40 centripetal acceleration free body diagram
A free body diagram consists of a diagrammatic representation of a single body or a subsystem of bodies isolated from its surroundings showing all the forces acting on it. In physics and engineering, a free body diagram (force diagram, or FBD)... The existence of an unbalanced force for a given situation can be quickly realized by looking at the free-body diagram for that situation. Free-body diagrams for three situations are shown below. Note that the actual magnitudes of the individual forces are indicated on the diagram. In each of the above situations, there is an unbalanced force.
Match That Free-Body Diagram. Net Force (and Acceleration) Ranking Tasks. However, your body, being in motion, tends to continue in motion while the car is skidding to a stop. It certainly might seem to you as though your body were experiencing a forwards force causing it to accelerate forwards.
Centripetal acceleration free body diagram
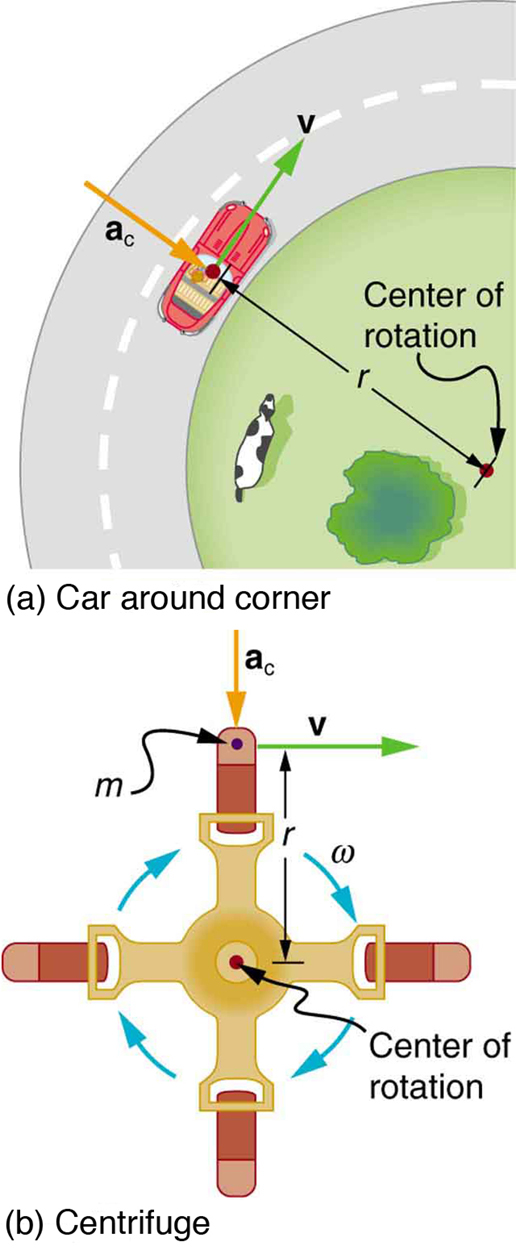
Centripetal Acceleration. Learning Objectives. By the end of this section, you will be able to This pointing is shown with the vector diagram in the figure. We call the acceleration of an object moving The direction of centripetal acceleration is toward the center of curvature, but what is its magnitude? I'm trained as a mathematician and I have some additional background in computer science and engineering, and a college education including college physics. I have always had a desire to really understand physics. Although I got all A grades in my physics classes, I felt like I didn't really understand it. There's something that I have never been able to quite articulate, that has always held me back. This lengthy post is an attempt to get at it, and to seek advice about how I can integrate ... centripetal acceleration which are universally. free body diagrams, wrote down the equation for. the equilibrium application of Newton's second. law. In their free body diagram, they incorrectly. included centripetal force when passing over the.
Centripetal acceleration free body diagram. The free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving forces. It is a diagram including all forces acting on a given object without the other object in the system. You need to first understand all the forces acting on the object and then represent these force by arrows in... The only acceleration responsible for keeping an object moving in a circle is the radial acceleration. Since the sum of all forces is the centripetal force, drawing centripetal force into a free body diagram is not necessary and usually not recommended. CENTRIPETAL ACCELERATION. Newton's first law of motion states that each body moves at a constant speed in a straight line unless a net external force acts upon the body. From Newton's second law and the free body diagram of the revolving rubber stopper, the horizontal component of... For each of the following situations, draw a free body diagram showing all of the forces acting on the object. Then write an equation expressing the sum of forces in the radial direction In this situations all forces act along one direction y and centripetal acceleration points up, so that ma = T − mg or.
