43 acetone molecular orbital diagram
Hybridization of s and p Orbitals. In BeH 2, we can generate two equivalent orbitals by combining the 2s orbital of beryllium and any one of the three degenerate 2p orbitals. By taking the sum and the difference of Be 2s and 2p z atomic orbitals, for example, we produce two new orbitals with major and minor lobes oriented along the z-axes, as shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\). Molecular Orbital Energies The orbital energies are given in eV, where 1 eV=96.49 kJ/mol. Orbitals with very low energy are core 1s orbitals. More antibonding orbitals than you might expect are sometimes listed, because d orbitals are always included for heavy atoms and p orbitals are included for H atoms.
Acetone molecular orbitals and partial charges. Acetone. Select an orbital to display. MO 1 MO 2 MO 3 MO 4 MO 5 MO 6 MO 7 MO 8 MO 9 MO 10 MO 11 MO 12 MO 13 MO 14 MO 15 MO 16 MO 17 MO 18 MO 19.
Acetone molecular orbital diagram
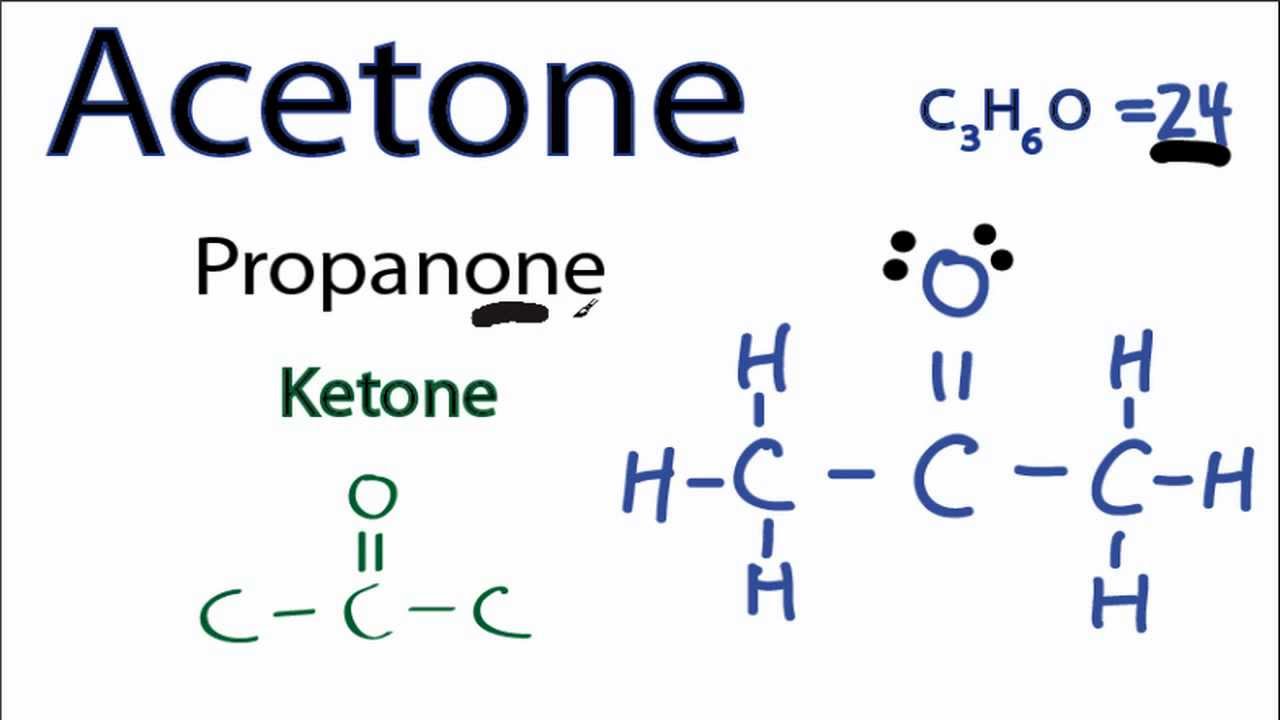
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory is the final theory pertaining to the bonding between molecules. In contrast to VSEPR and valence bond theory which describe bonding in terms of atomic orbitals, molecular orbital theory visualizes bonding in relation to molecular orbitals, which are orbitals that surround the entire molecule. The purpose of MO theory is to fill in the gap for some behavior that ... Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO 1. Acetone, C3H60(CH3COCH3) Lewis structure using dots to represent bonding electrons: Lewis structure using lines to represent pairs of bonding electrons: Label the carbon atoms A,B, &C. Carbon atom A: Total number of electron groups: Number of lone pairs: Number of bonding groups/pairs: Bond angles: Electron geometry: Molecular geometry: Hybridization: Number of hybrid orbitals: Carbon atom ...
