolysis is derived from the Greek words (glykys = sweet and lysis = splitting). It is a universal catabolic pathway in the living cells.
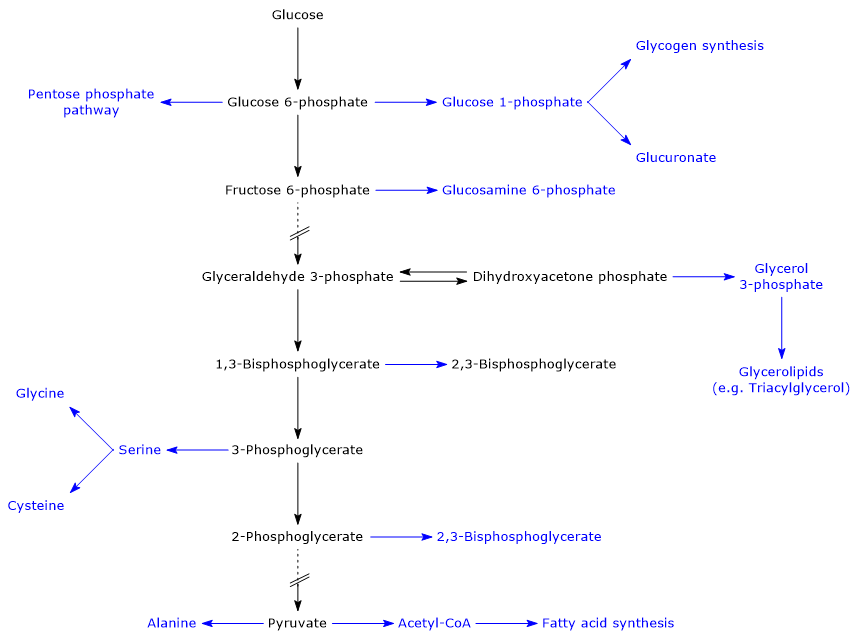
Glycolysis: Pathway, Cycle, Reaction, Diagram Glycolysis is a metabolic mechanism that transforms glucose (C6H12O6) to pyruvic acid (CH3COCOOH) without the use of oxygen. The high-energy molecules are formed using the free energy produced during this process. Adenosine triphosphate and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide are two high-energy compounds.
PDF The Krebs Cycle - Lake Washington Institute of Technology 46 Chapter 2 Cellular Respiration Copyright © 2003 Nelson Student Worksheet Solutions The Krebs Cycle, Solution LSM 2.2-4 Krebs Cycle Acetyl-CoA enters the cycle and ...
PDF Cellular Respiration - Exploring Nature 1) Glycolysis 2) Krebs Cycle 3) The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) This is a very simple overview of these 3 stages: Glycolysis (Stage 1) Glycolysis is the process where 1 glucose molecule, in the cell's cytoplasm, is broken down (through several steps) into 2 molecules of pyruvate, which is then used in the Kreb's Cycle (stage 2).
Cellular Respiration Lesson for Kids: Definition & Steps ... Glycolysis and the Krebs cycle each makes two molecules of ATP, and the ETC produces about 34 molecules of ATP. That is a total of about 38 ATP molecules from one glucose molecule. Where the ...












![Glycolysis | Microbiology [Master]](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images/wp-content/uploads/sites/1950/2017/05/31183350/cellular-20respiration.jpeg)










0 Response to "42 glycolysis diagram for kids"
Post a Comment