I am trying to draw a free body diagram for an object being swung in a vertical circle. I am specifically drawing the point where the minimum speed needed to achieve weightlessness is acquired at the top of the vertical circle. I initially thought that it like something like an object with only Fg acting downwards, but I realized that this cant be right because that would be ignoring the centripetal force. However if there is centripetal force than it can't be weightless as the definition of we... Normal or Centripetal Acceleration: Theory, solved exercises, images, animations and equations of Physics. In physics, we say that a body has acceleration when there is a change in the velocity vector, either in magnitude or direction. The centripetal acceleration is the change in velocity/time. The small diagram to the right shows the two velocitoies being subtracted to find the change. Draw a Free Body Force Diagram for the boy at the bottom of the circle. Draw the (two) forces that are acting on him AND note that the acceleration... Centripetal Acceleration Formula Proof. Consider a particle traversing a circular path of radius r with center O. Initially particle is at P with linear velocity The force that acts on a body moving in a circular path and is directed towards the centre around which the body is moving is called the centripetal force.
Centripetal Acceleration, Force Equations and Calculator. Centripetal Acceleration defines the distance that is covered and the direction of the movement. Since the velocity vector (the direction) of a body changes when moved in a circle - there is an acceleration. Chuck is playing on a tire attached hanging from a tree by a rope. The rope on the tire is 2.10 m long. A friend pulls him back until the rope is 42o from the vertical and releases him from rest. a) How fast will he be moving at the bottom of the swing? I have no idea how to set up this problem...I drew a free-body diagram and understand that the tension is going to be in the opposite direction of weight and in the direction of centripetal acceleration but I am stuck from there... Edit: So i f... Which free-body diagram describes the car at this instant? Car's velocity vector is pointing to the right. The arrow pointing towards the center of the earth is larger in magnitude than that of normal force. The centripetal acceleration points toward the center always and is greater in the free-body diagram. 1) If a turn in a road has a radius of 75 meters, calculate the centripetal acceleration of a car going through the turn at 60 mph. Do you think a real car could make it through this turn without losing traction? 2) If a car goes through the same turn radius as above where the overall directional change is 45, what is the maximum acceleration for a car that enters the turn at 60 mph and slows steadily to 40 mph as it exits the turn? Draw a free body diagram of the forces on the car assuming no ...
Draw a free body diagram for each of the following situations a car turning a. The word centripetal means directed toward the center when an object experiences uniform circular motion the object has a centripetal acceleration directed toward the center of the circle. Use case and activity diagram...