Acetone molecular orbital diagram. $\pi$ Molecular orbital diagram of compounds like urea, guanidine, acetone etc. Ask Question Asked 3 months ago. Active 3 months ago. Viewed 50 times 1 $\begingroup$ In my organic chemistry ... Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals. The truncated periodic table shown above provides the orbital electronic structure for the first eighteen elements (hydrogen through argon). According to the Aufbau principle, the electrons of an atom occupy quantum levels or orbitals starting from the lowest energy level, and proceeding to the highest, with each orbital holding a maximum of two paired electrons (opposite spins). … SF4 molecular geometry is see-saw with one pair of valence electrons. The nature of the molecule is polar. These atoms form a trigonal bipyramidal shape. The central sulfur atom has one lone pair and is bonded to four fluorine atoms. CF 4 (carbon tetrafluoride) The CF4 molecule consists of a total of 32 valence electrons.
Molecular orbital theory (MO theory) combines atomic or hybrid orbitals (AOs) to molecular orbitals (MOs). The sp hybrid orbitals combine and form a bonding σ orbital and an antibonding σ* orbital. The four p atomic orbitals form two π and two π* molecular orbitals. The energy sequence from the lowest to the highest MO is σ < π(y) = π(z) < π(y)* = π(z)* < σ*. WebMO Job Summary 53789: C3H6O acetone, Natural Bond Orbitals 6.0/NRT - Gaussian The molecular structure has been optimized at the B3LYP/6-31g* level of theory. Charges used for electrostatic maps are computed using the NBO method. The molecular vibrations are 12.12.2012 · A class of metal-free organic electroluminescent molecules is designed in which both singlet and triplet excitons contribute to light emission, leading …
1. Electrons are never found in an anti bonding molecular orbital. 2. Antibonding molecular orbitals hav electron density mainly outside the space between the two nuclei. 3. All antibonding molecular orbitals are higher in energy than the atomic orbitals of which they are composed. 2 and 3. The nitrosyl ion, NO⁺, has 10 bonding electrons and ... The IUPAC name of Acetone is 2 -propanone with a condensed chemical formula C 3 H 6 O. Acetone is made up of three carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms, and one oxygen atom. It is considered a ketone since there is a carbonyl group present in it. It is a methyl ketone that consists of propane bearing an oxo group at C - 2 carbon atom. Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in ... Molecular Orbital Theory. Shaun Williams, PhD. Constructing Molecular Orbitals from Atomic Orbitals. We typically use atomic orbitals (AOs) as a basis for constructing MOs; LCAO-MO (linear combination of atomic orbitals) - we have seen LCAO before when we built our hybrid orbitals in the previous section.
The frontier molecular orbitals, coefficients and energies relevant to the reaction are shown in Figure 1 with those of ketene' for comparisons. The plane geometry for the molecules with all bond angles fixed at 120except for C4C3C8(=C3CBC,) on Z were assumed.e The relative energy diagram shows that the LUMO of the ene-ketene ,Z and the HOMO of ...
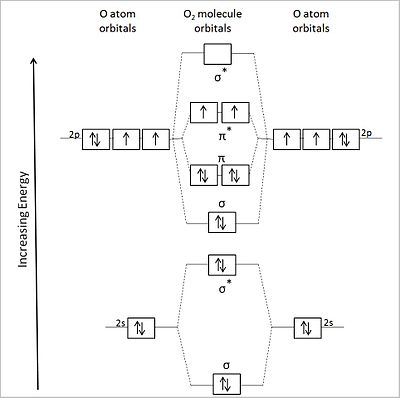
2 Lecture 2 Pi bond (π): bonding molecular orbital -The bonding electron density lies above and below, or in front and in back of the bonding axis, with no electron directly on the bonding axis, since 2p orbitals do not have any electron density at the nucleus.