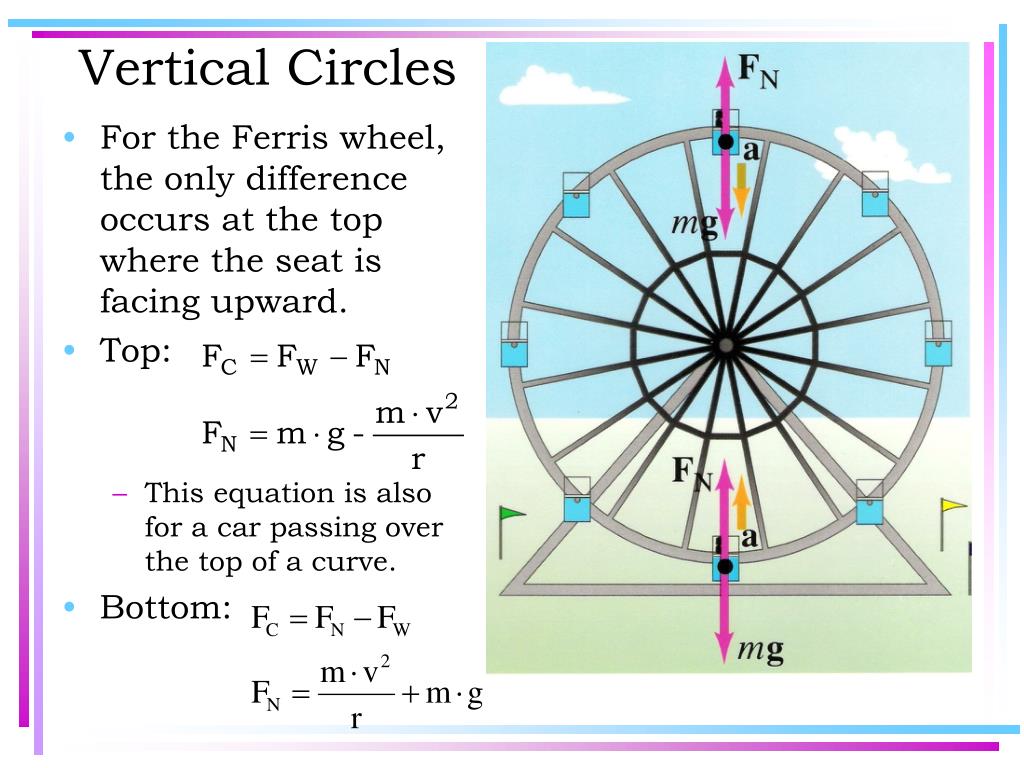
Our free body diagram looks considerably different, and therefore our application to Newton's 2nd Law for Circular Motion is considerably different as well. Since the force you feel is actually the normal force, we can solve for the normal force and expand the net centripetal force as shown
Here I walk through the examples of setting up free body diagrams with circular motion. This is only a preview, and I go through over 250 Physics examples...
I have this physics problem related to rotational motion. I feel like there is not enough information to solve without assuming uniform circular motion. But the problem says find **total** acceleration (Does this imply both centripetal and tangential acceleration is present?). I believe the centripetal acceleration should be -25 m/s^2 I'm not sure where to go from there. A hint in the right direction would be awesome! Thanks! > A student swings a ball at the end of a 1.00 m string in a fu...
Using physics, you can find the centripetal acceleration of objects as they move in a circle. For example, you can calculate the acceleration of a ferry boat making a turn at a constant speed. Here are three practice questions to help you with this concept.
I having difficulty in explaining to my son the free-body diagram for following problem The actual question is easy to solve using uniform circular motion equations (and has nothing to do with my question). In the free-body diagram below, what is the balancing force in the question mark?
. So, centripetal acceleration is greater at high speeds and in sharp curves (smaller radius), as you have noticed when driving a car. But it is a bit surprising 21. Draw a free body diagram for a satellite in an elliptical orbit showing why its speed increases as it approaches its parent body and decreases...
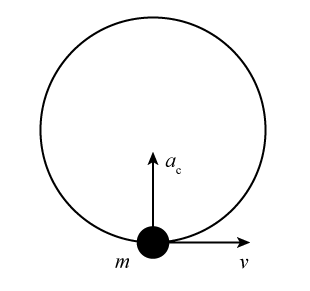
This pointing is shown with the vector diagram in the figure. We call the acceleration of an object moving in uniform circular motion (resulting from a net external force) the centripetal acceleration (a c a c size 12{a rSub { size 8{c} } } {}); centripetal means “toward the center” or “center seeking.”
(b) The free-body diagram for the pilot at the top of the loop is shown in Figure 6.8c. As we noted earlier, both the gravitational force exerted by the Earth and the force n top ex-erted by the seat on the pilot act downward, and so the net downward force that provides the centripetal acceleration has.
I don't really know if this is something that people here are interested in or have the expertise to do, but has anyone actually ran the numbers on the chain? Do we know F(L), where L is some parametrized distance, along the entire chain? For simplicity let's assume that the chain has reached its steady state height. And say the cup is height "h" above the ground, in addition to whatever variables and assumptions you need for the math. Like, this isn't as interesting as experiments or simulatio...
Centripetal Acceleration 13 Examples with full solutions Example 1 A 1500 kg car is moving on a flat road and negotiates a curve whose radius is 35m. 35m Example 1 - Step 1 (Free Body Diagram) F N Acceleration direction F ac F +y +x This static friction is the only horizontal force keeping the car...
shows a free-body diagram for a car on a frictionless banked curve. If the angle . is ideal for the speed and radius, then the net external force equals the necessary centripetal force. The only two external forces acting on the car are its weight
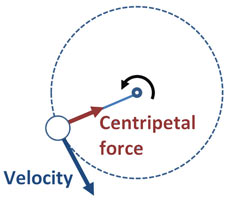
Centripetal and Centrifugal Force are the action-reaction force pair associated with circular motion. Centripetal Acceleration. Velocity is a vector - specifying how fast (or slow) a distance is covered and the direction of the movement. Since the velocity vector (the direction) of a body changes when moved in a circle - there is an acceleration.
Free Body Diagram. Table of Content. Illustration. Enquiry : How to Apply Equations of Motion to Any Problem? Centripetal Force. It is to be noticed here that during previous examples, we were using a concept called FBD implicitly which can now be brought to you conscious attention.
Centripetal acceleration points toward the center of the circular path of the train, but is felt by passengers as a force pushing them to the outer edge The "centrifugal force" is actually your body's inertia, or its resistance to the train's change in direction: your body wants to continue in a straight line...
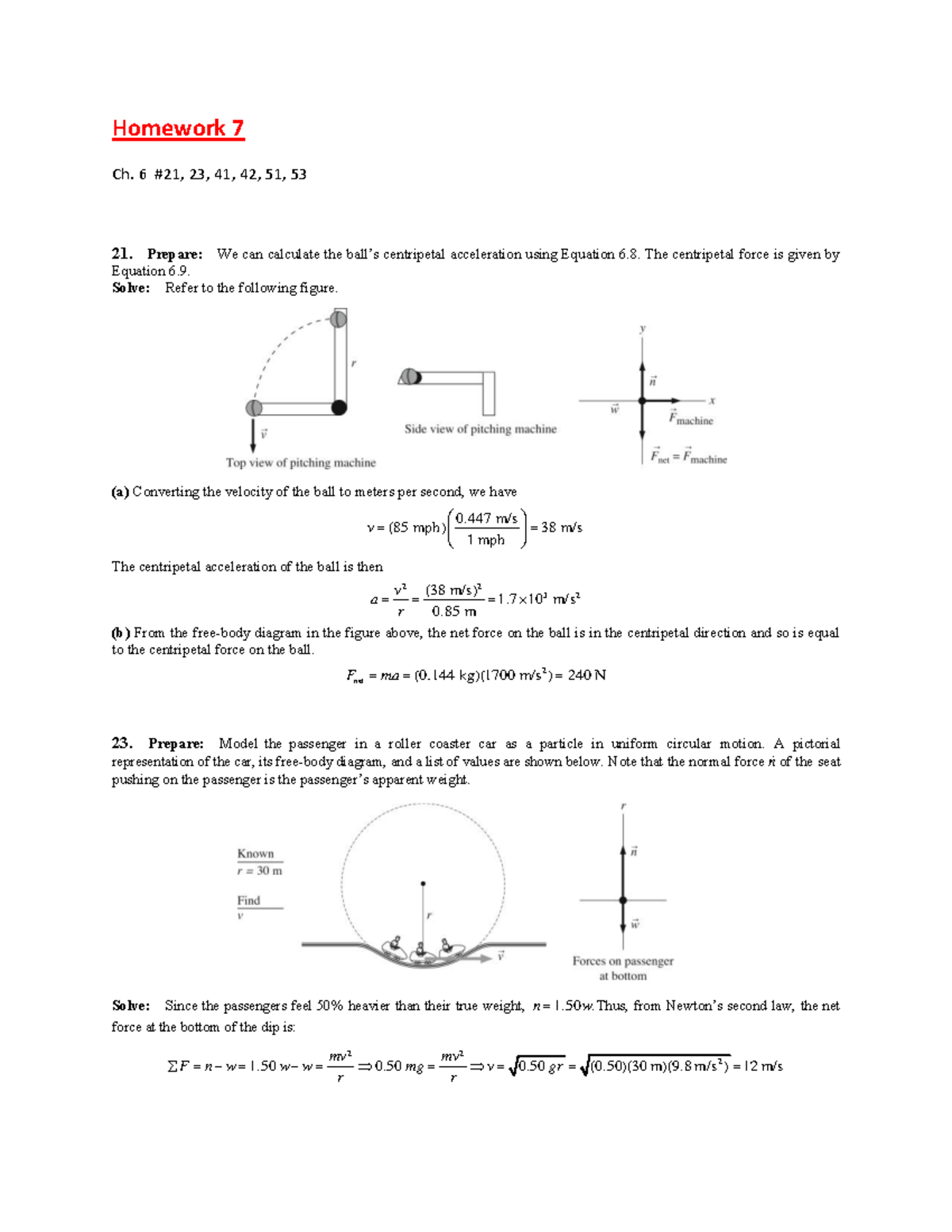
I’m confused about questions involving swinging a mass in a vertical circle, especially at the top. I’m having trouble conceptually grasping the force that allows the ball to be at the top because whenever I do problems, the free body diagram at the top always has all the forces (T, mg, and the net force due to the centripetal acceleration pointing inward because the net force is the sum of T and mg. So why does the ball make it to the top without collapsing)?
The direction of centripetal acceleration is toward the center of curvature, but what is its magnitude? So, centripetal acceleration is greater at high speeds and in sharp curves (smaller radius), as you have noticed when driving a car.