Natural Bond Orbitals in Acetone. Check the orbitals to display Natural Bond Orbitals C(1)-C(2) σ C(1)-H(1) σ C(1)-H(2) σ C(1)-H(3) σ C(2)-C(3) σ C(3)-H(4) σ C(3)-H(5) σ C(3)-H(6) σ C(2)-O σ C(2)-O π O lone pair (1) O lone pair (2) C(2)-O π* elpot surface : faster display ...
Bonding orbitals in Ethylene (Ethene) sp 2. Bonding orbitals in Formaldehyde. Bonding orbitals in Methane - sp 3 hybrids. Interaction of Bromine Br 2 and C=O on Propanone. Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. Molecular orbitals in Fluorine. Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen. Molecular orbitals in Hydrogen Fluoride. Molecular orbitals in Nitrogen
Photochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the chemical effects of light. Generally, this term is used to describe a chemical reaction caused by absorption of ultraviolet (wavelength from 100 to 400 nm), visible light (400–750 nm) or infrared radiation (750–2500 nm).. In nature, photochemistry is of immense importance as it is the basis of photosynthesis, …
Drawing the Molecular Orbital Diagram. Figure 1.9. 2: Structure of methane molecule. Consider CH 4 as a specific example of a molecule within the Td symmetry group. Before drawing the MO diagram, the valence atomic orbitals on the central atom and their symmetries must be noted.
The hybrid orbitals are more prominent outward so that their ability to overlap is stronger than that of normal orbitals. Molecular Formula: A chemical formula is a brief way of expressing the number and type of atoms that make up a particular chemical compound.
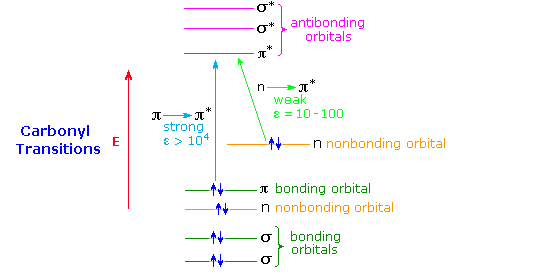
Transcribed image text: Provide a molecular orbital diagram for acetone (propanone) and use this diagram to explain the bond angles and geometry of the carbonyl group (10) What important type of reactivity arises from the polarisation of the carbonyl group? Rank the carbonyl compounds given below in terms of their relative reactivity with sodium borohydride Suggest two factors which combine to ...
We applied relativistic multiconfigurational all-electron ab initio calculations including the spin–orbit interaction to calculate the 3d4f resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) map (3d3/2 → 5f5/2 U M4 absorption edge and 4f5/2 → 3d3/2 U Mβ emission) of uranyl (UO22+). The calculated data are in excellent agreement with experimental results and allow a detailed …
The word comet derives from the Old English cometa from the Latin comēta or comētēs.That, in turn, is a romanization of the Greek κομήτης 'wearing long hair', and the Oxford English Dictionary notes that the term (ἀστὴρ) κομήτης already meant 'long-haired star, comet' in Greek. Κομήτης was derived from κομᾶν (koman) 'to wear the hair long', which was itself ...
Molecular Orbital Imaging of the Acetone S 2 Excited State Using Time-Resolved (e, 2 e) Electron Momentum Spectroscopy Masakazu Yamazaki, Keiya Oishi, Hiroyuki Nakazawa, Chaoyuan Zhu, and Masahiko Takahashi Phys. Rev. Lett. 114, 103005 - Published 13 March 2015 See Focus story: Catching a Molecule in an Excited State
For example, notice that the HOMO of acetone can be clearly interpreted as the orbital holding one of the lone pairs. If resonance is important the molecule cannot be represented by a single Lewis structure and the NBO analysis has to be extended to include combinations of the relevant NBOs to form Natural Localized Molecular Orbitals (NLMOs).
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
Answer (1 of 2): You can find the hybridization of acetone by individually finding the hybridization of carbon atoms The first and the third carbon atoms are similar and they have the same hybridization state as they are fully saturated with three hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom thus they hav...