What is the difference between tangential acceleration and centripetal acceleration. And when you are doing a problem, how do you know which equation to use? ​ For example, I am given this problem: A block of mass m is attached to a cord that is wrapped around the rim of a pulley, of radius R and hangs vertically, as shown (picture given to me). The pulley is a uniform disk and has mass M. When the block is released and the mass m accelerates down, what is the tension in the cord? ...
Free body diagram (centripetal force). Last Post. Oct 22, 2008. Component acceleration in free-body diagram. Last Post. Feb 16, 2012.
Centripetal force is a misleading term because, unlike the other forces we've dealt with like tension, the gravitational force, the normal force, and the force of friction, the centripetal force should not appear on a free-body diagram. You do NOT put a centripetal force on a free-body diagram for the same reason that ma does not appear on a ...
Example 1 - Step 1 (Free Body Diagram) +y +x This static friction is the only horizontal force keeping the car moving toward the centre of the arc (else the car will drive off the road). Presentation on theme: "Centripetal Acceleration 13 Examples with full solutions."—
A free body diagram is a graphical representation of the relative magnitude and direction of forces acting on a body in given conditions. In the last step, We draw FBD by drawing force vectors on a rigid body line diagram. And the Force vectors are drawn using an arrow in the direction of the acting...
The acceleration, called the centripetal acceleration, points toward the center of the circle. Note: Don't count the centripetal force as an additional force in the free-body-diagram! It refers to the required net force for circular motion. Page 4.
Kinematics is a subfield of physics, developed in classical mechanics, that describes the motion of points, bodies (objects), and systems of bodies (groups of objects) without considering the forces that cause them to move. Kinematics, as a field of study, is often referred to as the "geometry of motion" and is occasionally seen as a branch of mathematics.
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
Free-body diagrams revisited — I. James E. Court. centripetal acceleration of the exceptional cyclist in a turn. The Rotor is an amusement park ride that consists of a cylindrical, padded room with a radius of 2.46 m that spins once every 1.8 s. A 90 kg person steps inside.
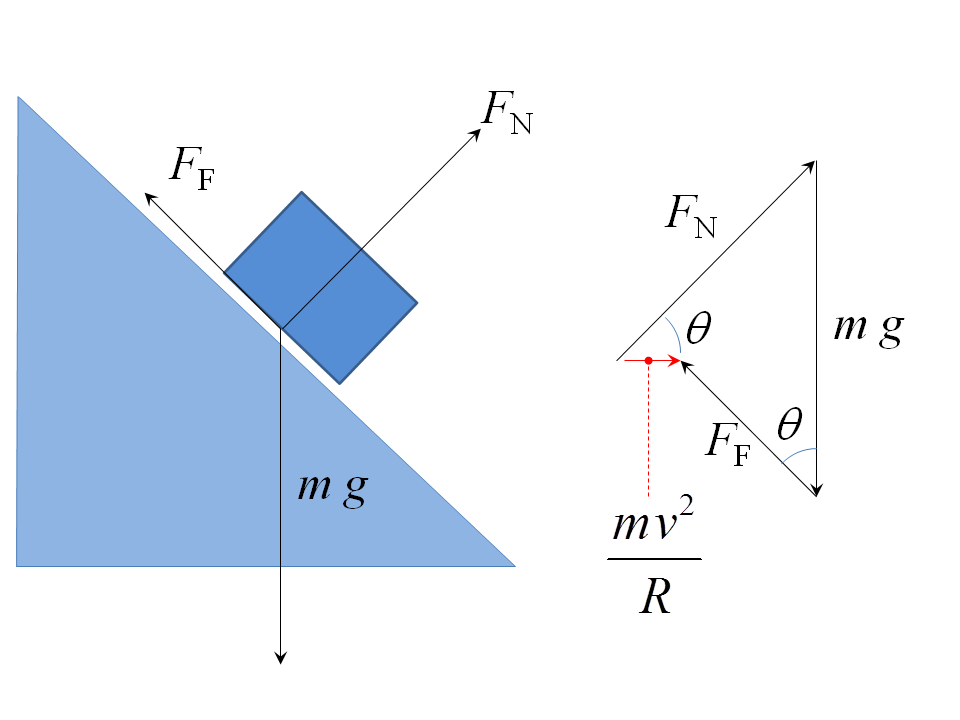
Example What must be the coefficient of friction between the tires and the level roadway to allow a car to make a curve of radius r = 350 m at a speed of 80 km/h?. For a level curve, the force of friction is the only horizontal force on a car and provides the centripetal force. This can be seen from the free-body diagram: The net force must be horizontal--pointing toward the center of the ...
Learn what centripetal acceleration means and how to calculate it. What is centripetal acceleration? This is the currently selected item.
An object of mass m1 of 4.00kg is tied to an object of mass m2 of 3.00kg with a string of length 0.5m. The combination is then swung in a verticular circular path on a second string of length 4.00m. The two strings are always colinear (they are on the same line). At the top of the motion, m2 has a speed of 4.00 m/s. Now, answer the following: a. What is the tension in the short string (the 0.5m string) at this moment? b. What is the tension in the long string (the 4.00m string) at this moment?...
A free-body diagram of the car on the track is shown below. Concepts: Uniform circular motion, Fc = mv2/r. Reasoning: In part (a) the frictional force must provide part of the centripetal acceleration, in part (b) the horizontal component of the normal force must provide all the centripetal acceleration.
centripetal acceleration which are universally. free body diagrams, wrote down the equation for. the equilibrium application of Newton's second. law. In their free body diagram, they incorrectly. included centripetal force when passing over the.
I'm trained as a mathematician and I have some additional background in computer science and engineering, and a college education including college physics. I have always had a desire to really understand physics. Although I got all A grades in my physics classes, I felt like I didn't really understand it. There's something that I have never been able to quite articulate, that has always held me back. This lengthy post is an attempt to get at it, and to seek advice about how I can integrate ...
Centripetal Acceleration. Learning Objectives. By the end of this section, you will be able to This pointing is shown with the vector diagram in the figure. We call the acceleration of an object moving The direction of centripetal acceleration is toward the center of curvature, but what is its magnitude?











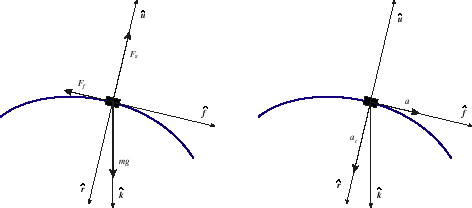



0 Response to "40 centripetal acceleration free body diagram"
Post a Comment