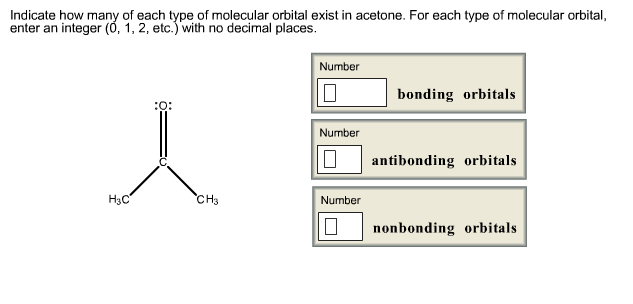
For each type of molecular orbital, enter an integer (0, 1, 2, etc.) with no decimal places. Question : Indicate how many of each type of molecular orbital exist in acetone. This problem has been solved!
Molecular Orbital Imaging of the Acetone S 2 Excited State Using Time-Resolved ( e , 2 e ) Electron Momentum Spectroscopy March 2015 Physical Review Letters 114(10):103005
Acetone is a manufactured chemical that is also found naturally in the environment. It is a colorless liquid with a distinct smell and taste. It evaporates easily, is flammable, and dissolves in water. It is also called dimethyl ketone, 2-propanone, and beta-ketopropane. Acetone is used to make plastic, fibers, drugs, and other chemicals.
01.11.2021 · The power conversion efficiencies (PCEs) of laboratory-sized organic solar cells (OSCs), usually processed from low-boiling-point and toxic solvents, have reached high values of over 18%. However ...
• Bonding molecular orbital: A MO in which electrons have a lower energy than they would have in isolated atomic orbitals. • Sigma (σ) bonding molecular orbital: A MO in which electron density is concentrated between two nuclei along the axis joining them and is cylindrically symmetrical.
Using the Frost Circle mnemonic, draw the molecular orbital diagram for a cyclopentadienyl carbanion (energy levels only). Indicate which MOs are bonding, non-bonding and anti-bonding. Use up and down arrows to represent the electrons present in each orbital. State whether a cyclopentadienyl carbanion is aromatic, anti-aromatic or neither. Use your diagram to explain. …
1. Acetone, C3H60(CH3COCH3) Lewis structure using dots to represent bonding electrons: Lewis structure using lines to represent pairs of bonding electrons: Label the carbon atoms A,B, &C. Carbon atom A: Total number of electron groups: Number of lone pairs: Number of bonding groups/pairs: Bond angles: Electron geometry: Molecular geometry: Hybridization: Number of hybrid orbitals: Carbon atom ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory is the final theory pertaining to the bonding between molecules. In contrast to VSEPR and valence bond theory which describe bonding in terms of atomic orbitals, molecular orbital theory visualizes bonding in relation to molecular orbitals, which are orbitals that surround the entire molecule. The purpose of MO theory is to fill in the gap for some behavior that ...









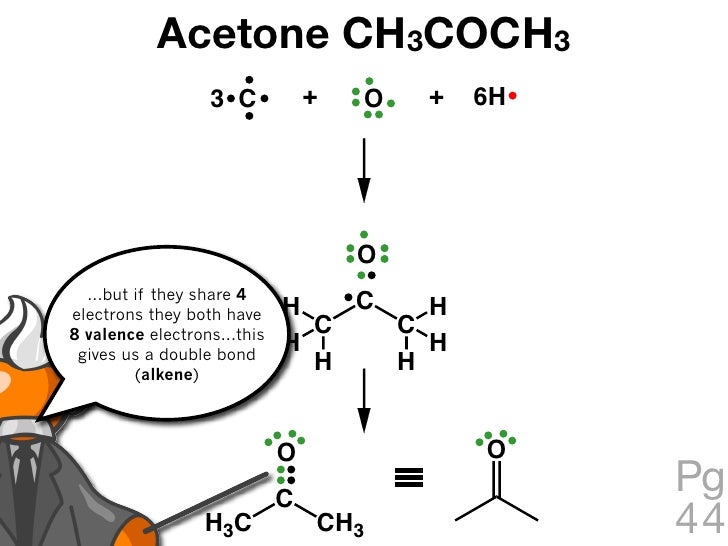





















0 Response to "43 acetone molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment